Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
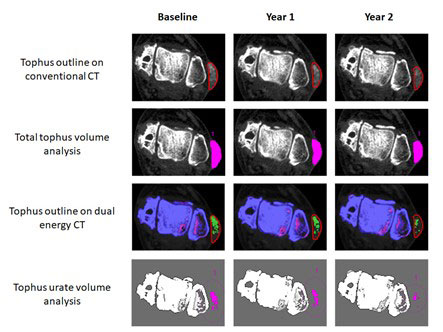
Background/Purpose: The gouty tophus is an organized structure composed of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals and chronic inflammatory soft tissue. Long-term urate-lowering therapy leads to gradual reduction in the size of tophi. However, it is unknown whether the composition of the tophus changes during urate-lowering therapy. Conventional computed tomography (CT) allows measurement of tophus volume in a reliable and reproducible manner. In addition to conventional CT properties, dual energy computed tomography (DECT) allows measurement of MSU crystals within tophi. The aim of this DECT study was to determine whether the composition of the tophus changes over time during urate-lowering therapy.
Methods: Serial DECT scans from 32 people with gout were obtained during a two-year study of allopurinol dosing. All participants received allopurinol dose-escalation, achieved the target SU during the study (< 6 mg/dL) and had evidence of DECT urate deposition within tophi at baseline. DECT scans of the feet and ankles were obtained at baseline, Year 1 and Year 2. Up to five index tophi were selected from each patient, with 103 separate tophi included in the analysis. Using manual outlining methods of conventional CT (CT) and DECT scans, the same index tophi were serially measured for total tophus volume and urate volume. For each tophus, the soft tissue volume was then calculated by subtracting the urate volume from the total tophus volume. Data were analyzed using general estimating equations (GEE) mixed models with analysis of covariance (ANCOVA).
Results: In response to allopurinol dose escalation, the mean (SD) serum urate reduced from 7.2 (0.5) mg/dL at baseline to 5.2 (0.3) mg/dL at Year 2. Within the analyzed tophi, the total tophus volume reduced over the two-year period; from mean (SD) 5.17 (5.55) cm3 to 2.61 (2.73) cm3, P< 0.001. Both the tophus urate volumes and tophus soft tissue volumes reduced over time (P< 0.001), but greater reductions in tophus urate volumes were observed (Figures 1 and 2). Overall, the tophus urate volume decreased by 70.6 [62.8, 78.4]%, and tophus soft tissue volume decreased by 37.8% [31.4, 44.1]%. The tophus urate:soft tissue ratio reduced from 0.15 [0.12, 0.19] at baseline to 0.05 [0.02, 0.09] at Year 2.
Conclusion: This dual energy CT study demonstrates that the composition of the tophus changes during urate-lowering therapy for gout management. While both urate and soft tissue volumes reduce over time, the chronic inflammatory soft tissue within the tophus is slower to respond than the MSU crystals.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen L, Gamble G, Horne A, Drake J, Doyle A, Uhlig T, Stamp L, Dalbeth N. Changes in Tophus Composition During Urate-Lowering Therapy: A Dual Energy CT Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-tophus-composition-during-urate-lowering-therapy-a-dual-energy-ct-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-tophus-composition-during-urate-lowering-therapy-a-dual-energy-ct-study/