Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Few studies, if any, have found association of the biochemical cause of gout (high serum urate) with functional limitation and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and productivity decrements in gout. We examined the associations of changes in serum urate in the immediate term with HRQoL using data from five intervention clinical trials of urate-lowering therapies (ULT).
Methods: Data were obtained from the following trials: Combining Lesinurad With Allopurinol in Inadequate Responders (CLEAR1 and CLEAR2; 1217 participants, 12 months); Long-term Allopurinol Safety Study Evaluating Outcomes in Gout (LASSO;1735 participants, 6 months); Lesinurad Monotherapy in Gout Subjects Intolerant to Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors (LIGHT; 214 participants, 6 months; Combination Treatment Study in Subjects With Tophaceous Gout With Lesinurad and Febuxostat (CRYSTAL; 330 participants, 12 months). We excluded participants in LASSO who had also taken part in CLEAR or LIGHT (n=154). HRQoL measures were assessed at baseline and at 3 monthly intervals (LASSO only at baseline and 6 months), serum urate was measured monthly in each trial.
Primary outcome measures were physical (PCS) and mental (MCS) health functioning taken using the respective component summary scores from Short-form 36 (SF-36) data, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index Score (HAQ-DI), Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS) score, Patient Global Assessment (PGA), and pain in the last week. For each outcome, we investigated the underlying distribution and then a series of corresponding random intercept and slope (month) generalized linear mixed models were used to test the adjusted effect of the fixed predictors on the outcome across all timepoints over the first six month. Serum urate, change in urate in the last month, number of flare-affected days in the last month, baseline BMI, age, number of comorbidities, sex, ethnicity, trial and treatment, and tophi status were modelled as fixed effects. Subject, and the month of trial were modelled as random effects.
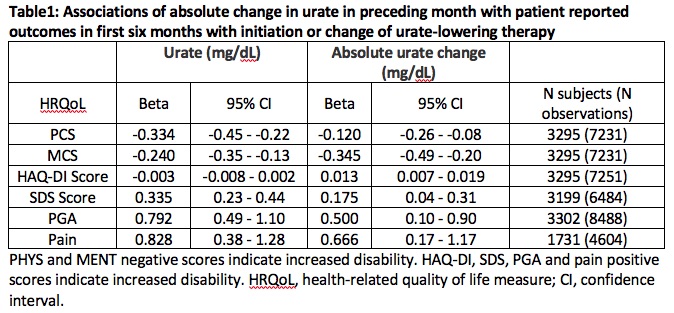
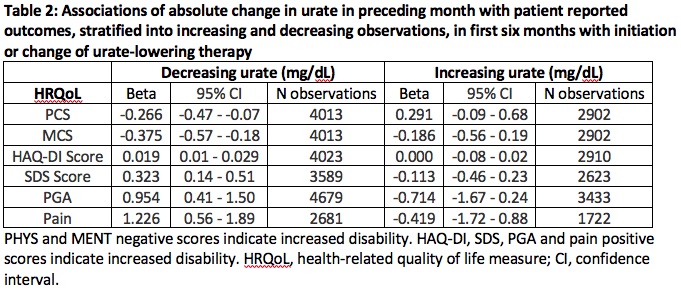
Results: Higher current serum urate correlated with reduced physical and mental health functioning, and increased disability and pain but not with HAQ-DI Score (Table 1). However absolute change in serum urate levels associated with poorer outcomes on the HAQ-DI scale (β (95% CI) = 0.013 (0.007 – 0.019)) and the five other measures. Observations were stratified into those which followed a month of serum urate reduction (n = 4023) or increase (n = 2910) (Table 2). Reduction of serum urate levels was associated with poorer outcomes in all six measures. Timepoints with increasing serum urate levels showed no significant associations with the outcomes.
Conclusion: High serum urate levels associate with poorer HRQoL outcomes. Importantly, very recent fluctuations in serum urate levels associate with reduced HRQoL, primarily driven by effects of reduction in serum urate. Clinical emphasis on maintaining stable and reduced concentrations of serum urate may improve patient reported functional outcomes. This study provides further support for serum urate as central to disease pathophysiology and its impact on an individual’s health.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Topless R, Merriman T, Noorbaloochi S, Singh J. Changes in Serum Urate, in the First 6-months of Initiation or Change of Urate-Lowering Therapy, Associate with Immediate Health-Related Quality of Life Outcomes in People with Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-urate-in-the-first-6-months-of-initiation-or-change-of-urate-lowering-therapy-associate-with-immediate-health-related-quality-of-life-outcomes-in-people-with-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-urate-in-the-first-6-months-of-initiation-or-change-of-urate-lowering-therapy-associate-with-immediate-health-related-quality-of-life-outcomes-in-people-with-gout/