Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is associated with autoimmune extrahepatic manifestations including increased production of autoantibodies such as rheumatoid factor (RF). Prior to the advent of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), HCV infection was treated with pegylated interferon (Peg-IFN) which is known to induce or exacerbate autoimmunity. It remains unclear whether HCV eradication was associated with reduction in autoantibodies, and whether results would differ between IFN-based and IFN-free regimens. In our research, we aimed to investigate changes in serum RF following viral eradication in patients with chronic HCV infection who were treated with either Peg-IFN or ribavirin plus DAA.
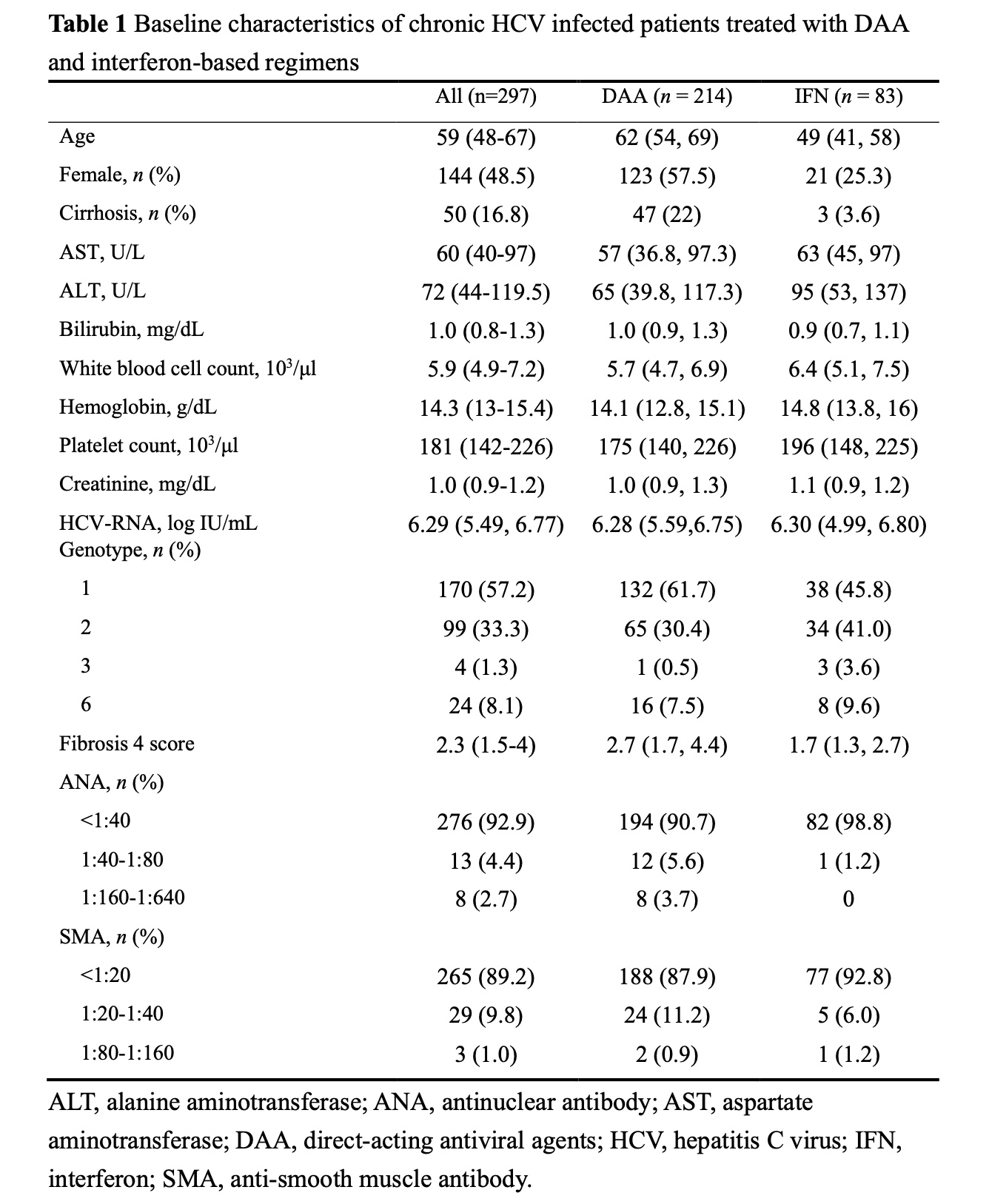
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of adult HCV patients treated at a teaching hospital in Taiwan. All patients had detectable HCV RNA at baseline (BL) and achieved sustained virological response (SVR) documented 12 or 24 weeks after treatment. Serum level of IgG RF was measured using latex immunoassay with a measurement of 15 IU/mL or above defining seropositivity. The changes from BL to SVR were analyzed and the results were compared between patients treated with IFN-based regimens and those with IFN-free DAAs. Subgroup analyses according to age, sex, presence of cirrhosis, HCV genotype, and BL ANA titer were performed.
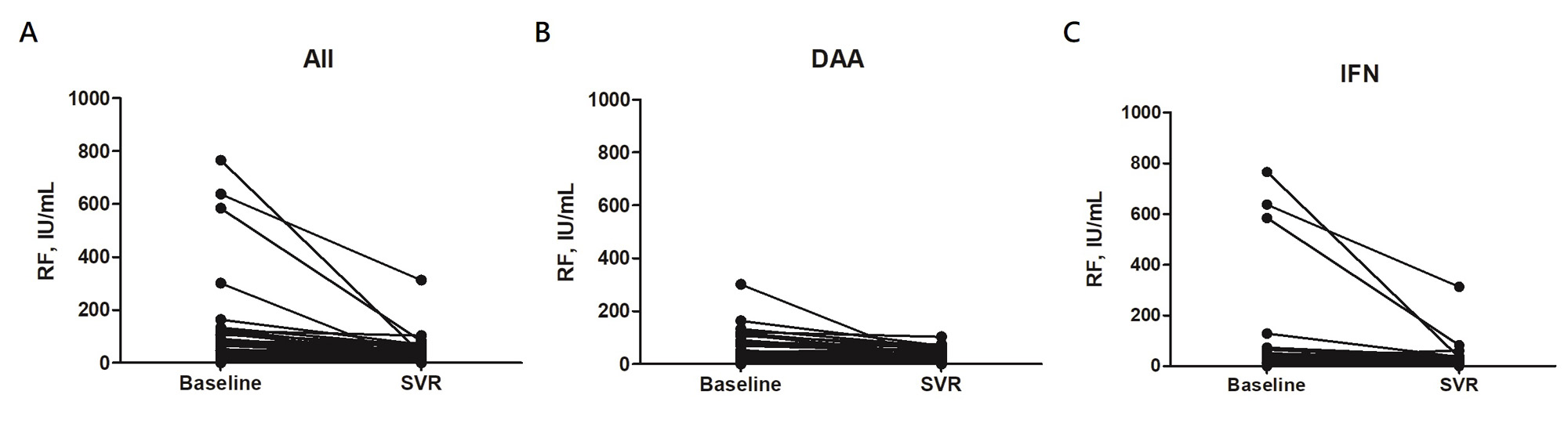
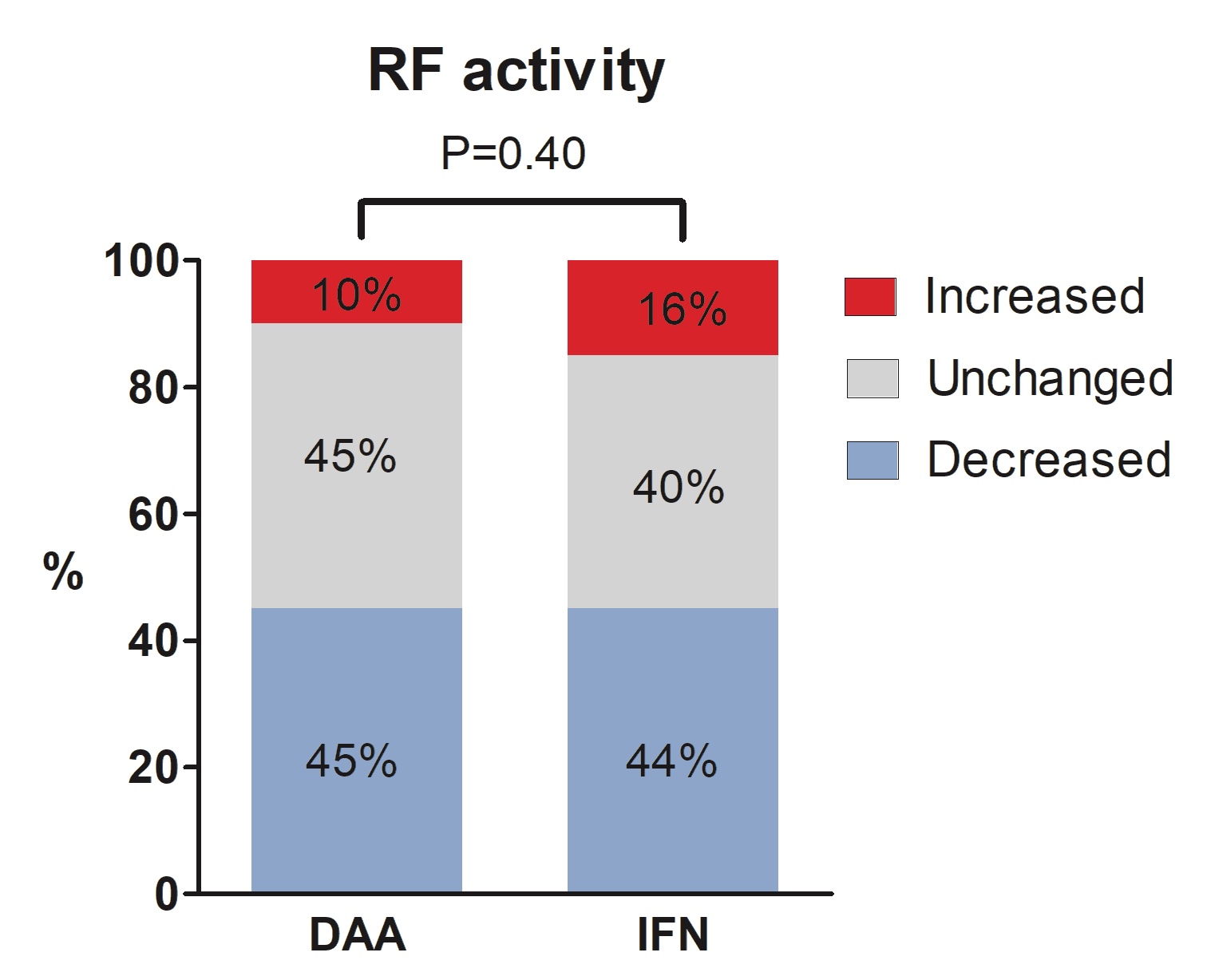
Results: This study enrolled 297 patients (median age 59; 48.5% female). Among them, 78 (26.3%) were RF-positive by qualitative serology at BL. This number decreased to 49 (16.5%) at SVR-12 or -24 (P < 0.001). Quantitatively, the median level of serum RF in the study cohort also decreased from 1.6 IU/mL (IQR undetectable (UD)-15.8) to UD (IQR, UD-6.6 IU/mL) (P < 0.001). Significant reductions in serum RF were observed in both treatment groups. The proportion with RF seropositivity decreased from 24.3% to 15.4% (P = 0.001) in patients treated with IFN-free agents (n = 214) and from 31.3% to 19.3% (P = 0.006) in patients treated with IFN-based regimens (n = 83), without significant difference between these two groups (P =0.40).
Serum RF level decreased significantly between BL and SVR-12 or -24 in all subgroups, including age ≥ 59 (n = 150; 1.0 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), age < 59 (n = 147; 2.6 vs. 1.2 IU/mL, P < 0.001), males (n = 153; 2.1 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), females (n = 144; 1.2 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), with cirrhosis (n = 50; 0.7 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), without cirrhosis (n = 247; 1.9 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), genotype 1 (n = 170; 0.8 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), non-genotype 1 (n = 127; 2.3 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), and with BL ANA < 1:40 (n = 276; 1.4 vs. UD IU/mL, P < 0.001), except for patients with BL ANA ≥ 1:40 (n = 21; 3.0 vs. 1.3 IU/mL, P = 0.064).
Conclusion: We found that both the serum RF level and proportion of RF seropositivity significantly decreased after the eradication of HCV infection, regardless of whether the patients were treated with IFN-free or IFN-based regimens. We further analyzed different subgroups of participants and observed similarly significant reductions in serum RF in all subgroups, except for patients with ANA titers higher than 1:40 at BL. These findings indicate that effective treatment for HCV could reduce the production of RF and may alter autoimmunity in patients with chronic HCV infection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lo J, Tsai Y, Tseng C, Hsu Y, Hsieh S. Changes in Serum Rheumatoid Factor Following Eradication of Hepatitis C Virus Infection with Interferon or Direct Antiviral Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-rheumatoid-factor-following-eradication-of-hepatitis-c-virus-infection-with-interferon-or-direct-antiviral-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-rheumatoid-factor-following-eradication-of-hepatitis-c-virus-infection-with-interferon-or-direct-antiviral-therapy/