Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The IL-23p19 inhibitor guselkumab has shown robust efficacy vs placebo (PBO) in the phase 3 DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 studies of adults with active PsA,1,2 with continuous overall clinical improvement observed through 2 years of DISCOVER-2.3 Guselkumab has previously been shown to significantly reduce levels of inflammatory biomarkers associated with PsA over 24 weeks.4 We assessed whether earlier changes (by Week [W] 24) in serum biomarker levels associate with long-term (W100) clinical response to guselkumab.
Methods: DISCOVER-2 enrolled biologic-naïve adults with active PsA ≥6 months defined by the CASPAR criteria, swollen and tender joint counts ≥5, and CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL. Patients (pts) were randomized 1:1:1 to guselkumab 100 mg at W0, W4, then every 4 weeks (Q4W); guselkumab at W0, W4, then Q8W; or PBO.2 Using Spearman linear regression and General linear model, serum cytokine levels determined in guselkumab-treated patients (pooled Q4W/Q8W) were assessed for: 1) correlations between reductions in cytokine levels, including selected Th17 cytokines (IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22), acute phase cytokines (C-reactive protein [CRP], serum amyloid protein A [SAA], IL-6), and β-defensin 2 (BD-2 [a biomarker of IL-17A pathway activation]), from baseline (BL) at W24 and in PsA disease severity from BL at W100, measured by changes in Disease Activity in PSoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA) scores, Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS), and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores (significant correlation defined as r >0.25 and p< 0.05); and 2) associations between changes in selected cytokine levels from BL through W24 and achievement of ACR50 response at W100.
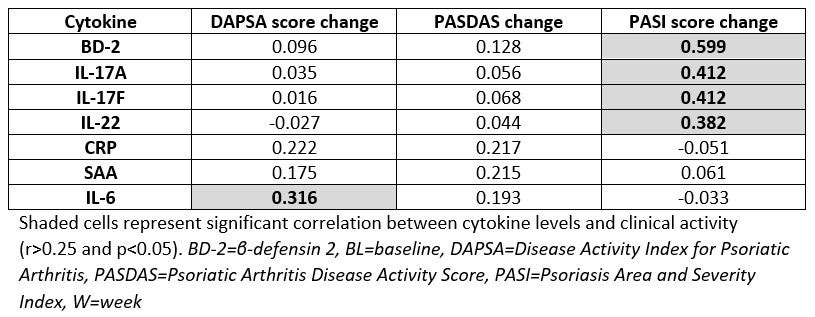
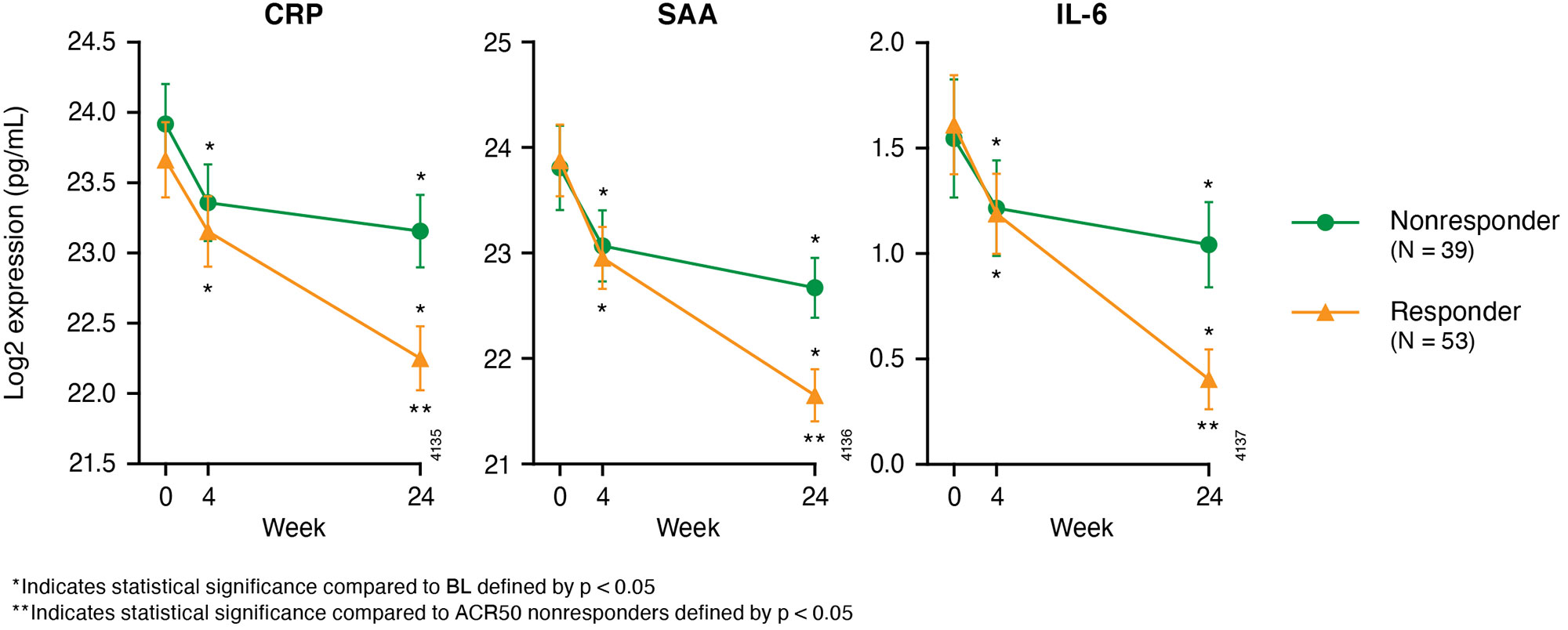
Results: BL demographics, disease severity, and medication use of guselkumab-treated DISCOVER-2 pts with available biomarker data (N=100) were generally consistent with the overall guselkumab-treated DISCOVER-2 population (N=493) (Table 1). With guselkumab treatment, PASI score change from BL at W100 correlated with changes from BL at W24 in serum BD-2, IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 levels (all r >0.25, p< 0.05; Table 2), though PASDAS and DAPSA score change at W100 did not correlate with changes in these biomarkers at W24. DAPSA score change at W100 correlated with changes at W24 in serum IL-6. W100 ACR50 responders (N=53) to guselkumab also demonstrated significantly lower serum CRP, SAA, and IL-6 levels at W24 than nonresponders (N=39) (p< 0.05; Fig 1).
Conclusion: This analysis reported correlations between earlier changes in Th17 cytokine levels and long-term reductions in PASI scores, and associations between earlier changes in acute phase cytokine levels and long-term ACR50 response with guselkumab. The substantial reductions in these cytokines from BL at W24 may portend durable improvements in skin and joint symptoms of PsA.
References:
1Deodhar A, et al. Lancet 2020;395:1115-25
2Mease P, et al. Lancet 2020;395:1126-36
3McInnes IB et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2022;74(3):475-85
4Sweet K et al. RMD Open 2021;7:e001679
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Siebert S, Schett G, P. Raychaudhuri S, Guma M, Chen W, Gao S, Chakravarty S, Shawi M, Rahman P. Changes in Serum Cytokines by Week 24 Correlate with Long-Term Efficacy of Guselkumab Through Two Years in Bio-Naïve Adults with PsA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-cytokines-by-week-24-correlate-with-long-term-efficacy-of-guselkumab-through-two-years-in-bio-naive-adults-with-psa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-cytokines-by-week-24-correlate-with-long-term-efficacy-of-guselkumab-through-two-years-in-bio-naive-adults-with-psa/