Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Prior research has shown that viruses may trigger JDM, although the degree to which COVID-19 may serve as a trigger for JDM remains unknown. We performed an internal review of our JDM case numbers prior to and after COVID to better assess the effect COVID had on JDM rates at our institution. To assess whether the JDM phenotype changed after the COVID pandemic, we performed a retrospective review of the disease characteristics of newly diagnosed JDM patients prior to and after the onset of the COVID pandemic.
Methods: The Cure JM biorepository houses clinical data, laboratory data, and patient samples obtained at the onset of JDM. The following information was obtained from newly diagnosed JDM patients: MSA(myositis specific antibody), DAS (disease activity score), flow cytometry results, vWF antigen, neopterin, CMAS(childhood myositis assessment scale), capillary end loop(ERL), LDH, Aldolase, ESR, CRP, IgG, complements, ANA, and age at diagnosis. We identified 10 patients with a diagnosis of JDM from January 1st 2020-July 1st 2021 who were designated as the post-COVID-19 group. This population was compared to a total of 51 patients diagnosed with JDM between Jan 1st 2010 and December 31st 2019 who were designated as the pre-COVID-19 group. Data analysis was performed using Welch T-testing. Research enrollment was impacted due to the COVID-19 pandemic. To better assess JDM rates, chart review and EMR reports were obtained to determine the total number of JDM diagnoses.
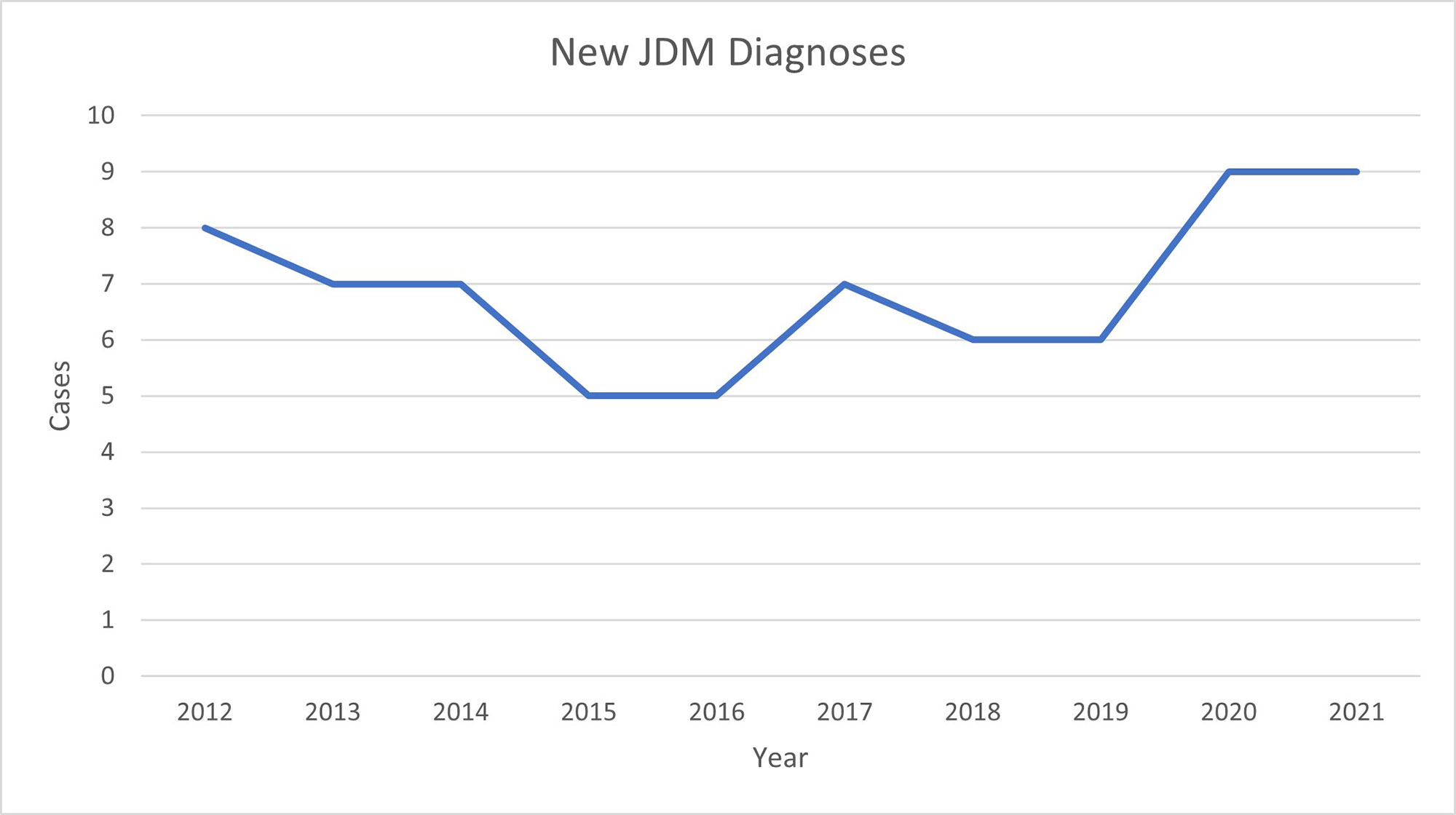
Results: T-testing showed no significant change in DAS, ERL count, T or B cell flow cytometry, vWF antigen, CK, CMAS, CRP, Aldolase, LDH, IgG, complements or ANA titer between the pre- and post- COVID-19 JDM groups. The analysis showed a significant change in NK cell population with a decrease in the absolute NK cell number (pre 163, post 90.75. P value 0.03), and NK cell percentage (pre 6.6%, post 3.625%, P value 0.008). The total number of new JDM cases rose from an average of 6.3 cases per year to an average 9 cases per year from January 1st 2020 to December 31st 2021.
Conclusion: This study showed a modest increase in the number of new JDM cases since the onset of the pandemic. Interestingly, the NK cell population in the post-COVID-19 JDM patients were significantly decreased. NK cells have multiple roles in not only immune regulation, but also the immune response to viruses. This study suggests that NK cells play a role in the development of in virally mediated JDM. Future studies will be important to further delineate the importance of NK cells in JDM patients after COVID. Markers of JDM disease severity, including DAS, Neopterin, CK, and CMAS, did not significantly change in our institution’s JDM population after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Costin C, Morgan G, Khojah A, Pachman L. Changes in Juvenile Dermatomyositis After the COVID-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis-after-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis-after-the-covid-19-pandemic/