Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: TNF inhibitors (TNFi) are widely used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study aims to analyse the profile of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) after 6 months (m) of treatment with TNFi in order to find cellular biomarkers of response.
Methods: This was a prospective bi-center pilot study including 50 RA patients under TNFi therapy. PBMC were isolated from patients at baseline and 6m of treatment, and flow-cytometry analysed. Clinical activity at baseline and 6m of TNFi treatment was assessed by DAS28. Clinical remission (DAS28²2.6) after 6m of treatment was considered as optimal response. The association between clinical remission and the percentage of change (Δ, 6m-0m) within each PBMC subset was analysed through multivariate log-regression model (odds ratio; 95% CI). All the analyses were adjusted by sex, age, concomitant-methotrexate, rheumatoid-factor and baseline-DAS28.
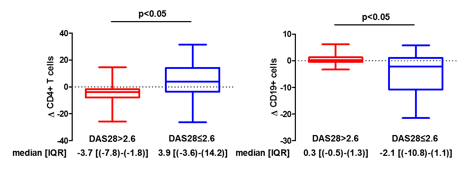
Results: Increased percentage of CD4+ T cells (ΔCD4+) was found after 6m of TNFi treatment in optimal responders; while suboptimal responders showed decreased percentage of this cell population (OR: 1.08; 95% CI: 1.01-1.16; p: 0.017). In addition, the percentage of B cells after 6m of TNFi treatment (ΔCD19+) decreased in optimal responders (OR: 0.7; 95% IC: 0.54-0.96; p: 0.024). This effect was essentially promoted by na•ve B cells (OR: 0.7; 95% IC: 0.47-0.93; p: 0.017). The other PBMC subsets (monocytes, NK and CD8+ T cells) did not show statistical differences.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that CD4+ T and B cells may be useful as cellular biomarkers of response to TNFi in RA patients.
Funding: ISCIII (PI16/00474; PI16/01092)
Figure Legend: Percentage of change of CD4+ T cells and CD19+ B cells after 6m of TNFi treatment according to clinical remission achievement (DAS28²2.6). The U Mann-Whitney test was applied considering p-value<0.05 as significant difference.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hernández-Breijo B, Gañán-Nieto I, Sobrino C, Navarro-Compán V, Martínez A, García-Hoz C, Bachiller J, Bonilla Hernán MG, Roy G, Vázquez M, Balsa A, Villar LM, Pascual-Salcedo D, Rodríguez-Martín E, Plasencia C. Changes in CD4+ T and B Cell Profile As Indicator of Clinical Remission to TNF Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-cd4-t-and-b-cell-profile-as-indicator-of-clinical-remission-to-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-cd4-t-and-b-cell-profile-as-indicator-of-clinical-remission-to-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/