Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Factor (RF) is an antibody against the Fc fragment of IgG that contributes to the Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) development. RF can bind the Fc fragment of infliximab, suggesting the hypothesis that it can also bind other monoclonal antibodies (mAB (Adalimumab, Golimumab and Infliximab)) and fusion proteins (FP (Etanercept)), leading to a lower drug levels and potential early withdrawal. Conversely, the absence of Fc fragment in Certolizumab Pegol (PEG) may lead to a higher retention rate in comparison with other drugs in RA patients (pts) with high RF titers. Objectives: a) to compare the retention rate to PEG vs. mAB and vs. FP in AR pts with high RF titers; b) to conduct the similar analysis but stratifying in naïve and non-naïve pts.
Methods: Longitudinal, retrospective and multicentre study including pts with RA and treated with any TNFi (mAB, FP or PEG) between 2010-2022. RF levels before TNFi initiation and the dates of both initiation and treatment withdrawal were collected. Log-rank test and Kaplan-Meier curves were conducted to evaluate the retention rate to the three molecular structures according to the level of RF considering the quartiles of the baseline titres as cut-offs: < 15, >60 and >200 UI/ml (negative, high, and very high levels, respectively). A sensitivity analysis was performed using a Propensity Score (PS) matching the PEG, mAB and FP populations according to the age, sex and previous TNFi use.
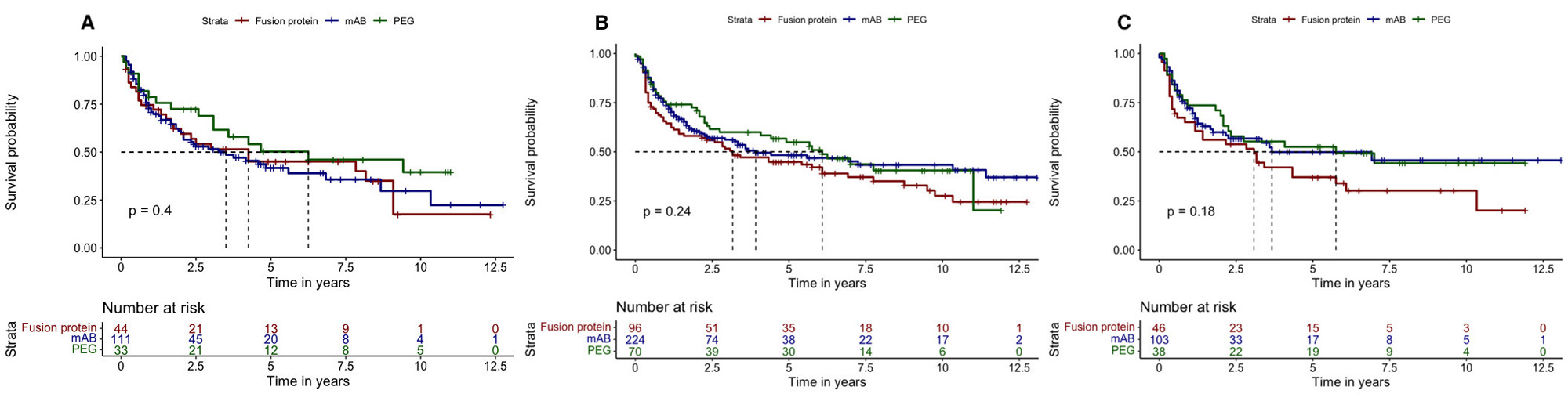
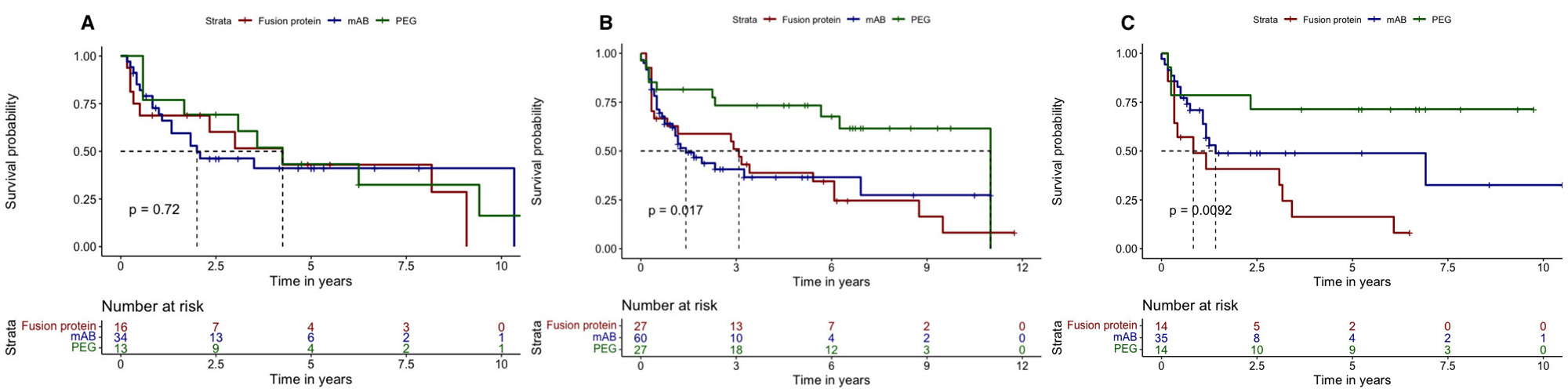
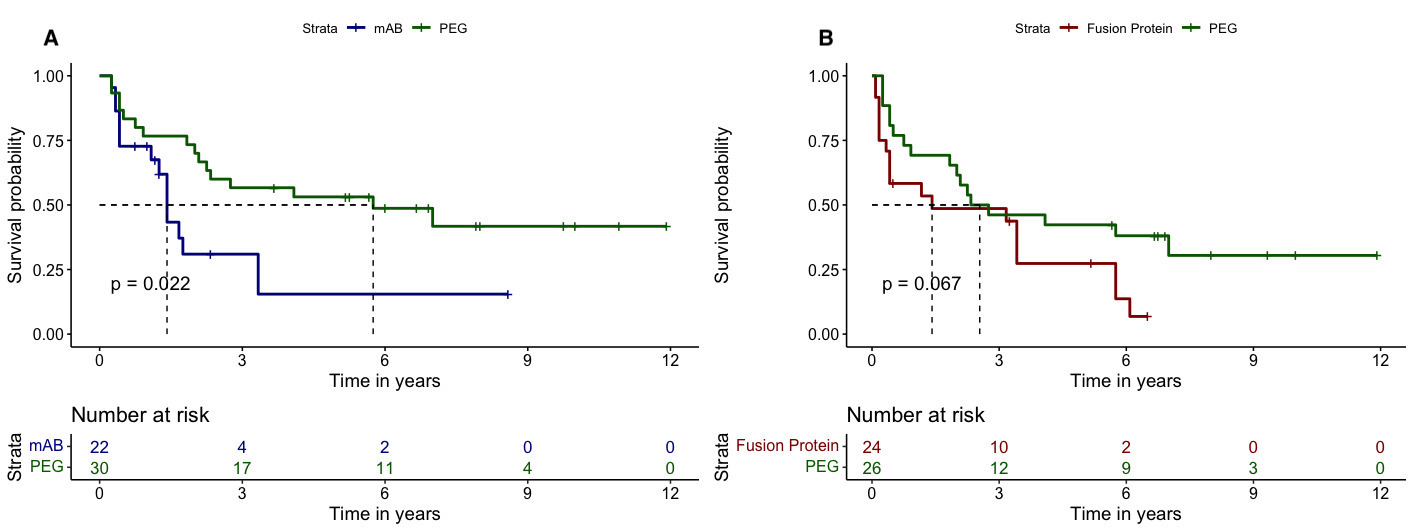
Results: A total of 755 pts with RA treated with TNFi (132 PEG, 441 mAB and 182 FP) and with available titres of RF were included (mean age 53 (12) years, 80.2% female and 70.7% naïve). In the total population, a similar retention rate to PEG, mAB and FP was found (6.1y (95%CI 3.7-NA), 4.2y (95%CI 3.3-8.7) and 4.6y (95%CI 2.9-7.8), respectively, p=0.380). According to the RF levels, the retention rate to the three molecular structures were similar in seronegative pts(F.1A), and in those with high (F.1B) and very high levels (F.1C). When selecting non-naïve pts, those with negative RF titres showed similar retention rates across molecular structures (F.2A). However, in non-naïve ptswith high levels of RF, those treated with PEG showed a significant longer retention rate in comparison with mAB and FP (median 11.0y (95%CI 6.3-NA), 1.4y (95%CI 1.1-NA) and 3.1y (95%CI 0.8-8.8) respectively, p=0.017)(F.2B). Similar results were obtained in non-naïve ptswith very high titres of RF (F.2C). In ptswith very high levels of RF, the sensitivity analysis using the PS showed a significant longer retention rate to PEG vs. mAB (median 5.8y (95%CI 2.3-NA) vs. 1.4y (95%CI 1.3-NA), respectively, p=0.022) irrespectively of the previous use of TNFi (F.3A). Likewise, PEG vs. FP showed a longer retention rate, although these differences were non-significant (median 2.5y (95%CI 1.8-NA) vs. 1.4y (95%CI 0.4-5.8), p=0.067)(F.3B).
Conclusion: High or very high RF titers before TNFi initiation were associated with a longer retention rate in non-naïve pts treated with PEG in comparison with mAB and FP. When matching the population using PS, very high levels of RF were associated with longer retention rate to PEG vs. mAB irrespectively of the previous use of TNFi. These results confirm the possible effect of the RF in binding the Fc fragment of the drug.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López Medina C, Calvo J, Abalos-Aguilera M, Cepas F, Plasencia-Rodríguez C, Martinez Feito A, Balsa A, Faré-García R, Juan Mas A, Ruiz-Esquide V, Sainz-Comas L, Díaz-Torné C, Godoy J, Anon Onate I, Mena Vazquez N, MANRIQUE S, Moreno Garcia M, Ortega Castro R, Escudero-Contreras A. Certolizumab Pegol Shows Longer Retention Rate in Comparison with Other TNF Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and High Rheumatoid Factor Titers at Baseline. a Multicentre and Retrospective Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-pegol-shows-longer-retention-rate-in-comparison-with-other-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-high-rheumatoid-factor-titers-at-baseline-a-multicentre-and-retrospect/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-pegol-shows-longer-retention-rate-in-comparison-with-other-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-high-rheumatoid-factor-titers-at-baseline-a-multicentre-and-retrospect/