Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) substantially improve symptoms in Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS), although 40% patients are unresponsive. Identifying biomarkers predictive of TNFi treatment response could help make informed therapeutic choices and understand mechanism of resistance.
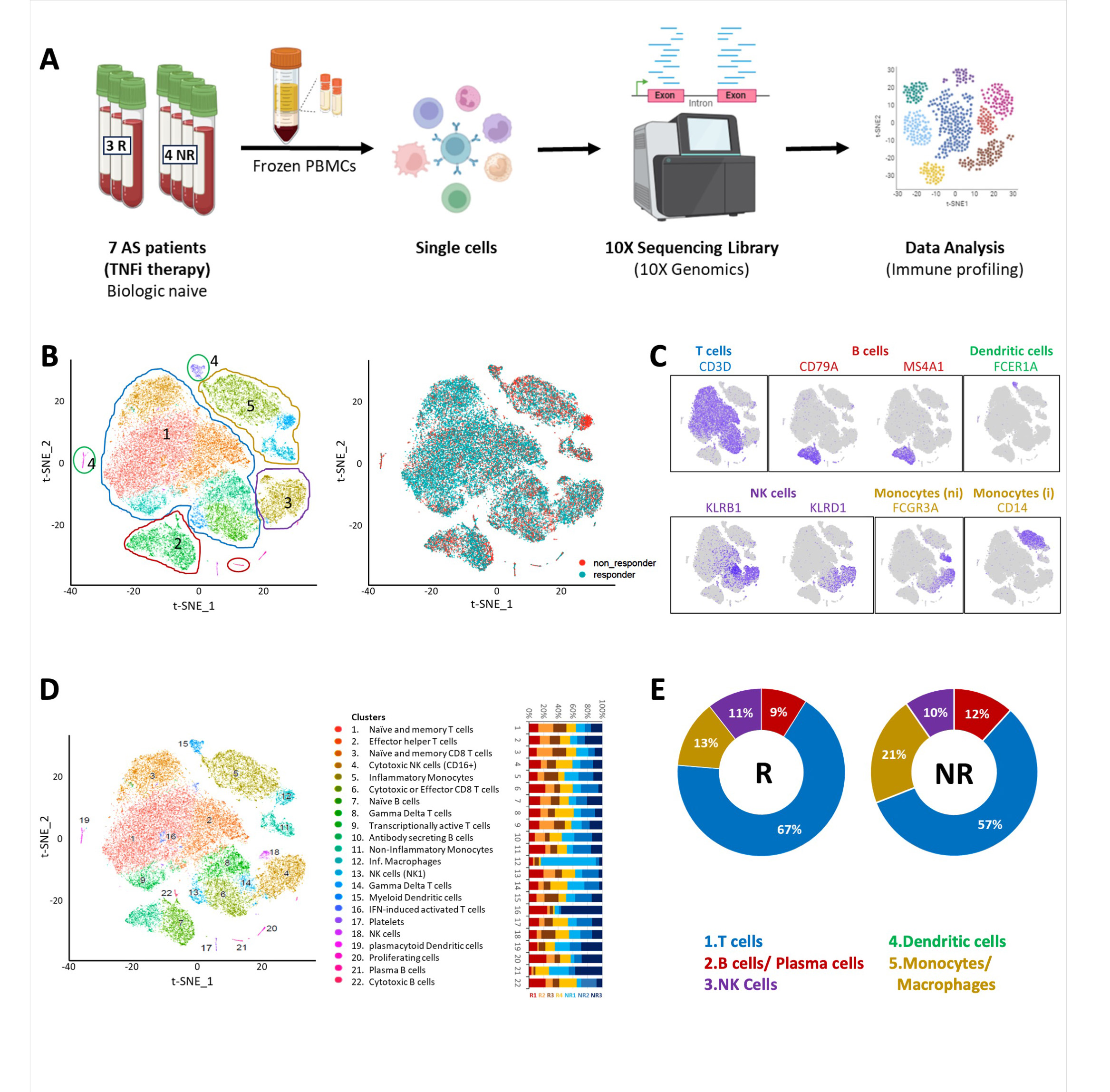
Methods: A total of 21 male biologic naïve patients with active AS, meeting the modified New York Criteria, were recruited for the study, 7 for test and 14 for validation cohort. PBMCs were isolated and scRNA-seq for transcriptome profiling (Figure 1A-D) performed in test cohort followed by validation using Nanostring nCounter gene expression assay, protein expression using flow cytometry and serum cytokines using ELISA. Response to therapy was assessed by the treating physician and include at least 50% reduction in BASDAI.
Results: Non-responders demonstrated a lower proportion of T cells and a higher proportion of monocytes as compared to responders (Figure 1E). Results were validated in the second cohort. A total of 73 differentially expressed genes were identified in total PBMCs. CXCR4 and CD74 were upregulated in the monocytes of non-responders, further validated Nanostring nCounter gene expression. A novel transcript AC114760.2 (antisense to STK17B) was downregulated in non-responders.
At baseline, expression level of interferon regulated genes (IRGs), STK17B and MIF receptors; CXCR4 and CD74, were upregulated in non-responders suggesting that in non-responders, monocytes involved in inflammasome formation are activated before start of the treatment, resulting in enhanced inflammatory response. After TNFi treatment, a relative decrease in the levels of CXCL10, CCL4, IL-1b, TNFa and MIF was observed in responders. MIF stimulation led to increased inflammatory cytokines in non-responders.
Conclusion: Baseline cellular immunophenotypic signature can help predict treatment responses to TNFi in AS patients and provide insight into pathogenic mechanisms.
Fig. 1E: The pie chart shows the percentages of B cells, T cells, monocytes and NK B cells across Responders (R) and Non-Responders (NR) with TNFi treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Talukdar A, Ibeh N, Machhar R, Aparnathi M, Keshavarazi S, Srinath A, Nakamura A, Inman R, Rahman P, Jurisica I, Haroon N. Cellular Immune Activation Signatures at Baseline Predict Response to TNF Inhibitors in Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cellular-immune-activation-signatures-at-baseline-predict-response-to-tnf-inhibitors-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cellular-immune-activation-signatures-at-baseline-predict-response-to-tnf-inhibitors-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/