Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 13, 2019
Title: 6W013: SLE – Clinical VI: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, & Outcomes (2882–2887)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Cell-bound complement activation products (CB-CAPs) are stable forms of classical complement activation ex-vivo, with high sensitivity and specificity for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We sought to compare the performance of CB-CAPs to the gold standard low complement C3 or C4 in distinguishing SLE from other rheumatic diseases and healthy individuals.
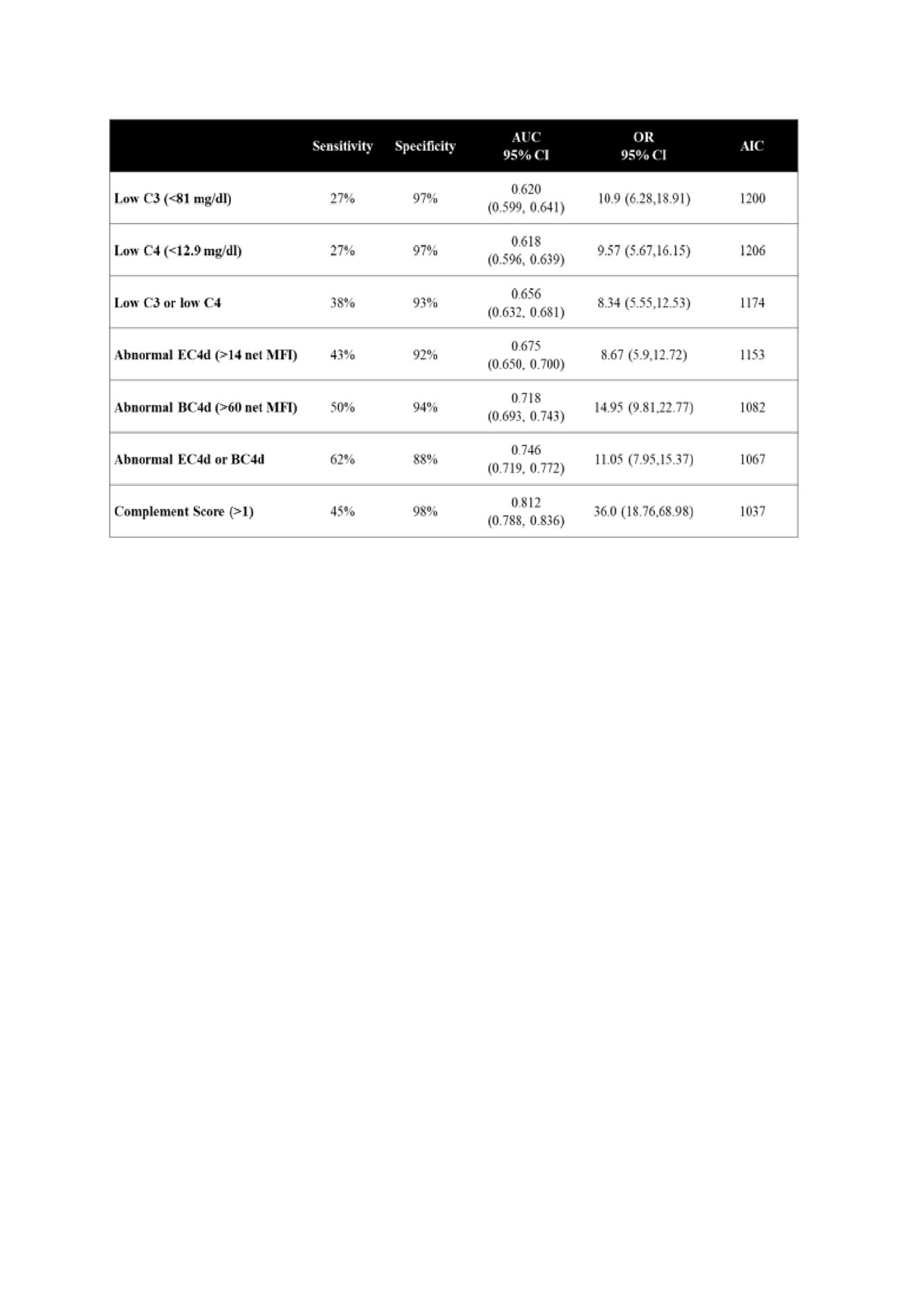
Methods: Multiple academic centers in the United States contributed to the adult ( >= 18 years) cross sectional cohort (n=1200) consisting of SLE (n=450), healthy individuals (n=252), and other rheumatic diseases (n=450; 189 RA, 88 Sjögren’s, 90 fibromyalgia, and 83 other connective tissue diseases). Abnormal CB-CAPs status (erythrocyte bound C4d [EC4d] and/or B-Lymphocyte bound C4d [BC4d] >99th percentile of normal healthy group) was determined using flow cytometry. Serum low C3 (< 81 mg/dl) and low C4 (< 12.9 mg/dl) levels was determined using immunoturbidimetry. Performance of the markers, either alone or in combination, to distinguish SLE from other rheumatic diseases and healthy controls were established using sensitivity, specificity, odds ratio (OR) and area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC). Youden Index (Sensitivity + Specificity – 100) and Akaike information criteria (AIC) were also calculated. The combination of 4 complement marker abnormalities was also evaluated using logistic regression and composite score cumulating the presence of these abnormalities was calculated.
Results: Abnormal CB-CAPs status yielded 62% sensitivity with 88% specificity in distinguishing SLE from the group with other diseases (Table). Youden index was 0.492±0.027. Low C3/C4 status yielded 38% sensitivity and 93% specificity in distinguishing SLE from the group with other diseases. Youden index for low C3/C4 (0.313±0.025) was significantly lower than the index associated with abnormal CB-CAPs status (p< 0.01). Specificity of low C3/C4 and abnormal CB-CAPs in distinguishing SLE from healthy individuals was 93% and 99%, respectively. AUC was significantly higher with BC4d (0.718) than with EC4d (0.675; p< 0.01), low C3 (0.620; p< 0.01), low C4 (0.618; p< 0.01) and low C3 and/or C4 status (0.656; p< 0.01). Average (SEM) composite score cumulating all 4 abnormalities (range 0-4) was higher in SLE (1.47±0.06) than disease control group (0.21±0.02) (p< 0.01) and healthy individuals (0.01±0.02) (p< 0.01). The cumulative complement scoring system yielded higher AUC (0.812), higher OR (36.0 CI95%: 18.8-69.0), lower AIC (1037) than low C3/C4 or abnormal CB- CAPS; score greater than 1 abnormality yielded 45% sensitivity and 98% specificity.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that the combination of CB-CAPs with low complement have superior diagnostic performance in SLE than either abnormality alone.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Narain S, Wallace D, Putterman C, Arriens C, Askanase A, Kalunian K, Collins C, Saxena A, Massarotti E, Alexander R, Ibarra C, O'Malley T, Conklin J, Ramsey-Goldman R, Ahearn J, Manzi S, Weinstein A, Dervieux T. Cell-bound Complement Activation Products in Combination with Low Complement C3 or C4 Have Superior Diagnostic Performance in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cell-bound-complement-activation-products-in-combination-with-low-complement-c3-or-c4-have-superior-diagnostic-performance-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cell-bound-complement-activation-products-in-combination-with-low-complement-c3-or-c4-have-superior-diagnostic-performance-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/