Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have markedly improved the treatment of many advanced cancers; however, they can result in immune-related adverse events (irAE) including ICI-inflammatory arthritis (ICI-IA). ICI-IA often resembles rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 9% of ICI-IA patients are CCP+. In RA, ACPA epitope expansion occurs in the years prior to onset of clinical disease. In this study we examined the degree of ACPA epitope expansion in CCP+ RA and ICI-IA patients.
Methods: We used clinical data and serum from 12 CCP+ ICI-IA patients enrolled in a prospective registry and 39 CCP+ RA patients enrolled in the CATCH-US early RA cohort. Anti-CCP screening was done using a commercial ELISA (positive >20 units/mL). Clinical differences between the two groups were compared using t-test, Fisher’s exact or Wilcoxon-rank sum. Clinical characteristics of CCP- ICI-IA patients were also included as a comparator. A custom, bead-based antigen array was used to identify ACPA reactivities to 16 putative RA-associated citrullinated proteins. Hierarchical clustering software was used to create heatmaps to identify ACPA levels. Z-scores for fluorescence intensity were calculated separately for each peptide, and fluorescence level above the mean was defined as a positive ACPA. The number of positive epitopes for each patient was determined and compared categorically between the ICI-IA and RA patients using Fisher’s exact. We also performed the assay on synovial fluid from 3 ICI-IA patients.
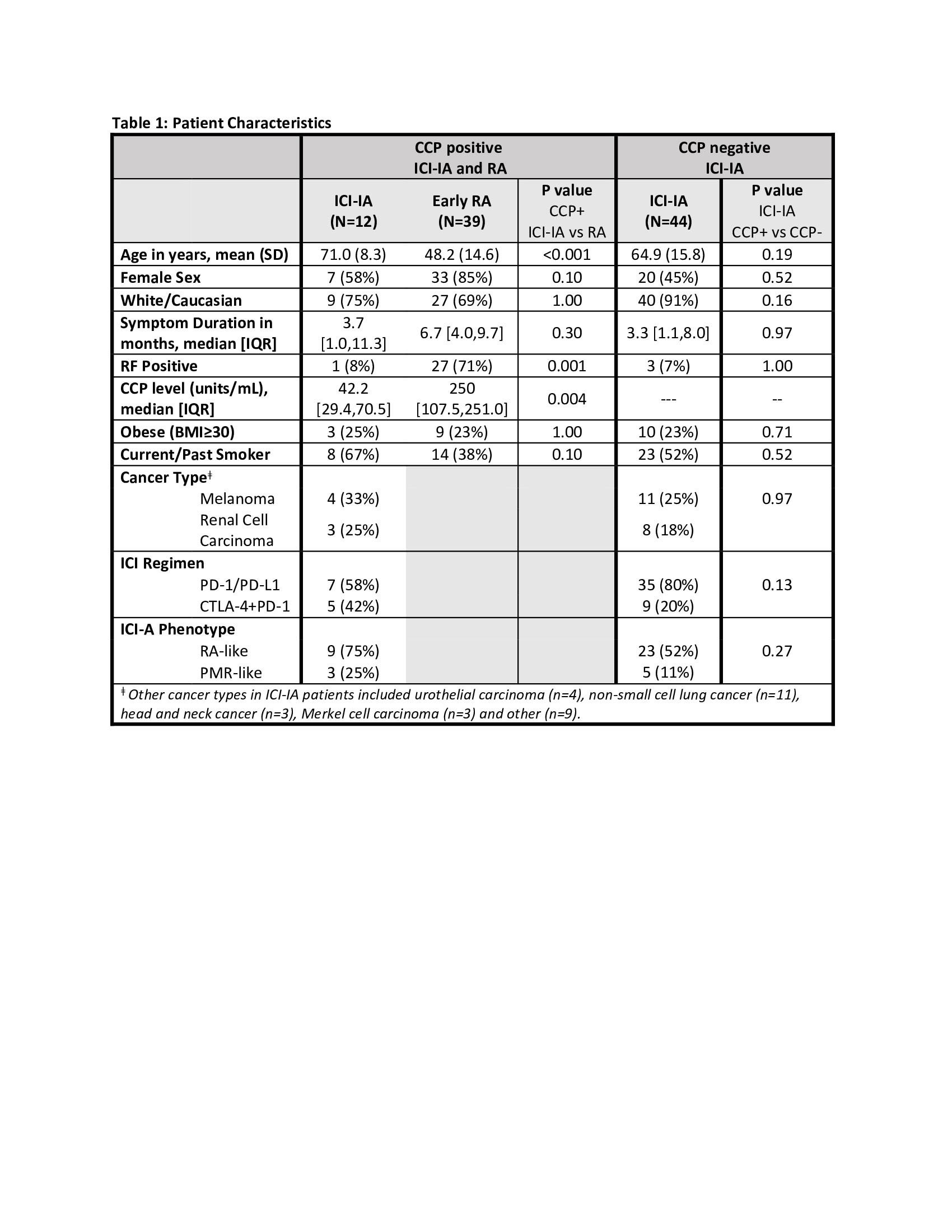
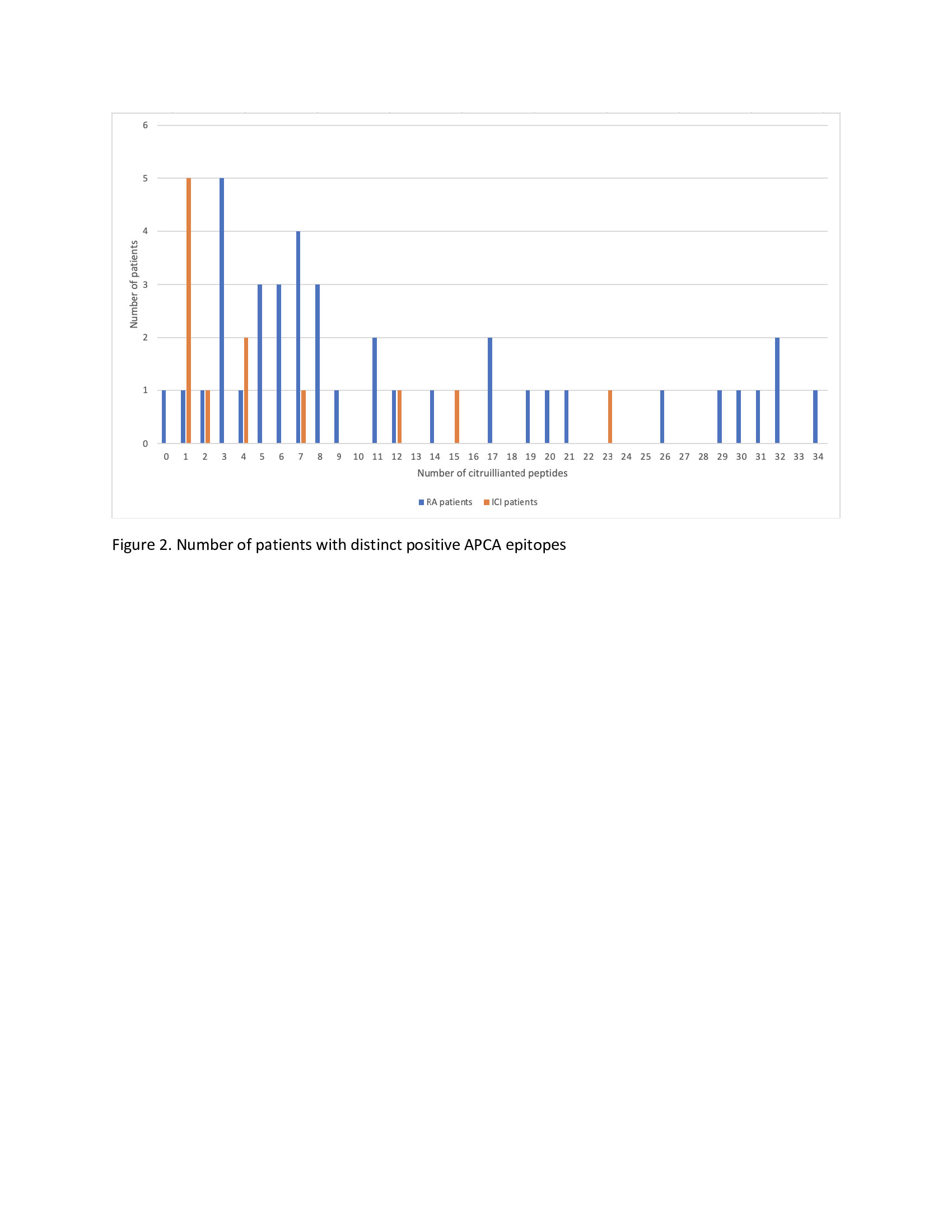
Results: Characteristics of CCP+, CCP- ICI-IA and CCP+ early RA are listed in Table 1. CCP+ and CCP- ICI-IA patients had similar characteristics. Compared to CCP+ early RA patients, however, CCP+ ICI-IA patients were older (p< 0.001), less likely to have positive rheumatoid factor (RF) (p< 0.001) and had lower titer of anti-CCP (p=0.004). There were trends toward RA patients being more likely female and less likely to be a current/former smoker (p=0.10). Median symptom duration for ICI-IA patients was 3.7 months compared to 6.7 months in RA patients. ACPA reactivities are displayed in Figure 1 with lower signal intensities (level of ACPA) and a lower number of distinct ACPA epitopes seen in the serum of ICI-IA patients compared to RA patients. Figure 2 highlights that among the ICI-IA patients, 67% were positive for 0-4 ACPA epitopes, 8% for 5-10 epitopes and 25% for >10 epitopes, as opposed to 23% of RA patients positive for 0-4 epitopes, 36% for 5-10 epitopes, and 41% for >10 epitopes (p=0.02). The one ICI-IA patient who was also RF positive had 12 positive ACPA epitopes. There were no significant differences in the median [IQR] number of ACPA epitopes in ICI-IA patients who were smokers vs. nonsmokers, RA-like vs. PMR-like, or who received ICI combination vs. ICI monotherapy. In the 3 ICI-IA patients with synovial fluid samples, synovial fluid ACPA was not demonstrated.
Conclusion: ICI-IA patients had lower ACPA titers and targeted fewer ACPA epitopes than early RA patients. It remains to be determined if ICI-IA represents an accelerated model of RA pathogenesis with ICI triggering an early transition from pre-clinical to clinical disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ghosh N, Rajesh D, Kirschmann J, Jannat-Khah, DrPH, MSPH D, Chan K, Goodman S, Bykerk V, Robinson W, Bass A. CCP+ Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Arthritis Patients Have Less ACPA Epitope Expansion Than CCP+ Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ccp-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-arthritis-patients-have-less-acpa-epitope-expansion-than-ccp-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ccp-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-arthritis-patients-have-less-acpa-epitope-expansion-than-ccp-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/