Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstracts
Session Time: 8:00AM-9:30AM
Background/Purpose: Understanding the roles of diverse fibroblast subsets is of great importance in elucidating the pathogenesis of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis (SSc). However, how the immunoregulatory function of fibroblasts contributes to SSc pathology remain poorly understood.
Methods: We analyzed affected skin and blood samples from SSc patients and healthy individuals using multiplex immunofluorescence staining, single-cell transcriptomics and flow cytometry. We investigated the CCL19-CCR7 axis in skin fibrosis using anti-CCL19 antibodies and Ccr7-deficient mice in a bleomycin-induced SSc model.
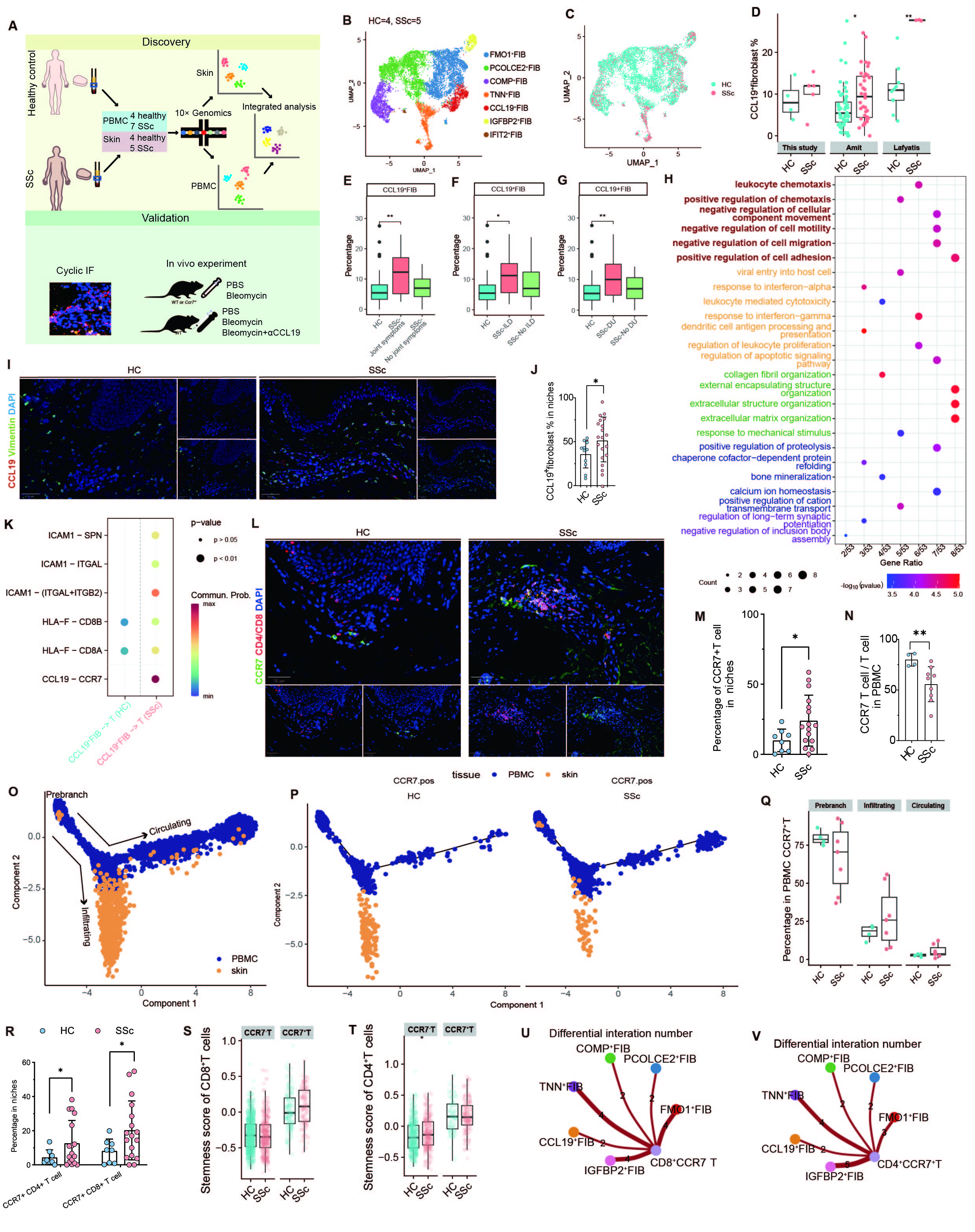
Results: We identified a proinflammatory fibroblast subset, CCL19+ fibroblast, which was upregulated in SSc dermis and associated with the severity of dermal fibrosis in SSc. Interestingly, CCL19+ fibroblasts highly expressed key genes involved in immune modulation, leukocytes migration and adhesion of leukocytes in SSc. CCL19-CCR7 was the most significant ligand-receptor pair from CCL19+ fibroblast to T cells in SSc compared to healthy controls. Trajectory pseudo-analysis of matched peripheral blood and skin T cell scRNA-seq showed that CCR7+ T cells were recruited from peripheral blood into dermal immune niches via the CCL19-CCR7 axis. These recruited CCR7+ T cells, especially CCR7+CD8+ T cells, displayed heightened stemness and cytotoxicity along with engaging in profibrotic interactions with ECM-producing fibroblast in SSc. In a mouse model of SSc, blocking the CCL19-CCR7 axis using an anti-CCL19 antibody or Ccr7 knockout attenuated dermal fibrosis and reduced T cell infiltration.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the pivotal role of CCL19+ fibroblasts in stromal-immune interactions, remodeling the fibrotic microenvironment and driving fibrosis progression through formation of dermal immune niches in SSc. The CCL19-CCR7 axis represents a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of SSc.
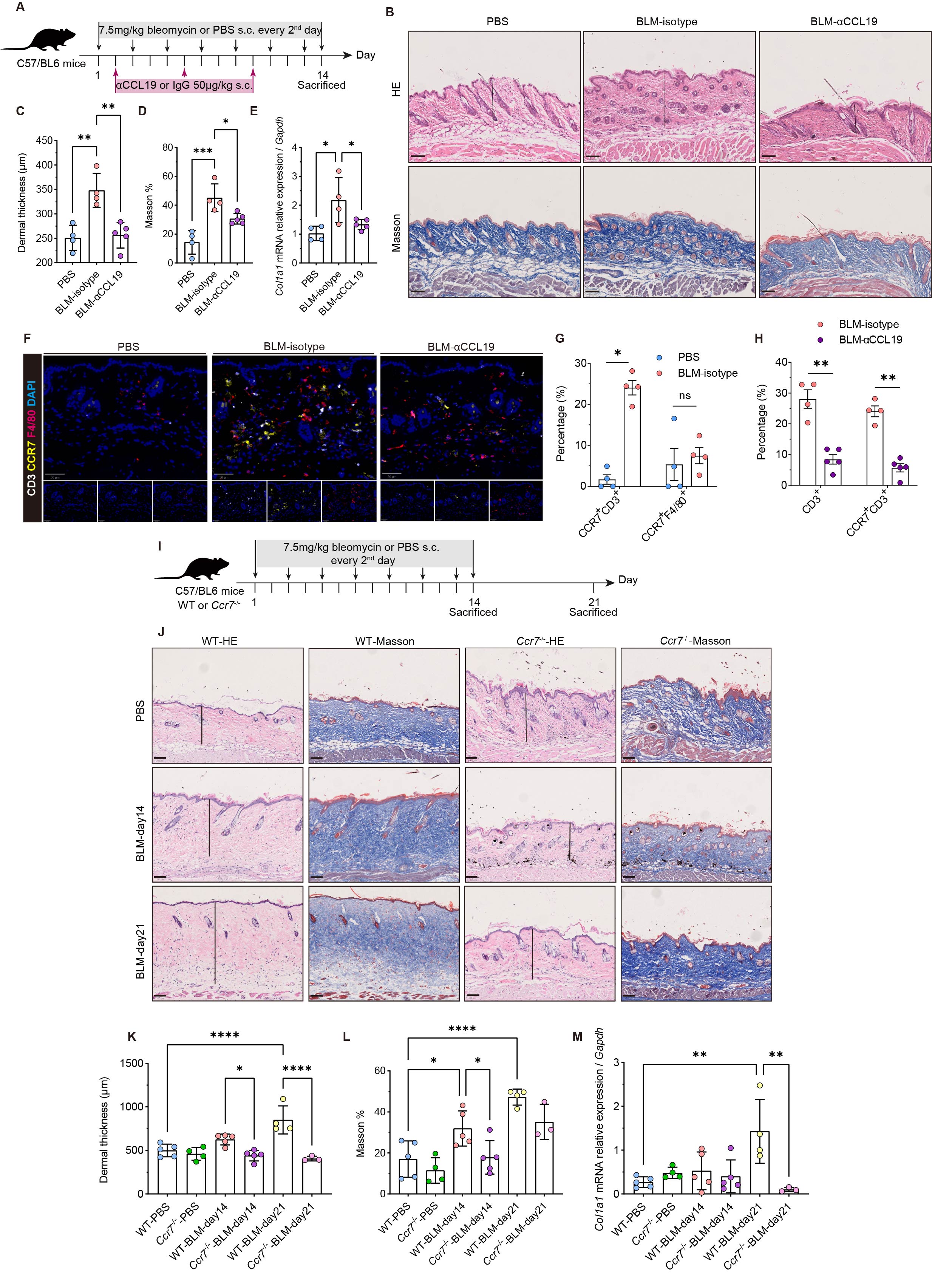
A, Schematic representation of the in vivo experiment. n = 4 mice in PBS and isotype antibody treated bleomycin group, n = 5 mice in anti-CCL19 antibody treated group. B, Representative H&E staining (top) and Masson staining (below) of the mice skin from the groups of mice depicted in A. Scale bar, 100 μm. C-E, Quantitative analysis of dermal thickness determined by H&E staining (μm) (C), collagen volume fraction calculated from Masson staining images, expressed as a percentage of the total dermis volume (D) and relative mRNA expression of Col1a1 (E). F, Representative staining for CD3, F4/80 and CCR7 in mice skin. Scale bar, 50 μm. G, Proportions of CD3+ T cells and F4/80+ macrophages in mice skin with or without bleomycin injection. H, Proportions of CD3+ T cells and CCR7+ CD3+ T cells in the skin of bleomycin-treated mice receiving isotypic or anti-CCL19 antibodies. I, Outlines of the design in wild-type and Ccr7-/- mice following bleomycin-induced dermal fibrosis. n = 5 mice in the WT control group and n = 4 in the Ccr7-/- control group. On day 14 of bleomycin injection, n = 5 mice in the WT and Ccr7-/- groups. On day 21 of bleomycin injection, n = 4 mice in the WT group and n = 3 in the Ccr7-/- group. J, Representative images of H&E and Masson staining of the skin of WT and Ccr7-/- mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. K-M, Quantitative analysis of dermal thickness (μm) (K), collagen volume fraction (L) and relative mRNA expression of Col1a1 (M). Data presented above are expressed as Mean ± SEM. p values were measured by one-way ANOVA and Holm-Šídák multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001.
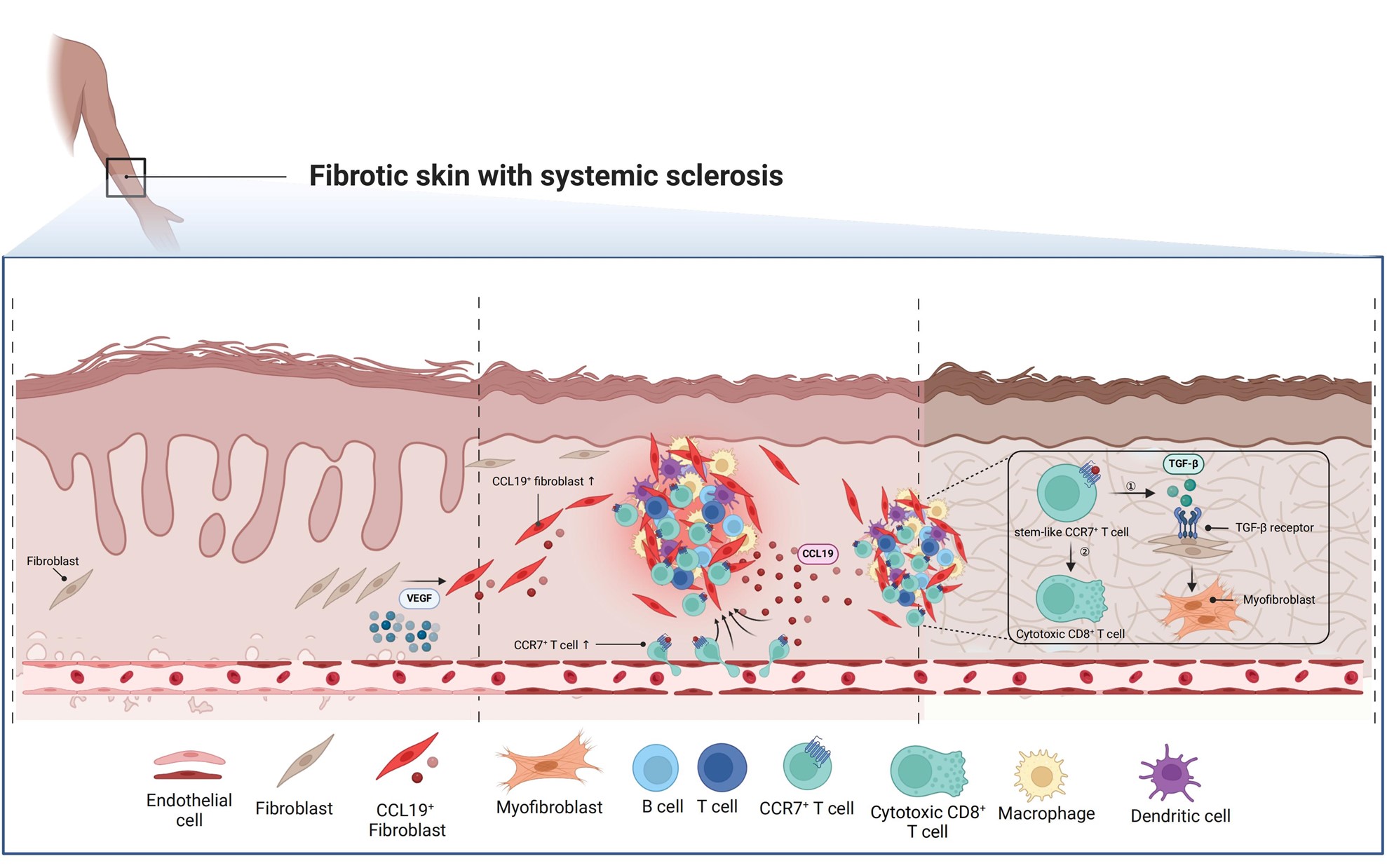
The unique fibrotic microenvironment linking immunopathology and fibrosis, defined as immune niches, is enriched in the affected dermis of SSc. VEGFA induces CCL19-expressing proinflammatory fibroblasts under vascular dysfunction. These proinflammatory fibroblasts continuously generate immune niches through chemokine secretion and recruitment of immune cells from peripheral blood, particularly CCR7+ T cells. These recruited T cells can subsequently interact with fibroblasts within the immune niches, establishing a positive feedback loop that drives the fibrosis progression. Created with BioRender.com.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guo W, Li Z, Xu D, Mu R. CCL19+ Fibroblasts Orchestrate Fibrotic Microenvironment via CCL19-CCR7 Axis in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ccl19-fibroblasts-orchestrate-fibrotic-microenvironment-via-ccl19-ccr7-axis-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ccl19-fibroblasts-orchestrate-fibrotic-microenvironment-via-ccl19-ccr7-axis-in-systemic-sclerosis/