Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) patients have increased cardiovascular(CV) risk with no data on CV risk scores in Indian patients.The primary objective was to study prevalence of traditional CV risk factors in RA. Secondary objectives were to assess performances of various CV risk scores with respect to each other and against subclinical atherosclerosis as measured by carotid intima media thickness(CIMT).
Methods: Patients fulfilling 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria for RA were included. Presence of traditional CV risk factors were recorded. 10-year-CV risks were predicted using Framingham Risk scoring using lipids (FRS-Lipids) and body mass index (FRS- BMI), QRISK-3, SCORE and the algorithm recommended by 2013-ACC/AHA guidelines(ASCVD) in patients who were 40 years or older. CIMT was measured on the far-wall of the common carotid artery at least 5 mm below its end. CIMT value greater than 0.90 mm or presence of plaque was chosen as marker of subclinical atherosclerosis.
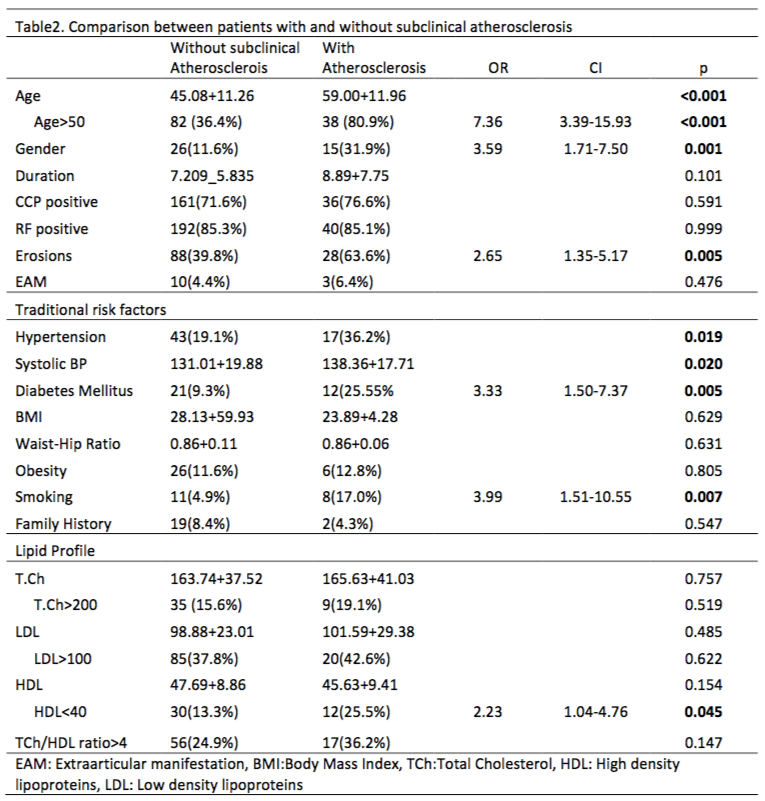
Results: Table 1 highlights clinical profile and risk factors in 334 enrolled patients. Friedman’s test for global variance of various showed significant difference among various risk predicting algorithms. Post-hoc analysis done with Wilcoxon-signed-rank test showed significant variability between each of them. When subclinical atherosclerosis assessed by CIMT was taken as reference, ASCVD and QRISK-3 showed maximum sensitivity Fig:1. Differences in disease characteristics and risk factors between patients with and without subclinical atherosclerosis and are underlined in Table 2.
Conclusion: There is considerable variablity between various risk scores and cannot be used indiscriminately in Indian RA patients. ASCVD and QRISK-3 scores had the maximum sensitivity in predicting subclinical atherosclerosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Muhammed H, Misra D, Ganguly S, Pattanaik S, Chaturvedi S, Singh H, Rai M, Anuja A, Mohindra N, Jain N, Kumar S, Agarwal V. Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Prevalence, Comparison of Risk Calculators and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Indian Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-risk-factors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-prevalence-comparison-of-risk-calculators-and-subclinical-atherosclerosis-in-indian-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-risk-factors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-prevalence-comparison-of-risk-calculators-and-subclinical-atherosclerosis-in-indian-patients/