Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
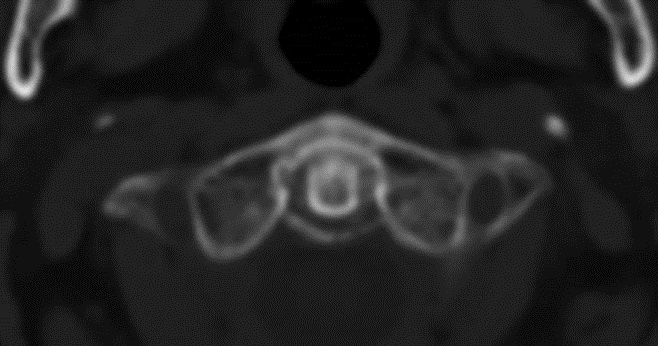
Background/Purpose: Chondrocalcinosis (CC) is commonly detected on
X-ray films of the knee, wrist, and symphysis pubis. Calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) deposition disease is sometimes associated with calcifications of the transverse ligament of the atlas (surrounding the odontoid process or periodontoid calcifications) and in rare occasions may manifest as an acute synovitis affecting the area involved (Crowned dense syndrome). In this study, we aimed to assess the presence of periodontoid calcifications (in the transverse ligament of the atlas) seen on cervical computed tomography (CT) scans of patients diagnosed with CPP arthritis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted assessing available cervical CT scans which were analyzed for periodontoid calcifications in one academic medical center during 2013-2023. All patients included were older than 60 years. Diagnosis of CPP crystal arthritis was considered if the patient had at least one previous acute synovitis with synovial fluid CPP crystals or CC on imaging and no other rheumatic inflammatory disease (such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis).
A review of cervical CT scans for periodontoid calcifications was performed by 2 independent (rheumatologists) observers. The presence of periodontoid calcifications was also assessed among a random sample of patients with either osteoarthritis (OA) or who suffered prior stroke, matched by age and gender (1:1) and serving as a control group. The frequency of periodontoid calcifications was compared between the CPP and the control groups. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive likelihood ratio (LR) for CPP based on the detection of periodontoid calcifications were calculated.
Results: 72 patients were included in both the CPP crystal arthritis group and the control group. Periodontoid calcifications were seen in 57 patients in the CPP group and only in 4 patients in the control group (79.2% vs 5.6% respectively), which was significantly higher (Yates’ correction for X2=76.9, P< 0.00001). According to our analysis, adding the presence of periodontoid calcifications on cervical CT in patients older than 60 years who are suspected of having CPP crystal arthritis (CC seen in the involved joint and not better explained by another inflammatory condition), may increase the sensitivity and specificity to 0.79 and 0.94 respectively. The positive LR was found to be 14.25.
Conclusion: Periodontoid calcifications seen on cervical CT were detected at a significantly higher frequency in patients with CPP crystal arthritis than in controls.
It is suggested that periodontoid calcifications may serve as another site for detecting CC (Knee, Wrist) when cervical CT is available for review.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brikman S, Shabshin N, Bieber A. Calcifications of the Transverse Ligament of the Atlas in Patients Diagnosed with Calciumpyrophosphate Crystal Arthritis – a Retrospective Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/calcifications-of-the-transverse-ligament-of-the-atlas-in-patients-diagnosed-with-calciumpyrophosphate-crystal-arthritis-a-retrospective-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/calcifications-of-the-transverse-ligament-of-the-atlas-in-patients-diagnosed-with-calciumpyrophosphate-crystal-arthritis-a-retrospective-observational-study/