Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1996–2018) Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoporosis related fractures cause significant morbidity and mortality. Bariatric weight loss surgery is an independent risk factor for osteoporosis. Post-surgery dual energy X-Ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans as well as close monitoring for calcium and vitamin D are suggested by current Bariatric surgery guidelines. This retrospective study of bariatric surgery patients was conducted to determine if current guidelines for osteoporosis screening are being adhered to. In addition, educational seminars were provided to increase bone health education to bariatric surgery providers and patients.
Methods: This was a single-center, retrospective study of patients who had bariatric surgery from 2018 through 2020. Qualifying surgeries were Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, Lap band and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Patients aged 18-49 were included. Excluded were patients with any history of steroid use, autoimmune disease, primary hyperparathyroidism and malabsorption disorders or those already being treated for bone loss. Demographics, type of surgery, pre and post-surgical vitamin D calcium levels and BMI were collected. Descriptive statistics and paired samples t-tests were used for comparisons. Two educational interventions were completed after the results of the retrospective data. One included an educational lecture on bone health guidelines for this population delivered to bariatric surgeons. Another lecture was directed towards patients who were planning or had completed surgery. Pre and post educational surveys were delivered.
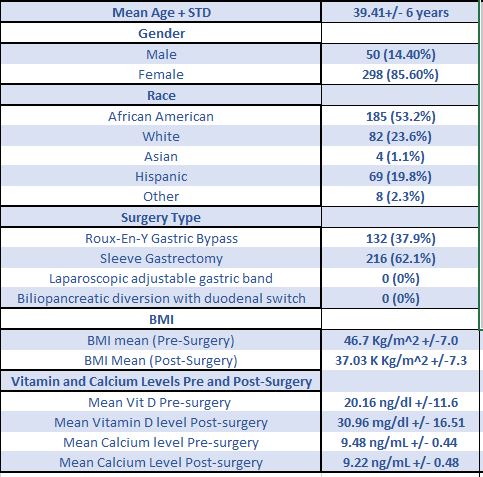
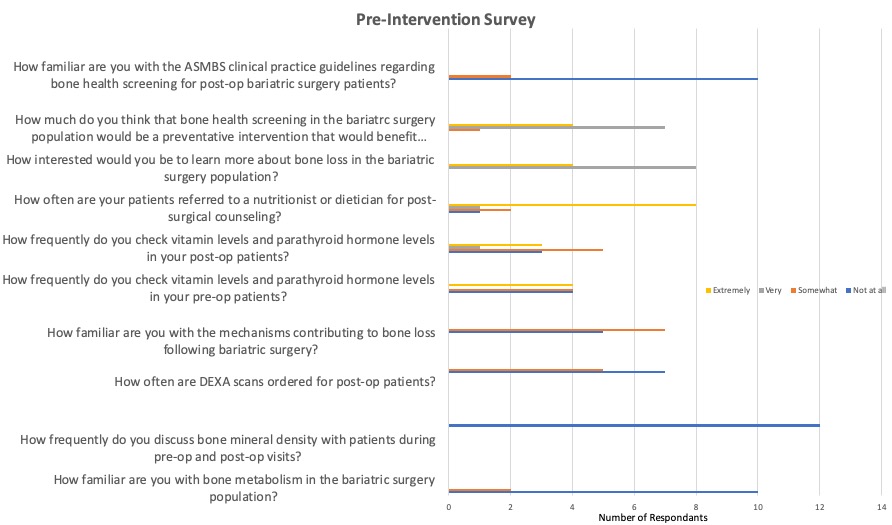
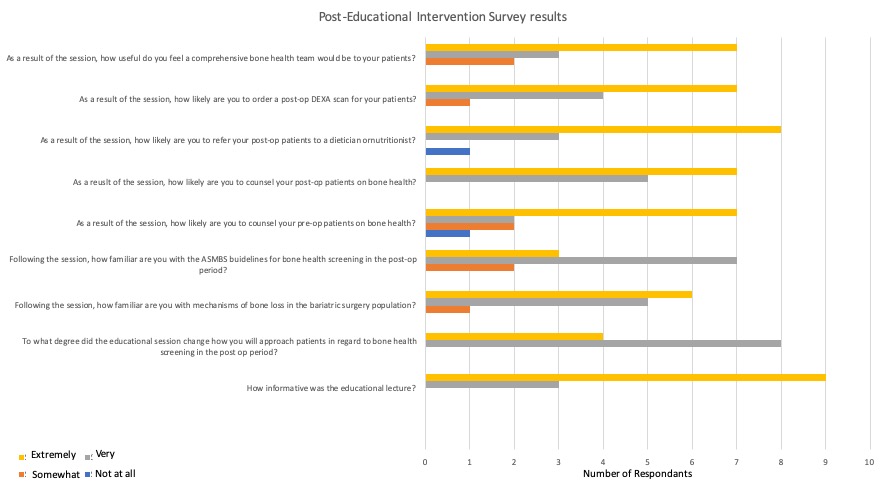
Results: 348 charts were reviewed. Demographic data and results are in Table 1. Calcium levels statistically decreased post-surgically while vitamin D levels increased . The decrease in calcium was most pronounced with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass as compared to sleeve gastrectomy 9.13 ng/ml vs. 9.27 ng/ml (P< 0.01). Only one patient in the study period had a post-surgical DEXA scan which revealed low bone mineral density for chronological age (Z score -2.7). Surveys following educational intervention revealed very positive results using Likert scale (Image1 and 2) but did not increase DEXA scans in the study period.
Conclusion: Screening with DEXA scans after bariatric surgery is not being done based on this brief retrospective study. This may be due to poor follow-up after surgery or the short study period following the interventions. Continued educational interventions may be successful if expanded to target primary care providers in addition to bariatric surgeons given the poor rate of patient follow-up. Our educational interventions were positively surveyed. Moreover this study found, post-surgically, calcium levels decreased and vitamin D level increased. In addition, calcium levels decreased more with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. The inverse relationship of Vitamin D with weight loss has been reported elsewhere presumed to be related to redistribution of adipose stored vitamin D. These findings raise another potential area for modification of practice. Perhaps in addition to guided Vitamin D management and supplementation more dedicated calcium supplementation management should also be considered for these patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Benck A, Zimmerman H, Trang A, Shakoor N, Khandelwal S. Bone Health Following Bariatric Surgery: A Single Center Quality Improvement Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bone-health-following-bariatric-surgery-a-single-center-quality-improvement-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bone-health-following-bariatric-surgery-a-single-center-quality-improvement-study/