Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: Omics
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with lupus nephritis (LN) have variable responses to standard-of-care therapy, and a third of patients with class III, IV, or V show a progressive decline in kidney function. Identifying distinct inflammatory processes associated with LN using non-invasive tools may improve treatment targeting. Here, we aimed to identify subgroups of LN patients that differ in systemic immune activity and to evaluate their relationship to kidney pathology.
Methods: Mass cytometry using four 48-marker panels was applied to characterize peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 140 patients with active, biopsy-proven proliferative (class III or IV +/- V, n=98) or membranous (class V, n=42) nephritis and 40 healthy controls in the Accelerated Medicine Partnership RA/SLE Network Phase II study. K-means clustering was used to stratify patients based on the proportions of 55 immune cell subsets defined using B cell-, T cell-, myeloid cell-, and NK cell-focused panels.
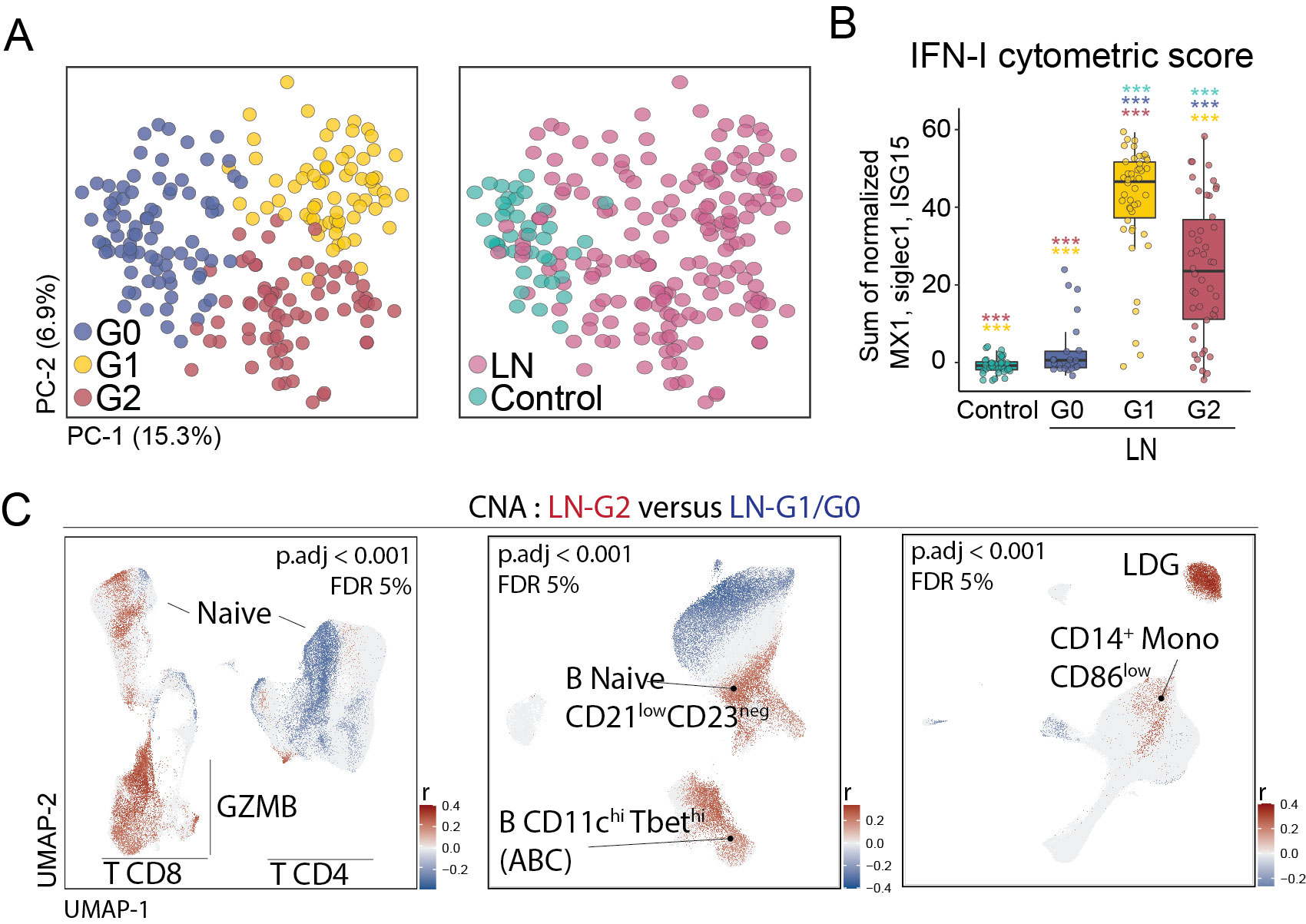
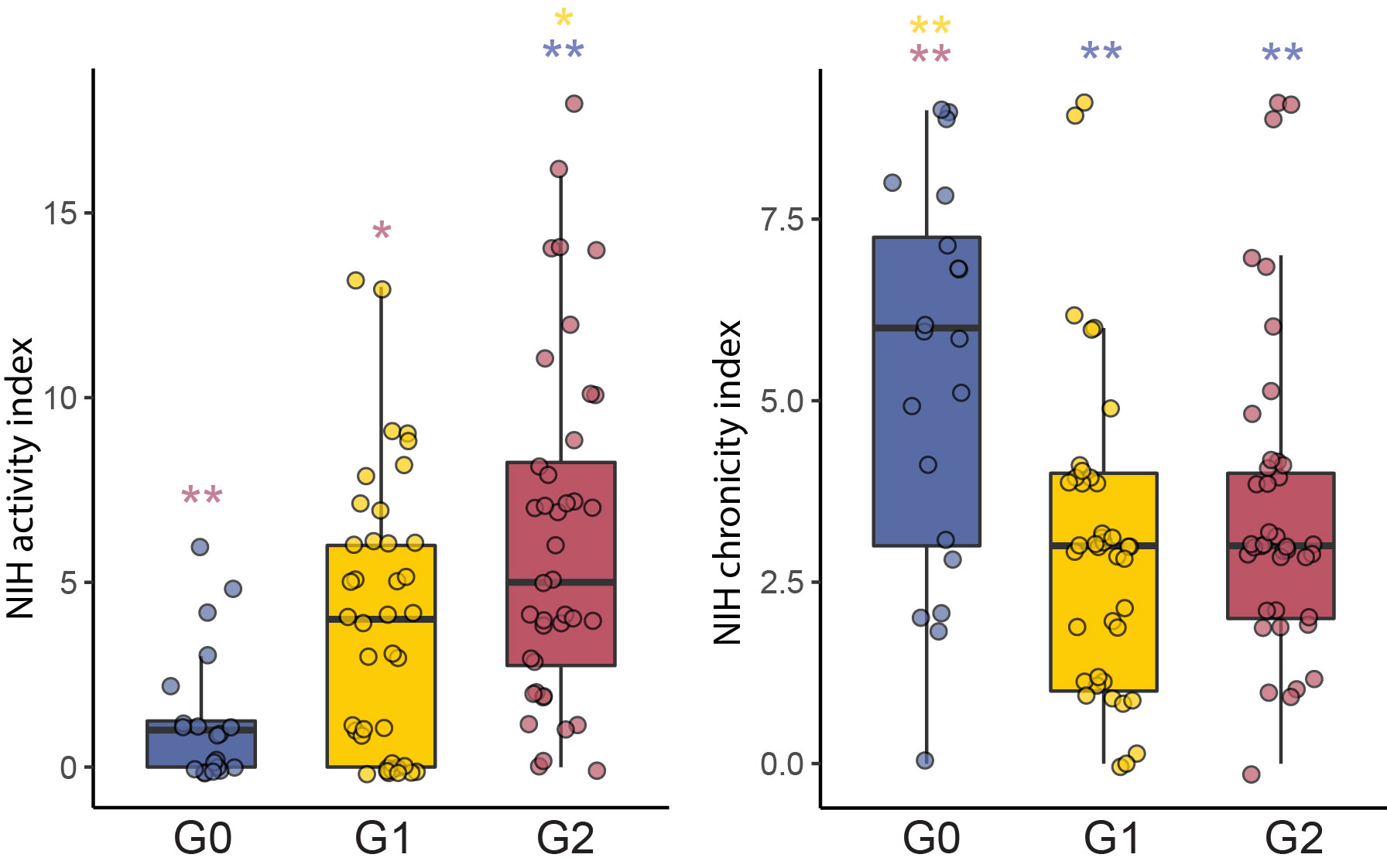
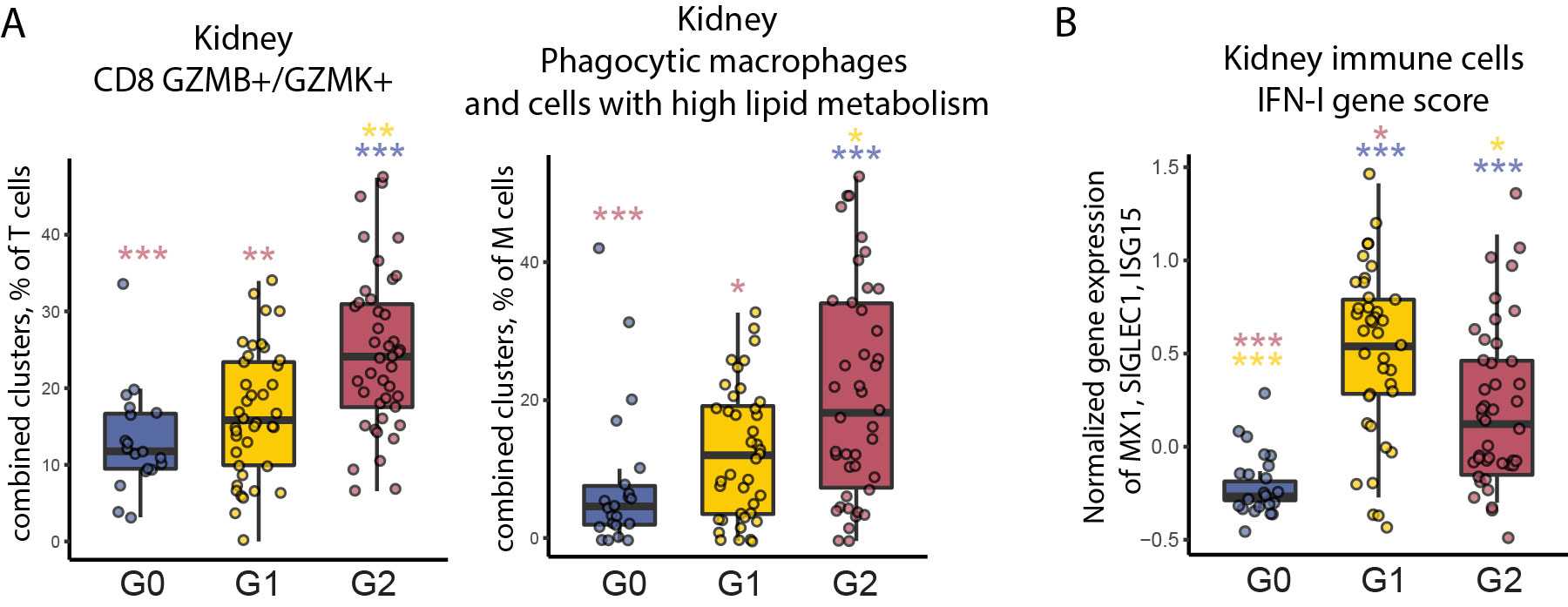
Results: Unsupervised analysis of all samples identified 3 patient subgroups based on blood immunophenotypes (Figure 1A). The first group (G0) included all controls and 20% LN patients; the two others (G1, G2) included only LN patients. A cytometric IFN-I score, based on MX1, siglec1 and ISG15 expression, was significantly different between the three groups; G0-LN patients had comparable scores to controls and G1 displayed the highest values (Figure 1B). G2 membership was driven by an increased proportion of GZMB+ GZMK+/- CD8 T cells, plus increased CD86dim monocytes and activated B cells including CD11chi cells (Figure 1C). G2 was associated with higher histologic activity scores, whereas G0 had higher chronicity scores, even after controlling for race, corticoid dose, immunosuppressant use, and previous history of renal biopsy (Figure 2). Complete renal response (CR), determined at 1 year in patients with baseline urine protein-creatinine ratio > 1, was more frequent in G2 than in G0/G1 LN patients, independently of history of previous renal biopsy (CR in G2 = 15 [41%] vs others = 9 [18%]; OR [95%CI] = 3.9 [1.3,12.5]; p.adj = 0.02). Finally, we asked whether the composition of immune cell infiltrates in the kidney, evaluated by scRNA-seq of kidney biopsies, differed between the 3 blood-defined subgroups. G2 patients had kidney T cell infiltrates enriched in GZMB+/GZMK+ CD8 T cell subsets and in myeloid cells with an activated and phagocytic profile compared to G0/G1 patients. In contrast, G1 patients showed the highest expression of IFN-I gene signature across the groups, consistent with the pattern seen in blood (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Blood immunophenotyping identified 3 groups of LN patients with different patterns of immune cell infiltration and likelihood of response to treatment. Cytometric profiles distinguished patients with a signature involving activated CD8 T cells, CD11chi B cells and activated myeloid cells (G2) from those with the highest IFN scores (G1). Patients with increased blood and kidney CD8 GZMB+GZMK+/- cells (G2) had increased renal activity scores at baseline and a higher likelihood of response at 1 year.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Horisberger A, Griffith A, Arazi A, Keegan J, Howard K, Sasaki T, Ghosh T, Fava A, Inamo J, Pulford J, Murzin E, Hancock B, Preisinger K, Gutierrez-Arcelus M, Eisenhaure T, Guthridge J, Hoover P, Dall'Era M, Wofsy D, Kamen D, Kalunian K, Furie R, Belmont H, Izmirly P, Clancy R, Hildeman D, Woodle s, Apruzzese W, McMahon M, Grossman J, Barnas J, Payan-Schober F, Ishimori M, RA SLE Network A, Kretzler M, Berthier C, Hodgin J, Demeke D, Putterman C, Hacohen N, Brenner M, Anolik J, Davidson A, James J, Raychaudhuri S, Petri M, Buyon J, Diamond B, In RA/SLE T, Zhang F, Lederer J, Rao D. Blood Immunophenotyping Distinguishes Three Subgroups of Lupus Nephritis Patients with Distinct Kidney Infiltrates and Interferon Signatures [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/blood-immunophenotyping-distinguishes-three-subgroups-of-lupus-nephritis-patients-with-distinct-kidney-infiltrates-and-interferon-signatures/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/blood-immunophenotyping-distinguishes-three-subgroups-of-lupus-nephritis-patients-with-distinct-kidney-infiltrates-and-interferon-signatures/