Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of rituximab (RTX) biosimilars compared to the originator in Canadians with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and describe outcomes following non-medical originator to biosimilar switching.
Methods: We included adults with GPA or MPA who started RTX originator or biosimilar for induction or maintenance, or switched from originator to biosimilar maintenance between 01/2018-09/2023. Participants were eligible if they started the index treatment in the prior 6 months or were followed within an existing vasculitis cohort. Six-month (M6) study outcomes were remission (Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score [BVAS] v3 of 0), relapse (rise in BVAS after achieving remission requiring treatment, classified as major if any BVAS/WG major items were present), change in Vasculitis Damage Index (VDI), and serious adverse events (SAEs).
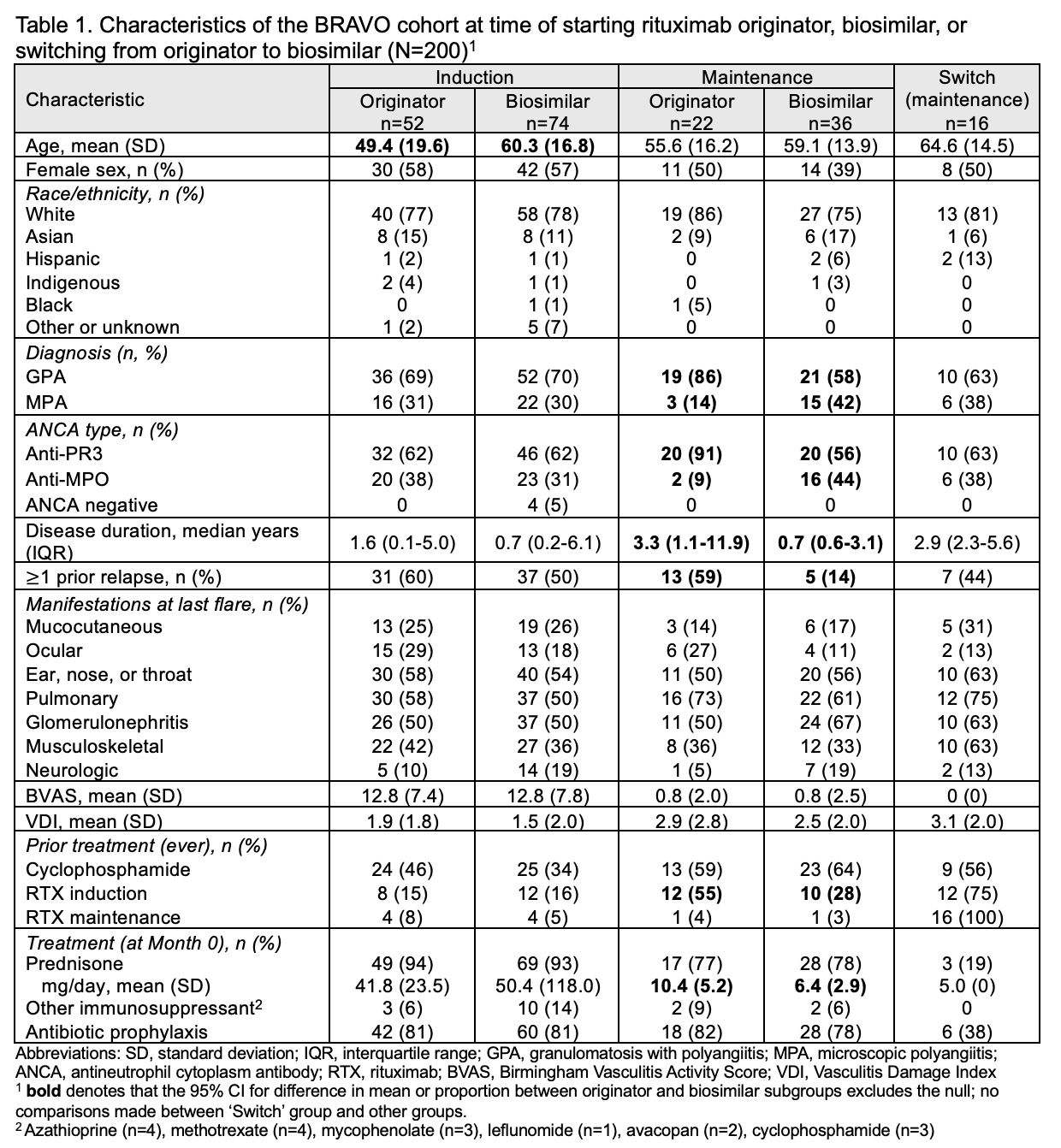
Results: We enrolled 200 participants treated with RTX from 9 centres: 126 who started induction (52 originator, 74 biosimilar), 58 who started maintenance (22 originator, 36 biosimilar), and 16 who switched from originator to biosimilar maintenance (median 2 years [IQR 1.4-2.2] of originator maintenance prior to switching). Mean age was 57.1 (SD 17.4), 53% were female, and 79% White. The majority had GPA (69%) and PR3-ANCA+ (64%) at diagnosis. The originator induction group was younger than the originator induction group (49.4 vs 60.3 years). The originator maintenance group had a higher proportion with PR3-ANCA+ (91% vs 56%), longer disease duration (mean 7.9 vs 3.0 years), more prior relapses (59% vs 14%), and a higher baseline prednisone dose (mean 10.4 mg vs 6.4 mg) compared to the biosimilar maintenance group (Table 1).
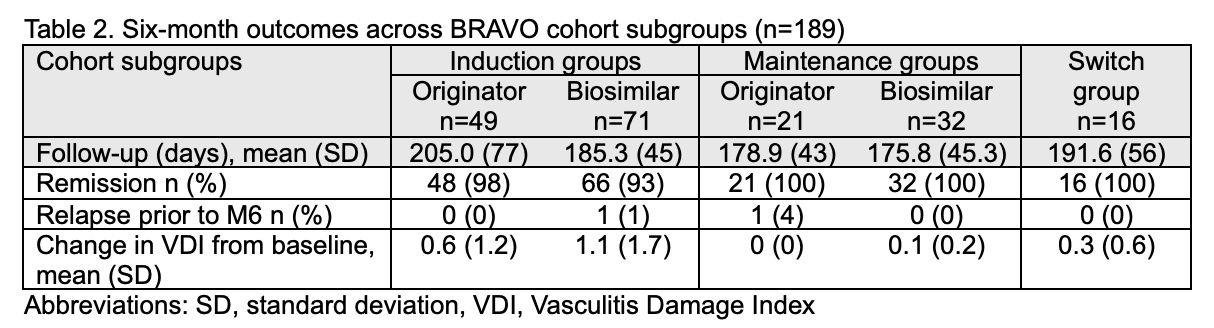
We report outcomes for 189 (95%) participants who had follow-up visits at M6 or died prior to this visit (mean follow-up 189 days, SD 56). Two minor relapses occurred, one in the biosimilar induction group (at 10 weeks) and one in the originator maintenance group (at 4 months), both in PR3-ANCA+ individuals. Among induction recipients, 48/49 (98%) in the originator group and 66/71 (93%) in the biosimilar group were alive and in remission at M6 (Table 2). All individuals who started RTX maintenance (originator or biosimilar) were in remission at the M6 visit, and those who switched from originator to biosimilar maintenance remained in remission during follow-up. Mean change in VDI was similar between biosimilar and originator subgroups.
One or more SAEs occurred in 4 (8%) of the originator induction group, 9 (13%) of the biosimilar induction group, 3 (13%) originator maintenance group, 1 (3%) in the biosimilar maintenance group, and 3 (19%) of the ‘switch’ group. Two deaths occurred in the biosimilar induction group (1 active vasculitis with alveolar hemorrhage, 1 COVID-19; both < 1 month from induction) and 1 death occurred in the switch group (infection, 5.5 months after switching).
Conclusion: In this cohort we did not observe differences in remission or relapses at 6 months between RTX originator or biosimilar induction or maintenance. Disease remained stable in those who switched from originator to biosimilar maintenance.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mendel A, Barra L, Bernatsky S, Clifford A, Dabaghjamanesh M, Dehghan N, Fifi-Mah A, Makhzoum J, Meunier R, Milman N, Soowamber M, Cohen Tervaert J, Yacyshyn E, Khalidi N, Pagnoux C. Biosimilars of Rituximab in ANCA-associated Vasculitis Compared to the Originator (BRAVO): 6-month Outcomes of a Longitudinal Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biosimilars-of-rituximab-in-anca-associated-vasculitis-compared-to-the-originator-bravo-6-month-outcomes-of-a-longitudinal-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biosimilars-of-rituximab-in-anca-associated-vasculitis-compared-to-the-originator-bravo-6-month-outcomes-of-a-longitudinal-cohort-study/