Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The aim of this study was to examine the longitudinal utility of a biomarker signature in conjunction with myositis autoantibodies (autoAbs) as biomarkers of disease outcome in refractory myositis patients treated with B cell depletion (BCD).
Methods: In the RIM Trial, all subjects received 1 gram of rituximab on 2 consecutive weeks. Using start of treatment as baseline, serum samples (n=177) were analyzed at 0, 8, 16, and 24 weeks after BCD with multiplexed sandwich immunoassays (Meso Scale Discovery) to quantify type -1 IFN-regulated and other pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines. Biomarker scores were generated based on a priori assignment from literature review for serum levels from the following pathways: type-1 IFN-inducible (IP-10, I-TAC, MCP1), Th1 (IFNγ, TNFα, IL2), Th2 (IL4, IL5, IL10, IL12, IL13), Th17 (IL6, IL17, IL1b) and regulatory cytokines (IL10 and TNFa). Biomarker scores are defined as the normalized sum of cytokine/chemokine levels adjusted to a 100-point scale. Myositis autoAbs (anti-synthetase (anti-syn) n=28, TIF1-g n=19, Mi-2 n=25, SRP n=21, MJ n=18, non-myositis associated (non-MAA) n=24, unidentified autoantibody n=9, and no autoantibodies n=33) determined by immunoprecipitation at baseline, were correlated with outcome measures. Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test was used for comparisons.
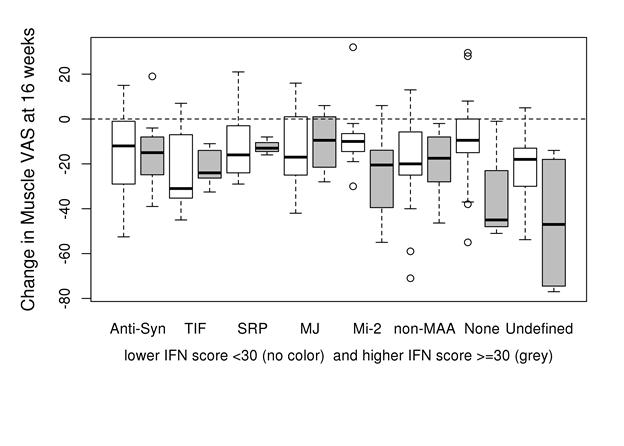
Results: The mean (SD) values for muscle disease and physician global disease activity VAS scores (0-100 mm) were 46 (22) and 49 (19). IFN scores (median values) were higher at baseline in patients with anti-syn; (43), TIF1-g (31) and Mi-2 (30) compared with other autoAb groups (p<0.001). No significant improvement in biomarker scores was detected at 8 weeks. However, at 16 weeks after BCD anti-syn and Mi-2 autoAb (+) patients and non-MAA had a greater improvement in IFN scores (– 6.7, – 6.1 and -7.2 p<.001) while TIF1-g (+) patients worsened by 7.0. The change in IFN score at 16 weeks correlated with percent change in muscle (r=0.27, p<0.001) and physician VAS (r=0.16, p=0.06). High IFN scores at baseline (>30) demonstrated the greatest clinical improvement based on global and muscle VAS among patients in certain autoAb groups (e.g., Mi-2, none and “undefined”) (IFN score-autoAb interaction p=0.075; Figure).
Regulatory scores were higher at baseline in patients with anti-syn (31) and non-MAA (32) vs. other groups (p=0.01). Regulatory score improved at 16 weeks in anti-syn (-5.8) and Mi-2 (-3.4) and non-MAA (-7.2, p=0.028). Th1 scores decreased in the anti-syn, Mi-2, non-MAA and to a lesser extent in the TIF-g group at 16 weeks (p=0.039) with the greatest improvement at 24 weeks (p=0.014) suggesting a longer time to improvement if the Th1 score is elevated. Th17 remained unchanged.
Conclusion: Biomarker signatures in conjunction with autoAbs prior to treatment help guide response to BCD in refractory myositis. In addition, biomarker and clinical response is greatest at 16 weeks after BCD.
Disclosure:
A. M. Reed,
None;
C. S. Crowson,
None;
M. S. Hein,
None;
C. Lopez de Padilla,
None;
H. Khun,
None;
R. Aggarwal,
None;
D. P. Ascherman,
None;
M. C. Levesque,
None;
C. V. Oddis,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarker-and-serologic-predictors-of-clinical-improvement-after-b-cell-depletion-in-refractory-adult-and-juvenile-dermatomyositis-dm-and-adult-polymyositis-pm-the-rim-rituximab-in-myosit/