Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Previous published works have raised the concern that methotrexate (MTX) might have a negative effect on immune response upon vaccine administration. At the beginning of the COVID-19 vaccination campaigns, there were controversial opinions regarding the possibility of temporary interrupting immunomodulatory treatments in rheumatic patients.
The objective of this study was to evaluate B and T cell responses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) after 1 or 2 weeks of MTX withdrawal following each COVID-19 vaccine dose and compare them with that of those who maintained MTX unchanged.
Methods: This is a single-centre, randomised, prospective study. Adult RA and PsA patients treated with MTX were recruited and randomly assigned to 3 groups: MTX-maintenance (n=72), MTX-withdrawal for 1 week (n=71) or MTX-withdrawal for 2 weeks (n=73) after each vaccine dose. Samples were collected before and 30 days after complete vaccination in 2021. Multi-antigen cytometric bead array assays to detect specific antibodies to several SARS-CoV-2 antigens and ELISPOT assays measuring interferon (IFN)-γ and interleukin (IL)-21 were performed. Multivariable analyses were used to control the effect of possible confounding variables.
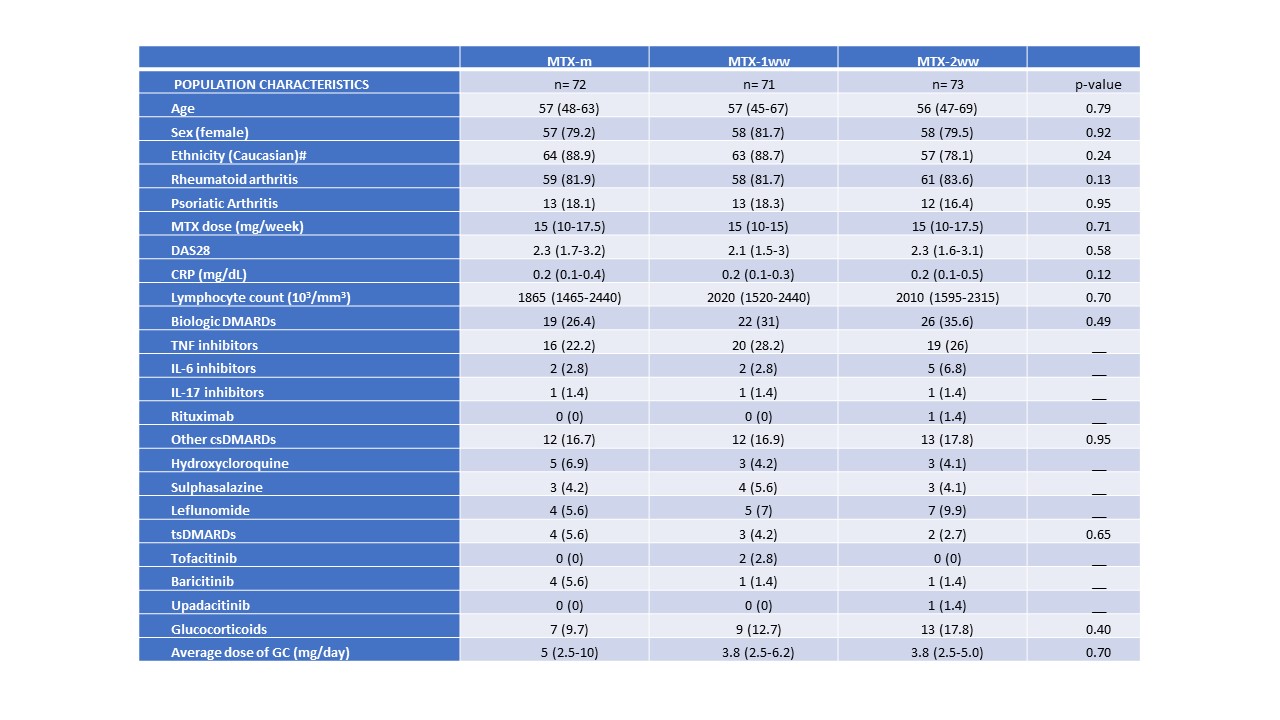
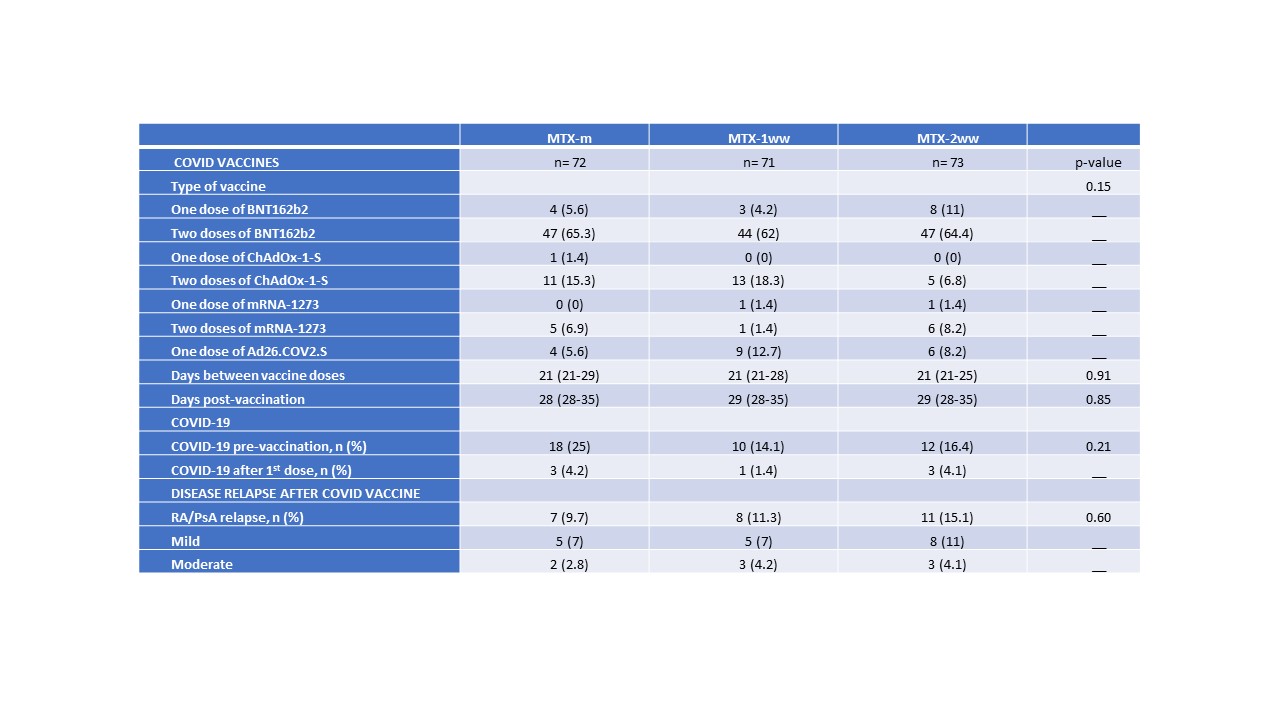
Results: The study population consisted of 216 patients (178 RA and 38 PsA), of which 47 had COVID-19 before vaccination. Participants were vaccinated with BNT162b2 (71%), ChadOX-1-S (14%), mRNA-1273 (6%) and Ad26.COV2.S (9%). Population characteristic are shown in Table 1. The types of COVID vaccines, the vaccine protocols and the occurrence of COVID, prior and after vaccination, as well as the differences of these variables across groups are shown in Table 2. MTX withdrawal in patients without previous COVID-19 was associated with higher levels of anti-RBD IgG (p=0.01) and neutralising antibodies (p=0.004), especially in the 2-week withdrawal group and with higher IFN-γ secretion upon stimulation with pools of SARS-CoV-2 S peptides (p< 0.001). Interestingly, no significant differences in the number of RA/PsA relapses were detected across groups (Table 2).
Conclusion: Our data indicate that a brief MTX interruption following COVID-19 vaccination doses in patients with RA or PsA improves humoral and cellular immune responses, without significant increase of relapses, especially in patients without previous infection.
MTX, methotrexate; ; MTX-m, methotrexate maintenance; MTW_1ww, 1 week of MTX withdrawal; MTX_2ww, 2 weeks of MTX withdrawal; DAS28, disease activity score in 28 joints; CRP, C-reactive protein; DMARDs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; csDMARDs, conventional synthetic DMARDs; tsDMARDs, targeted synthetic DMARDs; GC, glucocorticoids; COVID_19, coronavirus disease 2019 caused by the SARS-CoV_2 virus; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; PsA, psoriatic arthritis.
MTX, methotrexate; MTX-m, methotrexate maintenance; MTW_1ww, 1 week of MTX withdrawal; MTX_2ww, 2 weeks of MTX withdrawal; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; PsA, psoriatic arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vicente Rabaneda E, Martínez-Fleta P, Triguero-Martínez A, Roy E, Uriarte-Ecenarro M, Gutiérrez-Rodríguez F, Quiroga P, Romero A, Montes N, Esparcia Pinedo L, Alfranca M, Garcia-Vicuna R, Sánchez-Madrid F, González-Álvaro I, Castañeda S. Beneficial Effect of Temporary Methotrexate Interruption on B and T Cell Responses upon SARSCoV-2 Vaccination in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/beneficial-effect-of-temporary-methotrexate-interruption-on-b-and-t-cell-responses-upon-sarscov-2-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-or-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/beneficial-effect-of-temporary-methotrexate-interruption-on-b-and-t-cell-responses-upon-sarscov-2-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-or-psoriatic-arthritis/