Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Interleukin-34 (IL-34), a novel cytokine playing a critical role in osteoclastogenesis, recently was reported that its expression increases in the synovial tissue and sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, there has been no study on an association between IL-34 and RA-associated joint damage. We evaluated whether baseline serum IL-34 levels predict radiographic progression in RA patients.
Methods: Sera were obtained from consecutive patients with RA (n=100) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS, n=36). Fifty-nine gender- and age-matched healthy individuals served as controls. Synovial fluid (SF) samples were collected from another 18 patients with RA and 19 with osteoarthritis (OA). Clinical data were recorded at the time of sampling. Radiologic damage was assessed according to the modified Sharp/van der Heijde score (SHS) at baseline and at follow-up (n=78), an average of 1.7 years later. The IL-34 concentrations were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
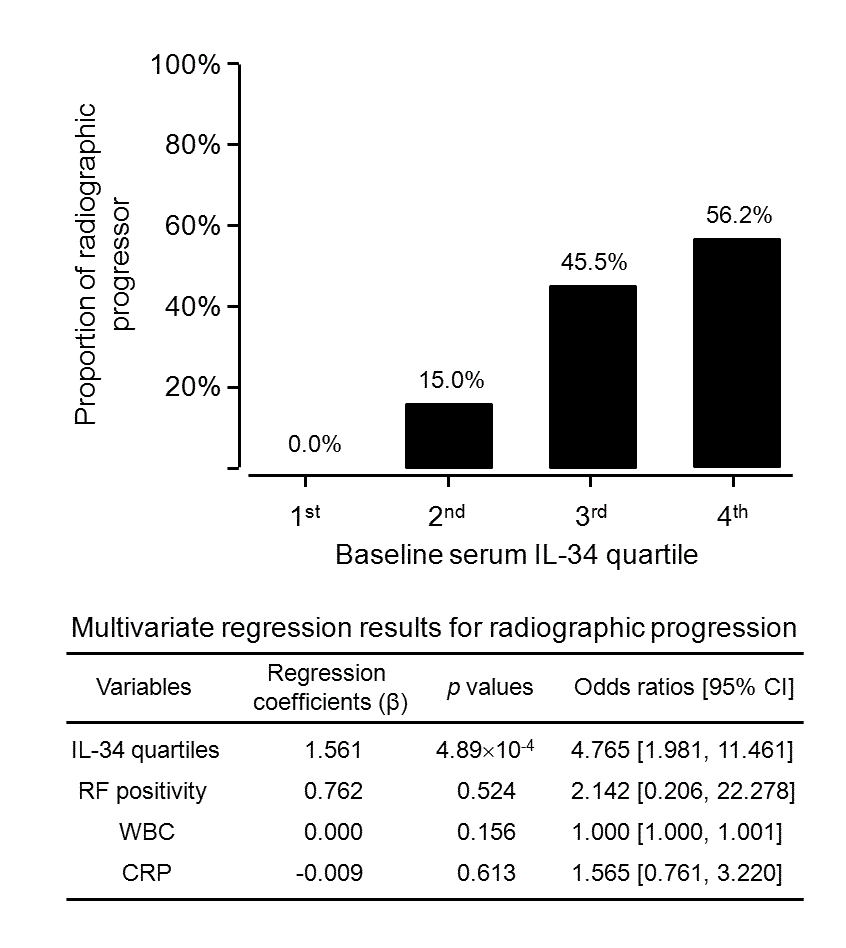
Results: Serum IL-34 levels were significantly higher in patients with RA (p=4.02 x 10-4) or AS (p=2.15 x 10-5) than those in controls. RA patients showed significantly higher SF IL-34 levels in the SF samples than OA patients (p=3.62 x 10-5). In RA, serum IL-34 levels were significantly associated with rheumatoid factor positivity (p=0.011), current smoking status (p=0.002), ESR levels (r=0.258, p=0.010), and C-reactive protein levels (r=0.262, p=0.008). ¥ÄSHS/year was positively correlated with serum IL-34 levels (r=0.474, p=0.029). Moreover, baseline IL-34 level quartiles was an independent predictor for radiographic progression in RA patients (odds ratio 4.765 [95% CI 19.810-11.461], p=4.89 x 10-4, Figure 1).
Conclusion: These results suggest that IL-34, a novel osteoclastogenic cytokine, play a role in RA-associated joint damage and it can be a biomarker for predicting the subsequent radiographic progression in RA patients.
.
Figure 1. Proportions of patients with subsequent radiographic progression according to the quartiles of baseline serum IL-34 levels.
Disclosure:
S. H. Chang,
None;
B. Y. Choi,
None;
H. J. Cho,
None;
H. J. Oh,
None;
E. H. Kang,
None;
Y. W. Song,
None;
Y. J. Lee,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-serum-interleukin-34-levels-predict-radiographic-progression-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/