Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: Abstracts: RA – Treatments III: Predictors of Response & Tapering
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: A key target of RA treatment is to achieve early and sustained remission in order to ensure lower levels of long-term structural joint damage and physical disability. Identifying predictive biomarkers may help guide treatment options to achieve this. Inflammatory biomarkers such as IL-10, a pleiotropic cytokine that drives B-cell responses and is associated with higher seropositivity for RF and anti-CCP in patients (pts) with RA,1 may provide clinical value as predictive biomarkers. We evaluated the association of baseline (BL) circulated biomarkers with disease activity (DA) measures and their ability to predict clinical response in MTX-naive, ACPA+ pts with early RA from a phase 3b study (AVERT-2; NCT02504268).2
Methods: Pts aged ≥ 18 years with early RA (≤ 6 months from diagnosis; ACR/EULAR 20103) were randomized to abatacept + MTX or abatacept placebo + MTX (referred to as MTX). Serum samples were collected over a 56-week period, with endpoints assessed at weeks 24 and 52.A broad selection of 113 inflammatory and immune response–related proteins were analyzed using either the Olink Target 96 multiplex immunoassay inflammation panel or selected panels from Myriad Rules-Based Medicine. BL biomarker and clinical DA measures were analyzed using Spearman’s correlation, with changes from BL in select biomarkers analyzed via repeated measures mixed-effects models. Logistic regression predicted response to treatment with BL age, Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), pain (measured via visual assessment scale), and ACPA positivity as covariates.
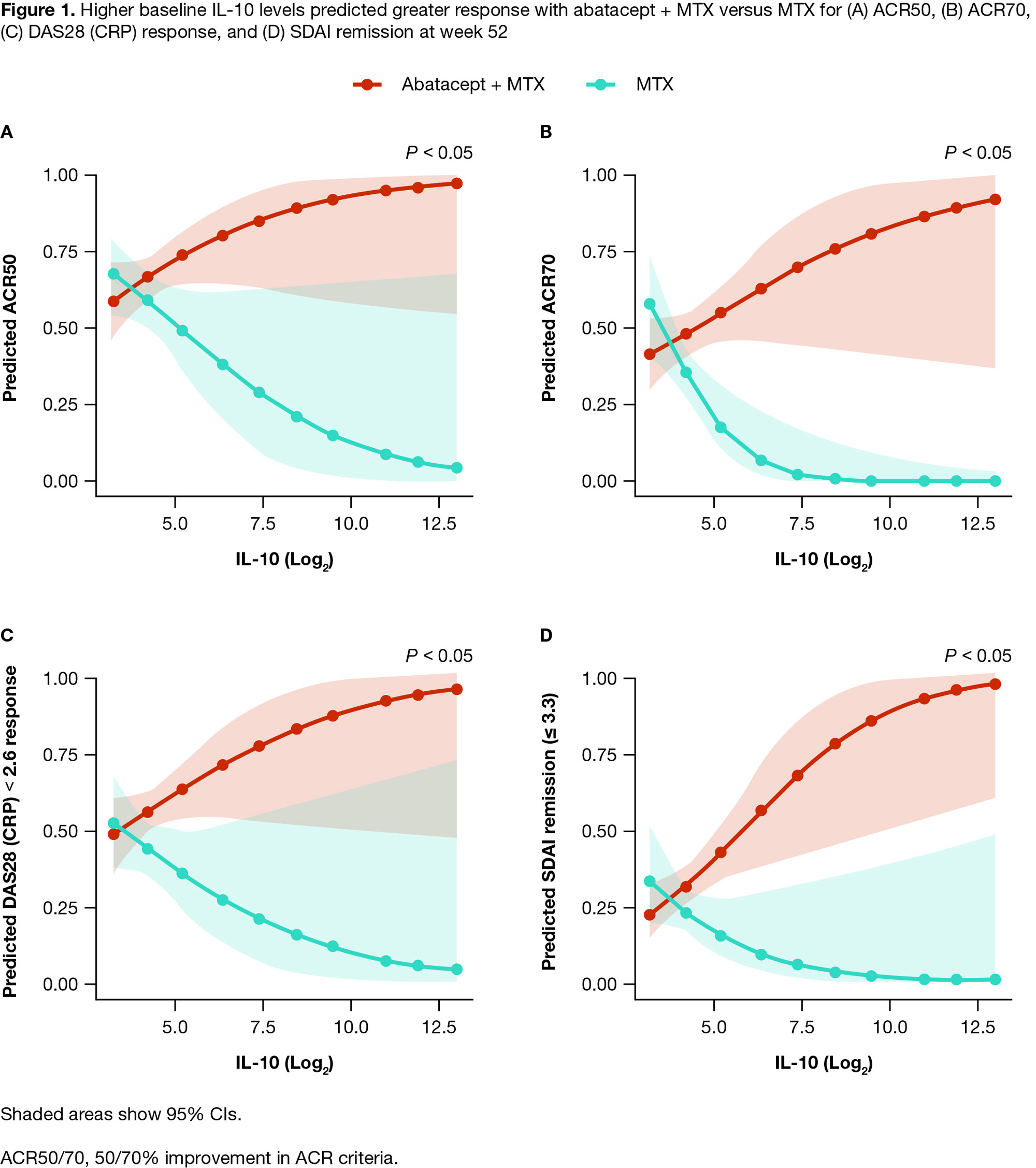
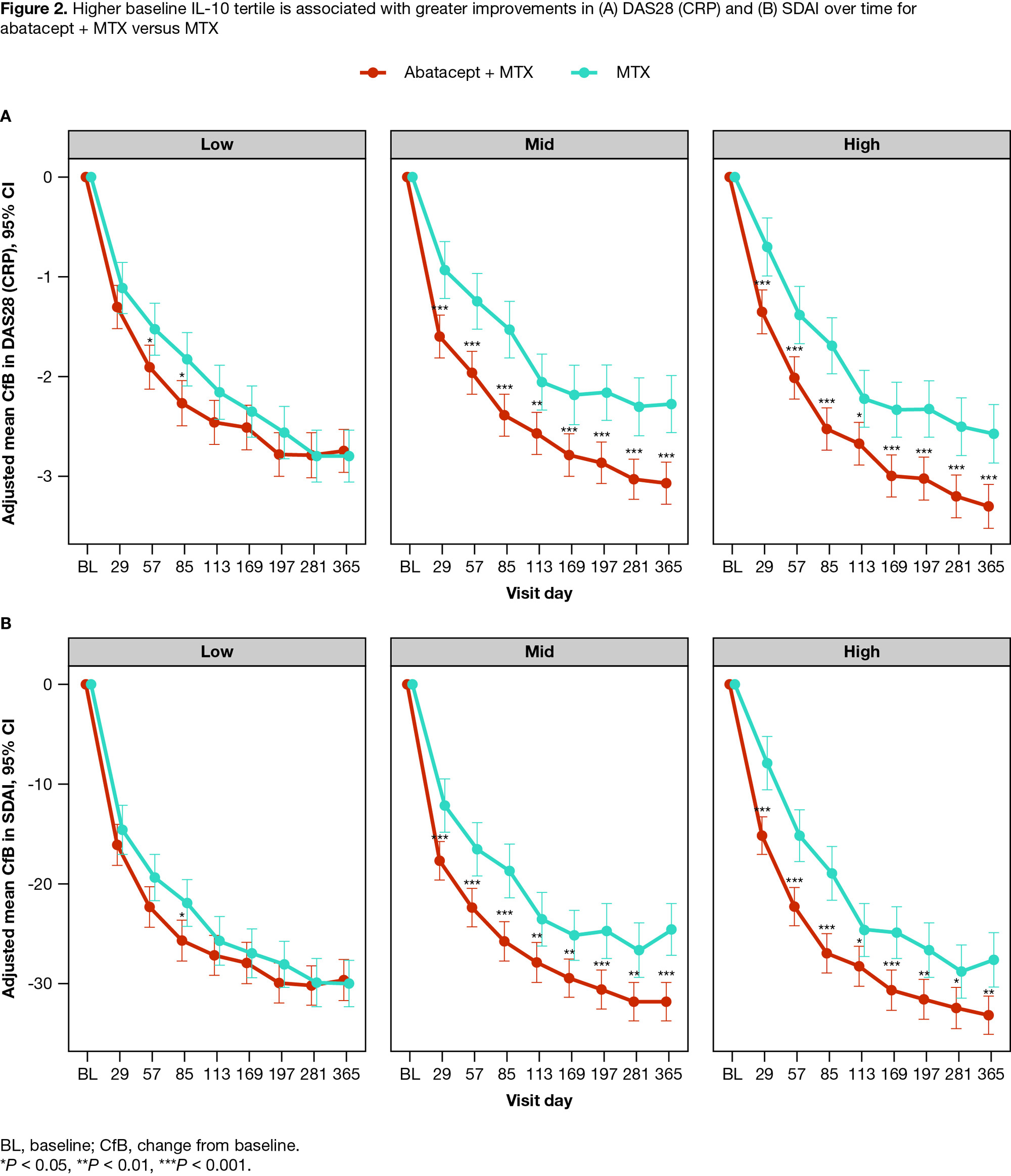
Results: Of 752 pts in the intent-to-treat population, 446 from the abatacept + MTX arm and 300 from the MTX arm were included in the biomarker analyses. BL characteristics were well-balanced between treatments. Of the 15 biomarkers significantly associated with ≥ 2 BL DA measures, at both weeks 24 and 52, pts receiving abatacept + MTX showed significantly greater reductions in all biomarker levels compared with MTX (P < 0.05 to P < 0.001) with a change from BL in 13 biomarkers demonstrating significant associations with DA measure reduction (P < 0.05). Higher BL levels of IL-10 predicted greater clinical improvement, assessed by ACR and DAS28 (CRP) (< 2.6) responses and SDAI remission (≤ 3.3), with abatacept + MTX vs MTX (P < 0.05 at week 52) (Figure 1). Further, a higher BL IL-10 concentration tertile was significantly associated with greater improvements in DAS28 (CRP) and SDAI on abatacept + MTX vs MTX (P < 0.05 to P < 0.001 at days 29–365) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Higher BL IL-10 levels predicted greater clinical response for pts treated with abatacept + MTX vs MTX. Increased IL-10 levels may reflect greater interactions between CD4+ T-helper cells and autoantibody-producing B cells. These findings may help clinicians to identify pts most likely to respond favorably to the abatacept mechanism of action. A prospective study is warranted to confirm whether screening for IL-10 in the clinical setting can help guide treatment options for pts with RA.
References
- Hernández-Bello J, et al. Cytokine 2017;95:88–96.
- Emery P, et al. Rheumatol Ther 2023;10:707–27.
- Aletaha D, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:2569–81.
Medical writing: Lauren McDonagh (Caudex), funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liu J, Li Y, Fu K, Wu C, Schafer P, Connolly S, Catlett I, Maldonado M, Wong R, Emery P, Tanaka Y, Bykerk V, Bingham C, Huizinga T, Fleischmann R. Baseline IL-10 Levels as a Predictive Biomarker for Achieving Clinical Response with Abatacept in ACPA+ Patients with Early RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-il-10-levels-as-a-predictive-biomarker-for-achieving-clinical-response-with-abatacept-in-acpa-patients-with-early-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-il-10-levels-as-a-predictive-biomarker-for-achieving-clinical-response-with-abatacept-in-acpa-patients-with-early-ra/