Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the leading cause of death in SSc. Several international observational studies have evaluated characteristics of ILD in their SSc patient populations, however these studies do not necessarily reflect the US SSc patient population. The purpose of this analysis was to assess the baseline characteristics of SSc patients with and without restrictive lung disease (RLD) in a US based longitudinal registry.
Methods: The Collaborative National Quality and Efficacy Registry (CONQUER) for Systemic Sclerosis is a multicenter US based registry of patients with early SSc within 5 years of first non-Raynaud’s symptom enrolled at 13 expert centers. All patients are >18 years old and fulfill the 2013 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for SSc. All patients who had a pulmonary function test (PFT) at baseline on or before April 1, 2020 were included in this analysis. As a high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) Chest at baseline was not available to characterize ILD for all patients, patients were characterized as RLD based on force vital capacity (FVC) % predicted < 80% or total lung capacity (TLC) % predicted < 80%. Chi-squared test and Fisher’s Exact test were performed for categorical variables. T-test was performed for continuous variables. Multivariable modeling with stepwise selection was performed to predict RLD. A p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
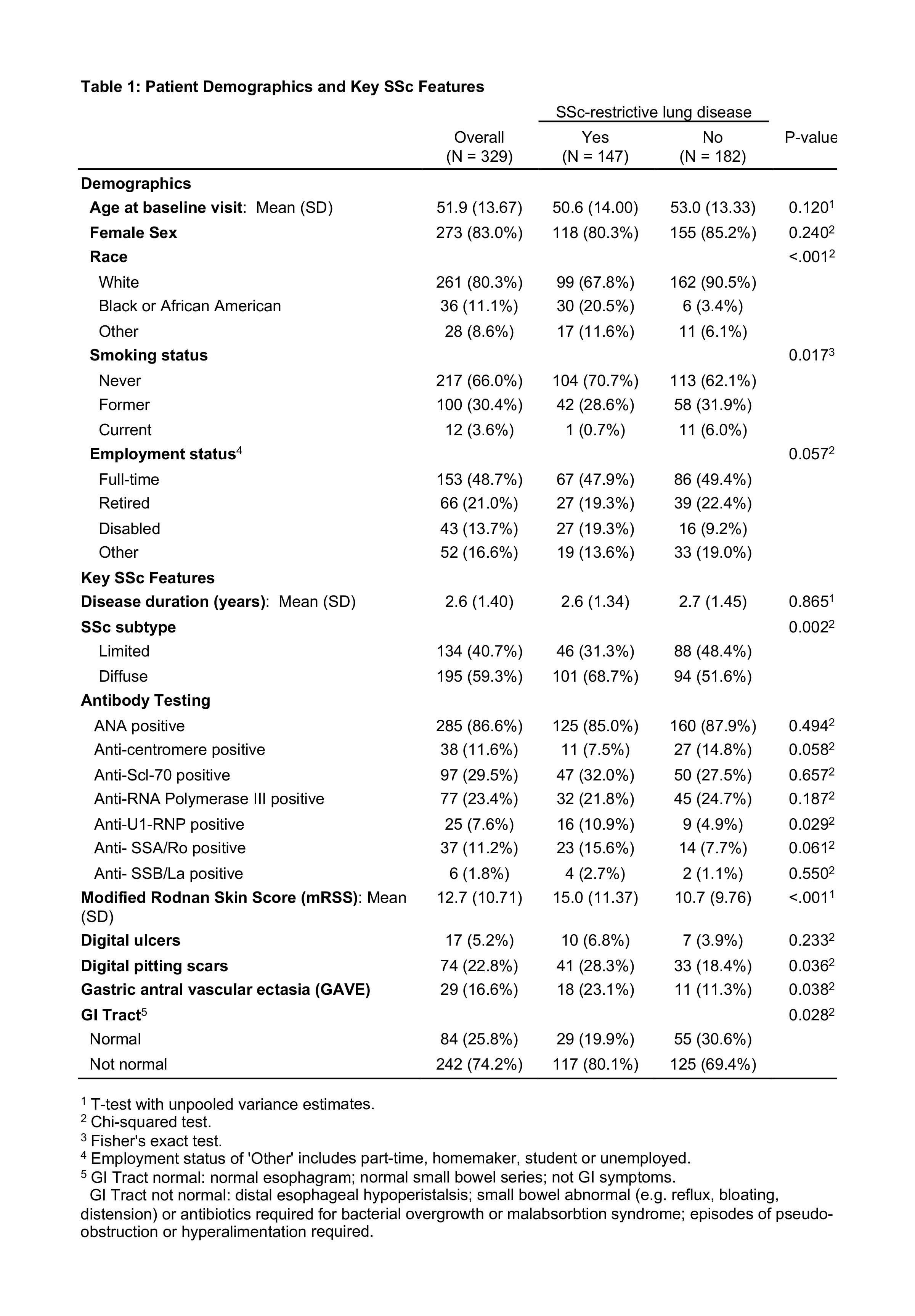
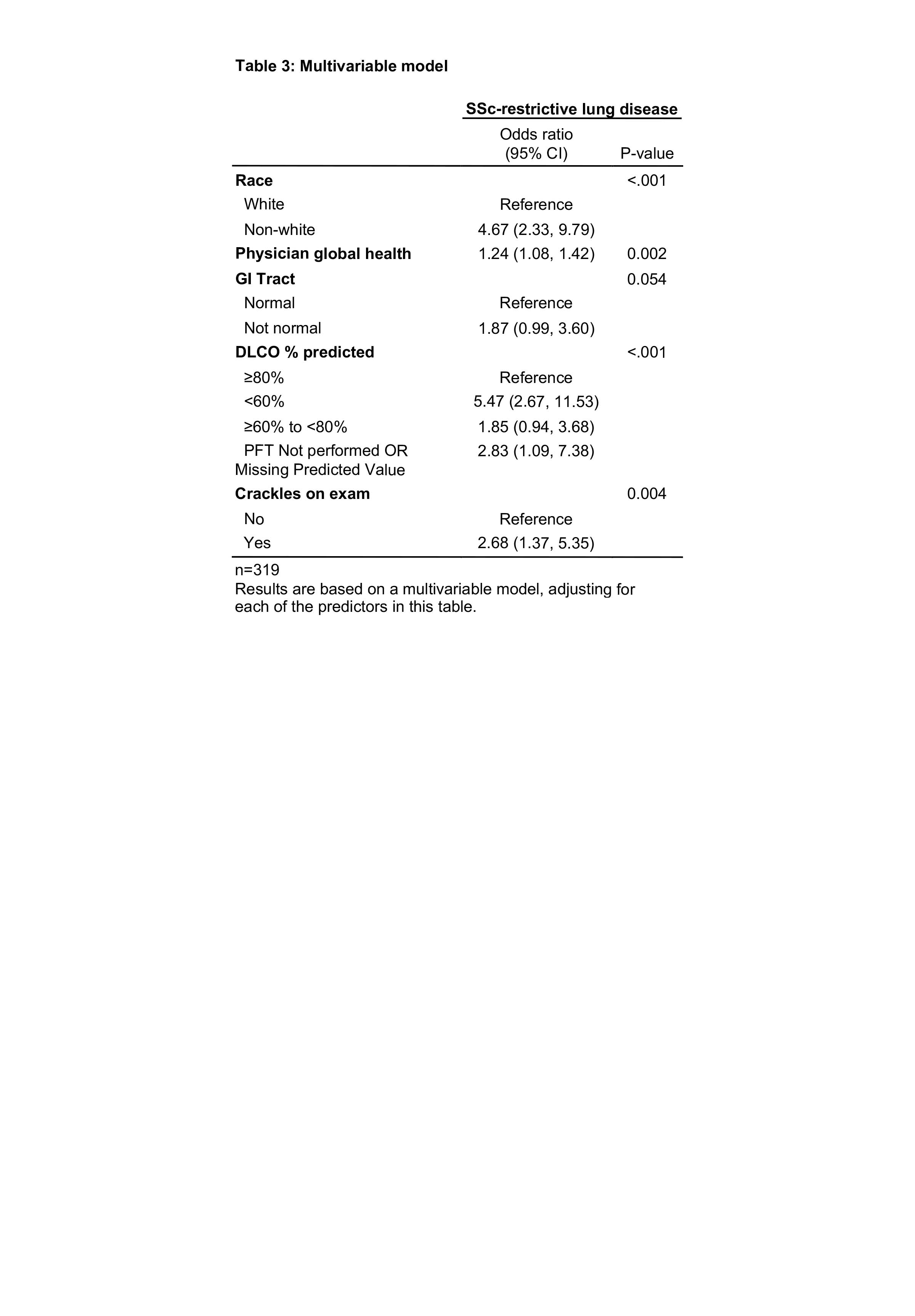
Results: 329 patients underwent PFTs at baseline with 147 (45%) patients characterized as RLD. There was no significant difference in age, sex or disease duration between patients with and without RLD. Patients with RLD had a mean disease duration of 2.6 years and a mean FVC of 67% at baseline. RLD patients compared to no RLD were more likely to be non-white (African American, Asian or other) and have diffuse disease, a higher modified Rodnan skin score, digital pitting scars and abnormal GI symptoms including gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE), esophageal dysmotility, small bowel dysfunction or malabsorption (Table 1). RLD patients who underwent HRCT also were more likely to have a patulous esophagus on HRCT compared to those patients without RLD (Table 2). In multivariable analysis, non-white race, crackles on exam, DLCO< 60%, and higher physician global health assessment scores were found to be independently associated with RLD (Table 3).
Conclusion: We found that SSc patients with RLD enrolled in CONQUER had more diffuse disease and significant GI manifestations compared to patients without RLD. Non-white race was independently associated with RLD. Interestingly, patients with RLD had early disease yet already significant restrictive defects on PFTs, suggesting that even earlier detection methods are necessary. Further investigation into the factors associated with ILD and its progression is warranted as we collect long-term prospective data on this growing cohort of US SSc patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Castelino F, VanBuren J, Startup E, Assassi S, Bernstein E, Chung L, Correia C, Evnin L, Frech T, Gordon J, Hant F, Hummers L, Khanna D, Sandorfi N, Shah A, Shanmugam V, Steen V. Baseline Characteristics of Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) Patients with Restrictive Lung Disease in a Multi-Center United States Based Longitudinal Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-characteristics-of-systemic-sclerosis-ssc-patients-with-restrictive-lung-disease-in-a-multi-center-united-states-based-longitudinal-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-characteristics-of-systemic-sclerosis-ssc-patients-with-restrictive-lung-disease-in-a-multi-center-united-states-based-longitudinal-registry/