Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI), an oral, selective Janus kinase (JAK)1 and JAK2 inhibitor, improved disease activity in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) receiving standard background therapy in a phase 2 trial1. There were no meaningful reductions in least squares mean change from baseline (BL) in levels of serologic biomarkers for SLE with BARI treatment, including anti-double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (anti-dsDNA) antibodies and complement component (C)3 and C41. The objective was to evaluate the median change from BL in serologic biomarkers in subgroups and the overall population of BARI-treated patients (pts) with SLE, in addition to the SLE Responder Index-4 (SRI-4) response by normalization of anti-dsDNA.
Methods: Data were assessed from the phase 2 trial JAHH (NCT02708095). All pts met ACR or SLICC classification criteria for SLE 2,3. The median change from BL in anti-dsDNA, IgG, C3, C4, anti-Smith, Anti-cardiolipin IgM (aCL IgM), Anti-cardiolipin IgG (aCL IgG), Anti-cardiolipin IgA (aCL IgA), Anti-nuclear ribonucleoprotein (anti-RNP), Anti- Sjogren’s-syndrome-related (SS) antigen-A (Ro/SSA) and Anti-SS antigen-B (Ro/SSB) were evaluated over time among the following populations at BL: anti-dsDNA positive (≥30 IU/mL), low C3 (< 90 mg/dL), low C4 (< 10 mg/dL), anti-Smith (≥30 IU/mL), aCL IgM ( >12MPL), aCL IgG (>14 GPL), aCL IgA (>11 APL), anti-RNP (≥30 IU/mL), Ro/SSA and Ro/SSB (>20 IU/mL). Statistical tests were conducted for BARI 2-mg and 4-mg compared with placebo (PBO). Among pts who were anti-dsDNA positive at BL, SRI-4 responder rate was compared for those who stayed positive or achieved normal levels by Week (Wk) 24.
Results: Among pts who were anti-dsDNA positive at BL, significant decreases of anti-dsDNA antibodies were observed for BARI 2-mg and 4-mg compared to PBO beginning at Wks 2 and 4, respectively, and continuing through Wk 24 (Fig 1). Moreover, reductions of IgG levels were found for BARI-treated pts including significant decreases for BARI 4-mg compared to PBO at Wks 12 and 24. Among pts who had low levels of C3 and C4 at BL, no significant differences in median change from BL were observed over time with BARI compared to PBO. Among pts who had high levels of anti-Smith and aCL IgM at baseline, significant decreases in median levels were observed over time for BARI 4-mg compared with PBO (Fig 2 and 3). However, no significant changes in median values from BL were observed for aCL IgG, aCL IgA, anti-RNP, Ro/SSA and Ro/SSB autoantibodies. For pts who were anti-dsDNA positive at BL, no relationship in SRI-4 responder rate was observed for those who stayed positive or achieved normal levels by Wk 24, possibly due to the limited sample size.
Conclusion: BARI treatment resulted in a rapid and sustained significant decrease in anti-dsDNA antibodies compared to PBO among anti-dsDNA positive pts with SLE at BL. Treatment with BARI 4-mg also resulted in a statistically significant decrease in IgG and anti-cardiolipin IgM levels at Wks 12 and 24, and anti-Smith at Wk 24, compared to PBO. These data suggest that BARI may have an effect on B cell activity in SLE.
1 Wallace D et al. Lancet 2018; 392:222-231.
2 Hochberg et al. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 1725-1734.
3 Petri et al. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 2677-2686.
 Figure 1. Median change from baseline in anti-dsDNA (IU/mL) (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01 for BARI vs. PBO, BARI=baricitinib; Ig=immunoglobulin; PBO=placebo)
Figure 1. Median change from baseline in anti-dsDNA (IU/mL) (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01 for BARI vs. PBO, BARI=baricitinib; Ig=immunoglobulin; PBO=placebo)
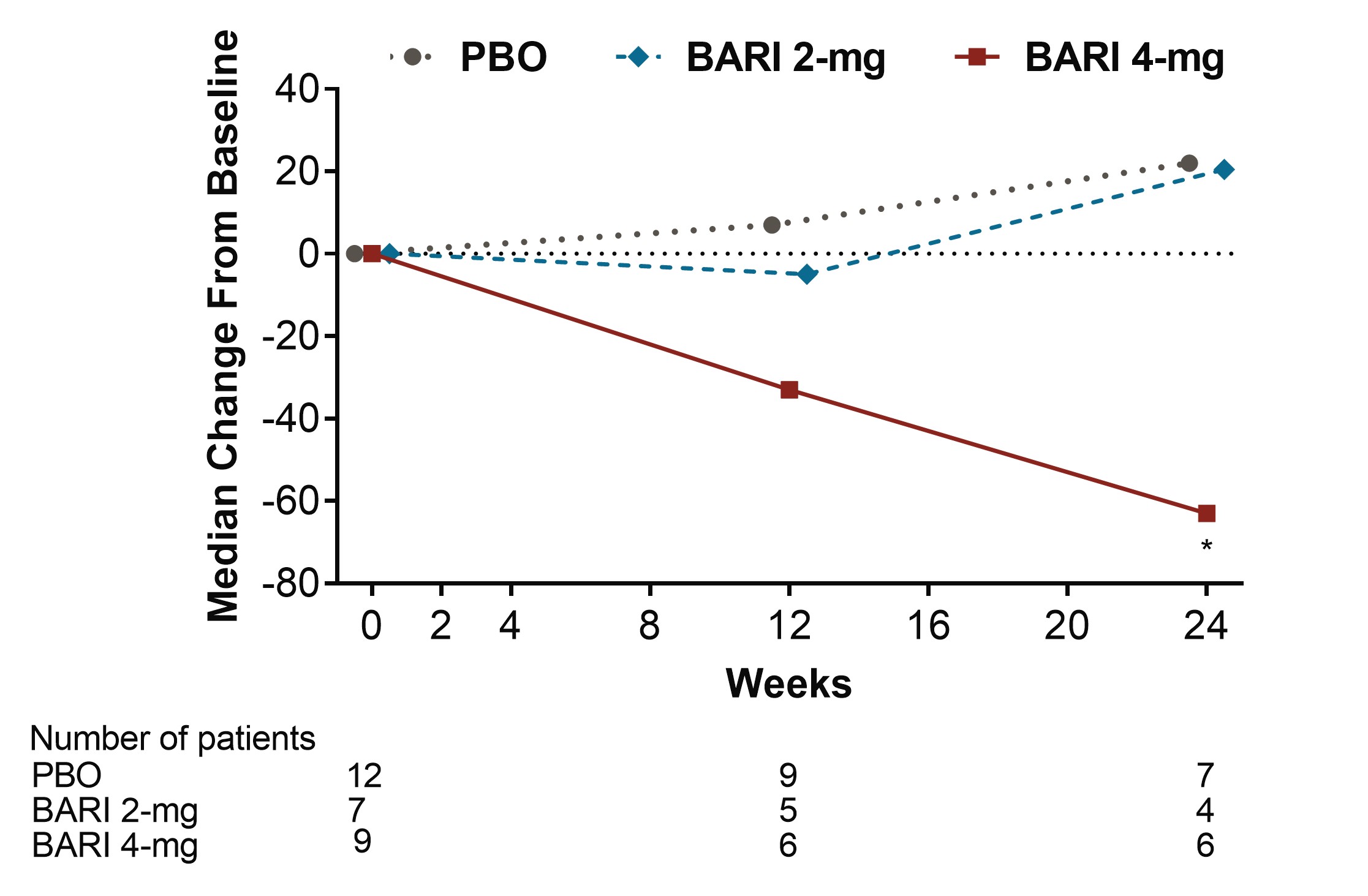 Figure 2. Median change from baseline in Anti-Smith (IU/mL) (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01 for BARI vs. PBO, BARI=baricitinib; Ig=immunoglobulin; PBO=placebo)
Figure 2. Median change from baseline in Anti-Smith (IU/mL) (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01 for BARI vs. PBO, BARI=baricitinib; Ig=immunoglobulin; PBO=placebo)
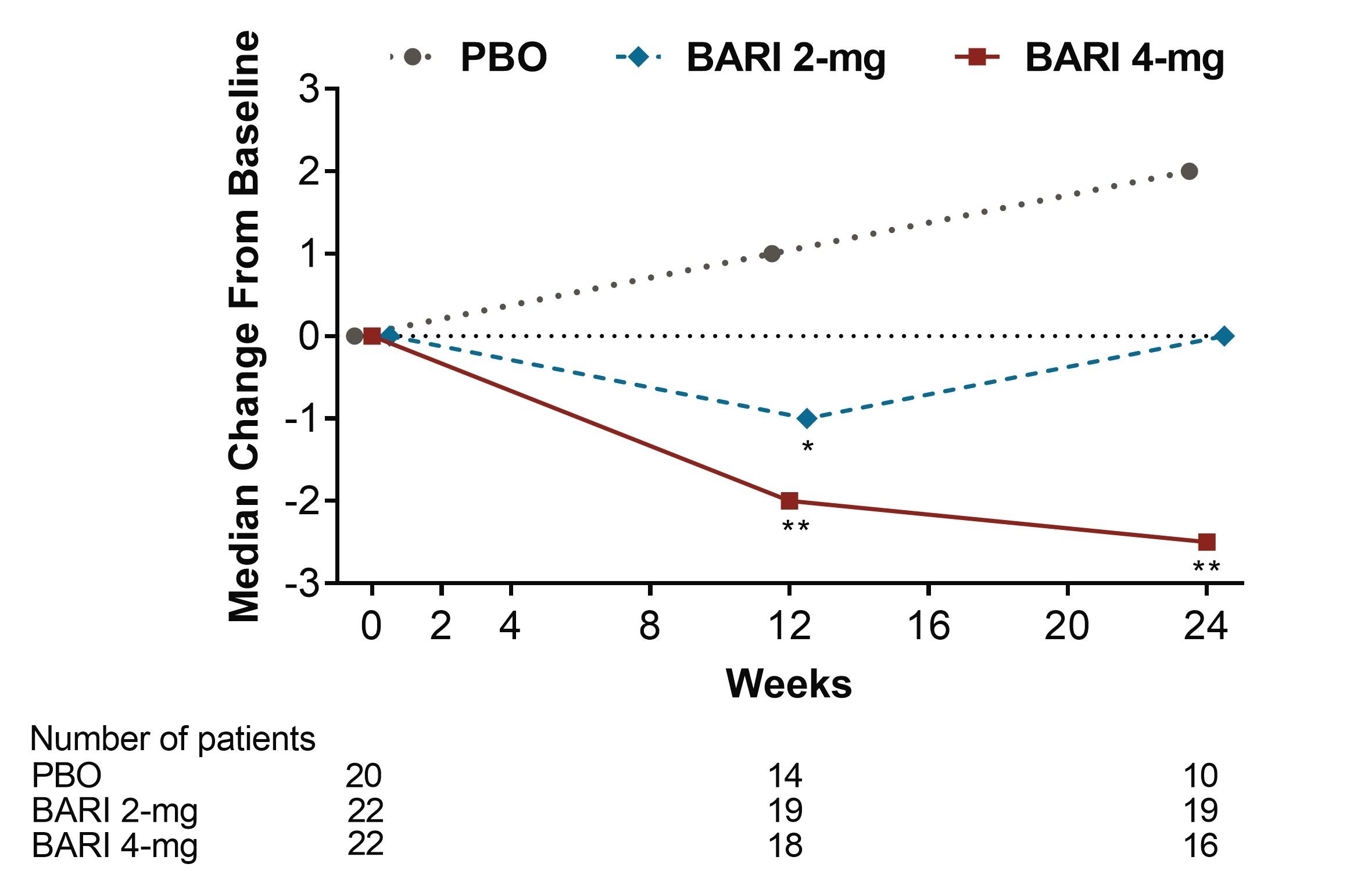 Figure 3. Median change from baseline in Anti-Cardiolipin IgM (IU/mL) (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01 for BARI vs. PBO, BARI=baricitinib; Ig=immunoglobulin; PBO=placebo)
Figure 3. Median change from baseline in Anti-Cardiolipin IgM (IU/mL) (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01 for BARI vs. PBO, BARI=baricitinib; Ig=immunoglobulin; PBO=placebo)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dörner T, Van Vollenhaven R, Doria A, Jia B, Fantini D, Terres J, Silk M, de Bono S, Fischer P, Wallace D. Baricitinib Decreases Anti-dsDNA and IgG Antibodies in Adults with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from a Phase 2 Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baricitinib-decreases-anti-dsdna-and-igg-antibodies-in-adults-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-from-a-phase-2-double-blind-randomized-placebo-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baricitinib-decreases-anti-dsdna-and-igg-antibodies-in-adults-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-from-a-phase-2-double-blind-randomized-placebo-controlled-trial/
