Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
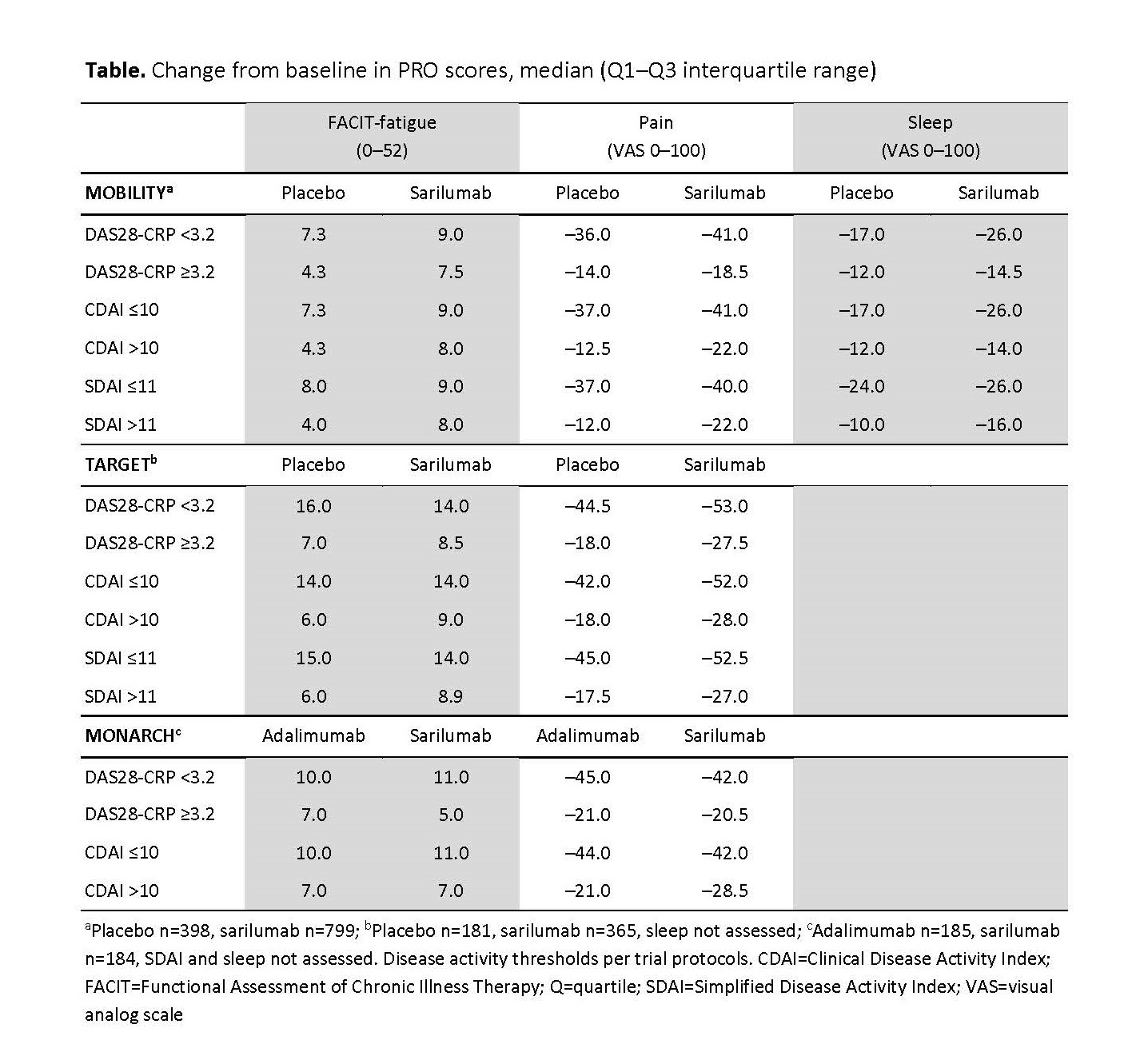
Background/Purpose: Sarilumab is a human IL-6 receptor inhibitor approved for the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active RA. The relationship between disease activity, sarilumab treatment, and improvements in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) has not been well studied. Here, we assess the association between disease activity and PROs in 3 sarilumab phase 3 trials.
Methods: This post hoc analysis included patients from 2 placebo-controlled trials (MOBILITY [NCT01061736] and TARGET [NCT01709578], with sarilumab dose groups of 150 mg and 200 mg every 2 weeks [q2w] combined for this analysis) and the active-controlled MONARCH (NCT02332590; sarilumab 200 mg vs adalimumab 40 mg q2w) trial. Associations between PRO improvement and achievement of low disease activity (LDA) were tested at Week 24. All statistics are descriptive.
Results: Across all trials, PRO improvements were numerically larger in patients who achieved LDA than in those who did not (Table). Sarilumab was associated with numerically larger PRO improvements than placebo, in patients who did and also in those who did not achieve LDA (Table). In the active-comparator trial, improvements in PROs were generally comparable between sarilumab and adalimumab (Table).
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis, achieving LDA was associated with increased PRO improvements. In patients who did not achieve LDA, the improvements were numerically more favorable with sarilumab than with placebo. There is an emerging concept that changes in PROs may also occur via different mechanisms than just suppression of inflammation, potentially via IL-6 inhibition (Taylor PC, et al. J Clin Med. 2019;8[6]:831), which may account for some of the results seen here.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burmester G, Gossec L, van Hoogstraten H, Praestgaard A, St John G, Huizinga T, Aletaha D, Fleischmann R. Associations Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity and Patient-reported Outcomes in Sarilumab Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-sarilumab-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-sarilumab-clinical-trials/