Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anemia is a common comorbidity in patients (pts) with RA, and changes in hemoglobin (Hb) levels are associated with changes in inflammatory disease activity. Since IL-6 is a central mediator and is known to impact iron metabolism/bioavailability it could contribute to anemia of chronic disease. We hypothesize that if IL-6 inhibition by sarilumab improves Hb levels, resulting in better clinical efficacy and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in anemic RA pts vs comparators (placebo [PBO]+MTX or adalimumab), it might do so through its effects on Hb. In this post hoc analysis we assessed the association of low Hb level with clinical efficacy measures and PROs in 3 sarilumab phase III studies: TARGET (NCT01709578), MOBILITY (NCT01061736), MONARCH (NCT02332590).
Methods: Patients enrolled in MOBILITY and TARGET received either PBO or sarilumab 150 mg or 200 mg subcutaneously (SC) every 2 wks (q2w), in combination with MTX (52 wks) or in combination with weekly csDMARD (24 wks). Analysis used combination therapy pooled data from TARGET and MOBILITY through 24 wks. In MONARCH, pts received either adalimumab 40 mg or sarilumab 200 mg SC q2w monotherapy (24 wks). We evaluated mean changes from baseline to Wk 24 in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), CRP, 28-joint Disease Activity score-CRP (DAS28-CRP), pain visual analogue scale (VAS), patient global assessment (PtGA), stratified by Hb levels as low (Hb< 12.0 g/dL [females]/< 13.0 g/dl [males]) vs normal (Hb 12.0 to 15.5 g/dL[females]/13.5 to 17.5 g/dL [males]). Bivariate linear regression was performed to evaluate relationships between Hb level and outcomes from baseline to Wk 24. Mean change from baseline in efficacy measures and PROs were summarized as mean (SD) values.
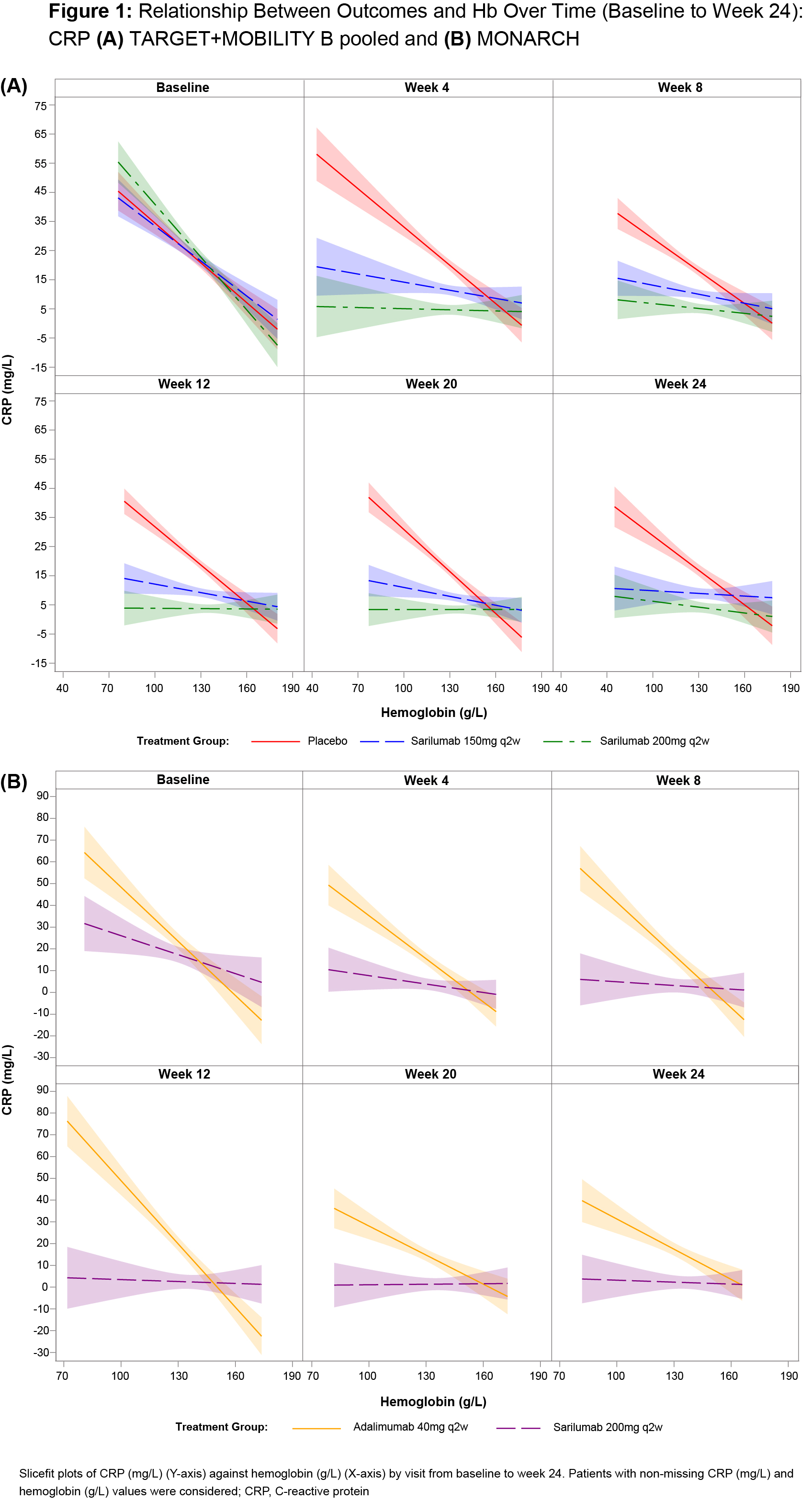
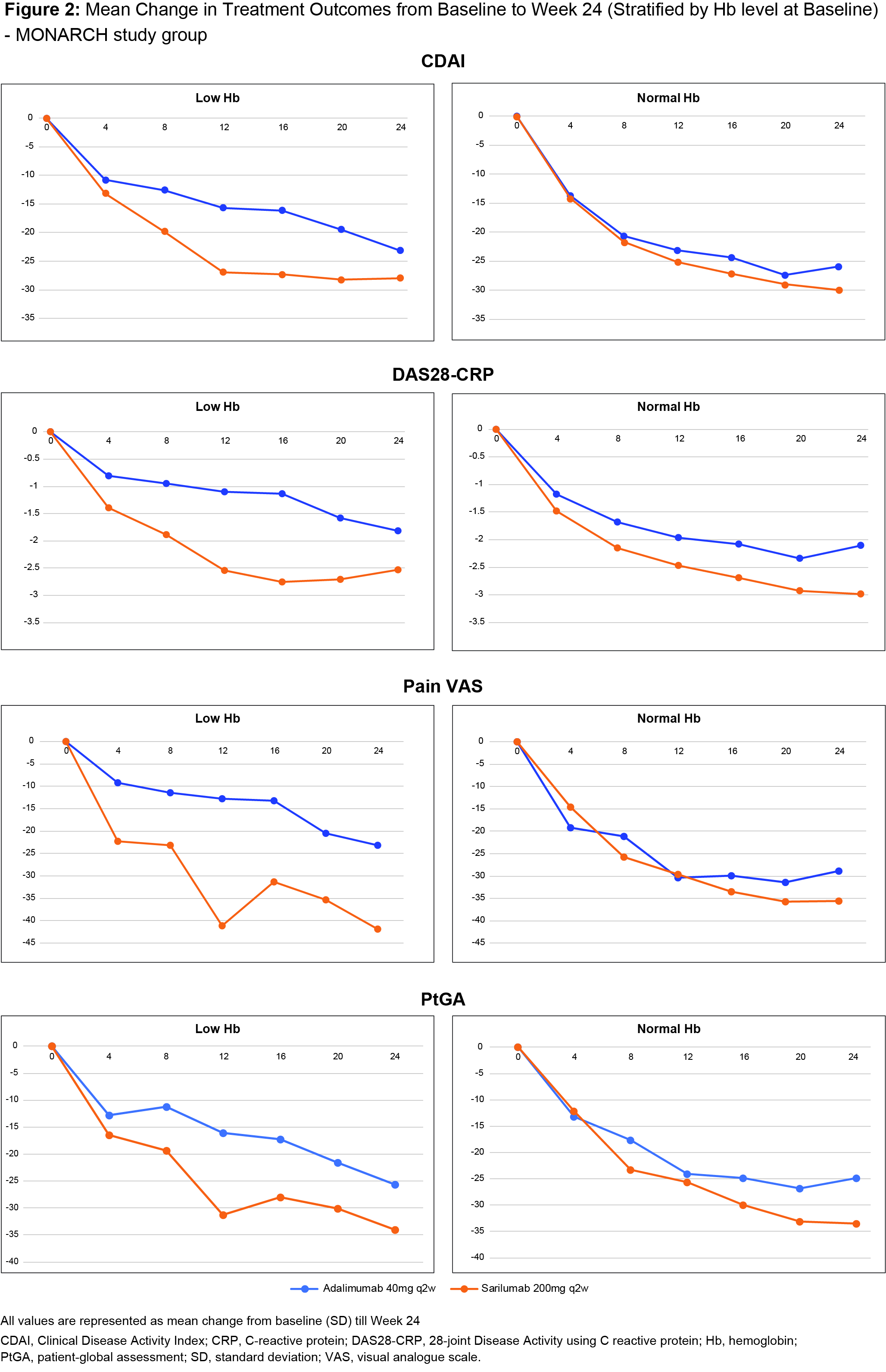
Results: Low Hb was observed in 34% of pts in the pooled group (N = 1743, TARGET+MOBILITY) and in 25% of pts in the monotherapy group (N = 369, MONARCH). Baseline characteristics, demographics and concomitant medications were similar between groups (Table 1). Over 24 wks, higher Hb levels were associated with better clinical efficacy/pain outcomes in all evaluated study groups. Fig 1 shows a steady disassociation between Hb level and CRP in sarilumab-treated pts from baseline to Wk 24 in both study groups. A similar trend was also observed for other efficacy measures and PROs (data not shown). Mean change from baseline to Wk 24 in CDAI, DAS28 CRP, Pain VAS, PtGA was similar in both groups, irrespective of the baseline Hb levels (low vs normal; Fig 2). Effect size (difference between sarilumab and adalimumab) was larger for low Hb subgroup, especially in MONARCH (Fig 2; combination therapy, data not shown). The safety profile of sarilumab has been previously reported and was not part of this analysis.
Conclusion: In this analysis, by Week 24, in sarilumab-treated patients with low Hb levels, we observed better clinical efficacy measures and PROs than with adalimumab in the MONARCH Study. Furthermore, the positive effect of sarilumab was independent of the baseline Hb level (low vs normal). The observed dissociation indicates that the drug’s efficacy is not ‘solely’ mediated by its effects on Hb.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rubbert Roth A, Furst* D, Fiore S, Praestgaard A, Bykerk V, Bingham III C, Charles-Schoeman C. Association of Low Hemoglobin with Efficacy and Patient-reported Outcomes in Three Phase III Studies of Sarilumab (TARGET, MOBILITY and MONARCH) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-low-hemoglobin-with-efficacy-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-three-phase-iii-studies-of-sarilumab-target-mobility-and-monarch/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-low-hemoglobin-with-efficacy-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-three-phase-iii-studies-of-sarilumab-target-mobility-and-monarch/