Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1442–1487) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory disease that involves the deposition of immunocomplexes on vital organs, including the heart. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of long-term mortality in SLE patients, and their increased risk of cardiovascular events is attributed to disease characteristics, such as the systemic inflammatory state associated with the disease. In this study we aimed to evaluate the association of disease characteristics, such as the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) and anti-double stranded DNA antibodies (anti-dsDNA) titers, with echocardiographic parameters in patients with SLE.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study. We recruited 75 SLE patients aged ≥ 18 years who fulfill the 2019 EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria for SLE. Patients with a previous cardiovascular event, another connective tissue disease or pregnancy were excluded. A transthoracic echocardiogram was performed by two certified echocardiographers blinded to clinical information. A blood sample was drawn to measure anti-dsDNA antibody titers and disease activity was evaluated with SLEDAI. Correlations were assessed with Spearman’s correlation coefficient (rs). A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
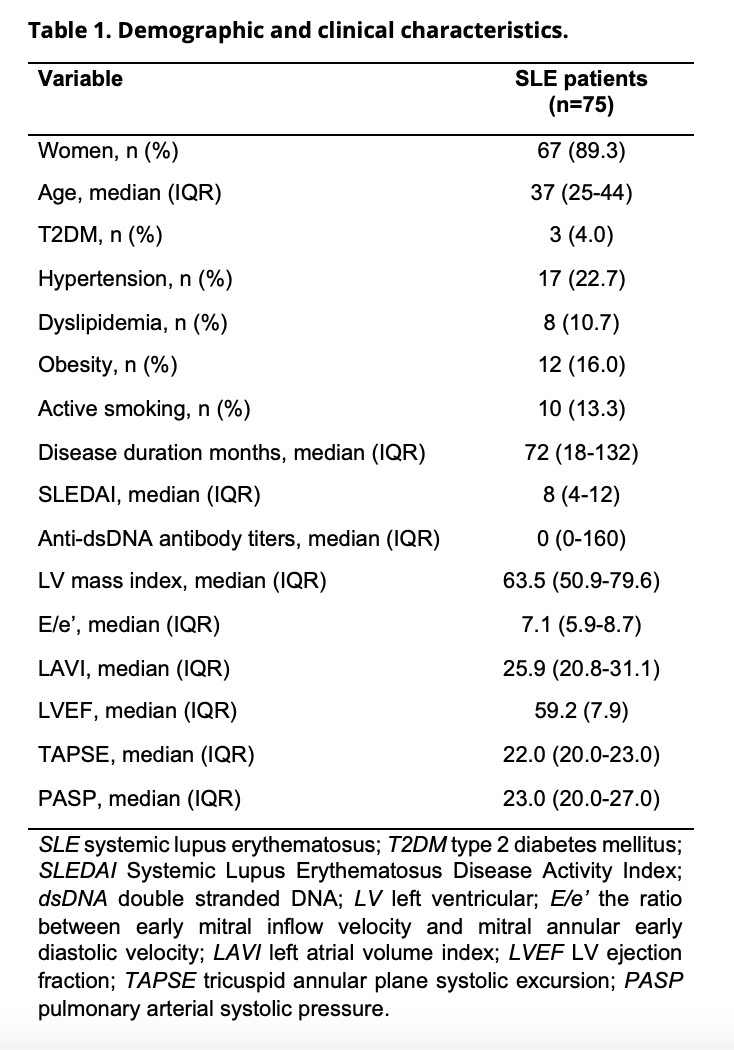
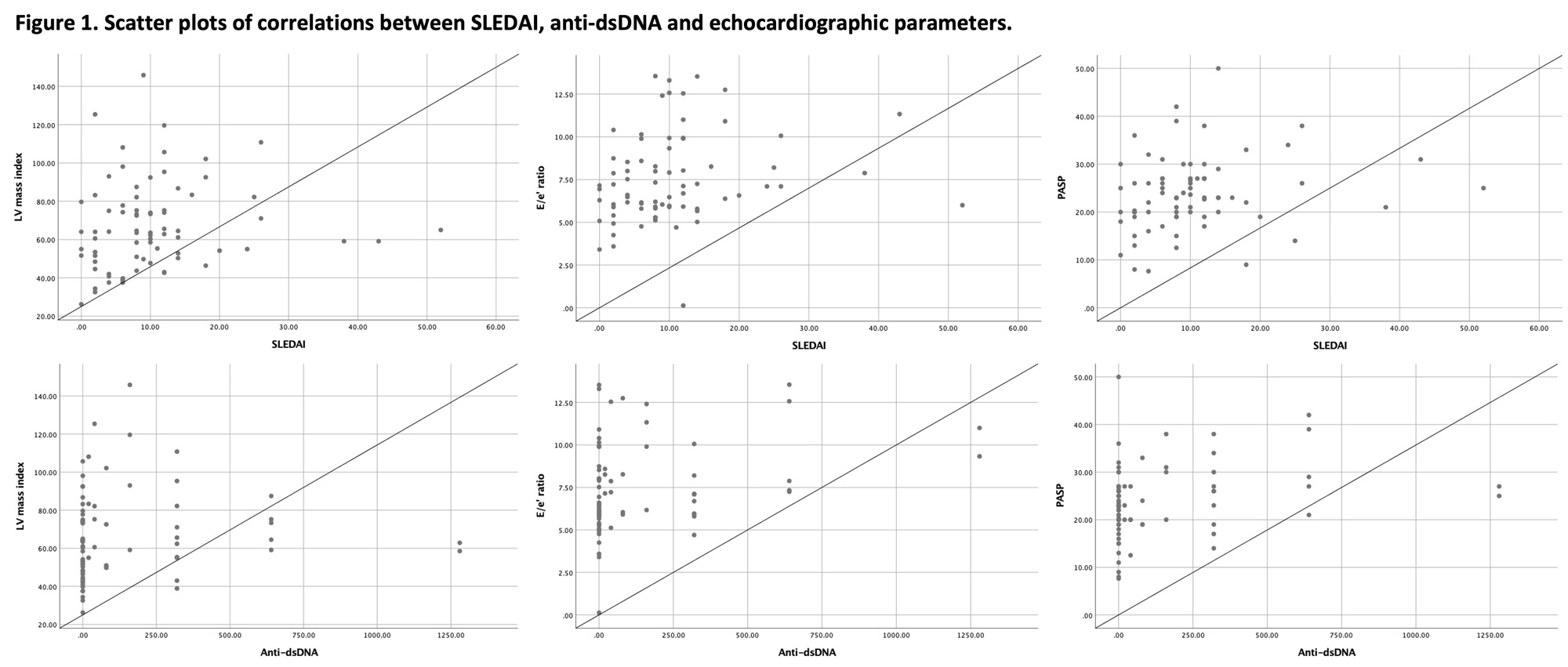
Results: Median age of SLE patients was 37 (25-44) years with a median SLEDAI of 8.0 (4.0-12.0). The rest of demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1. We found a positive correlation between SLEDAI and left ventricular mass index (rs=0.243, p=0.036), between SLEDAI and the ratio between early mitral inflow velocity and mitral annular early diastolic velocity (E/e’) (rs=0.277, p=0.016) and between SLEDAI and pulmonary arterial systolic pressure (PASP) (rs=0.271, p=0.019). We also found a positive correlation between anti-dsDNA and left ventricular mass index (rs=0.264, p=0.022), between anti-dsDNA and E/e’ (rs=0.295, p=0.010), and between anti-dsDNA and PASP (rs=0.292, p=0.011) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated significant associations between higher SLEDAI and anti-dsDNA with increased left ventricular mass index, E/e’ and PASP, which could lead to the progression of ventricular hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, and pulmonary hypertension respectively, suggesting a potential role of disease activity and anti-dsDNA in the development of adverse cardiac remodeling and function in SLE patients. A transthoracic echocardiogram may be helpful to detect early cardiovascular abnormalities, especially in patients with high disease activity and anti-dsDNA titers, and therefore, should be considered as part of the cardiovascular evaluation of SLE patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guajardo-Jauregui N, Colunga I, Azpiri-López J, Galarza-Delgado D, Cardenas-De la Garza J, Arvizu-Rivera R. Association of Disease Activity and Anti-Double Stranded DNA Antibodies Titers with Echocardiographic Parameters in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-disease-activity-and-anti-double-stranded-dna-antibodies-titers-with-echocardiographic-parameters-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-disease-activity-and-anti-double-stranded-dna-antibodies-titers-with-echocardiographic-parameters-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients/