Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II (1919–1922)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:15PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is associated with accelerated atherosclerosis due to underlying inflammation. Whether inflammatory burden and drugs used to suppress inflammation over time are associated with cardiovascular (CV) events remained unclear. This study aims to examine the time-varying effect of C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and the use of drugs including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on the risk of CV events independent of traditional CV risk factors in PsA patients.
Methods: A retrospective cohort analysis was performed in patients with PsA who were recruited from 2008 to 2015 and followed till the end of 2019. The outcome was occurrence of a first CV event. Framingham risk score (FRS) was used to quantify the traditional CV risk. Cox proportional hazard models with time-varying CRP levels and drugs used were analyzed to identify the risk factors for CV events in PsA patients. Kaplan-Meier survival curve and log-rank test was used to illustrate CV event free survival distribution.
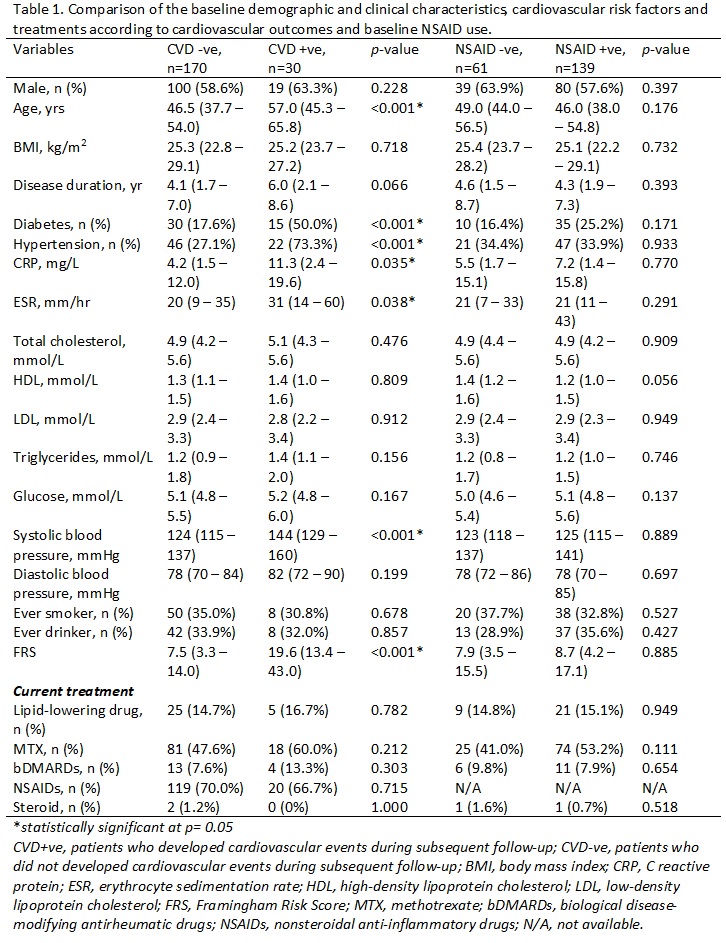
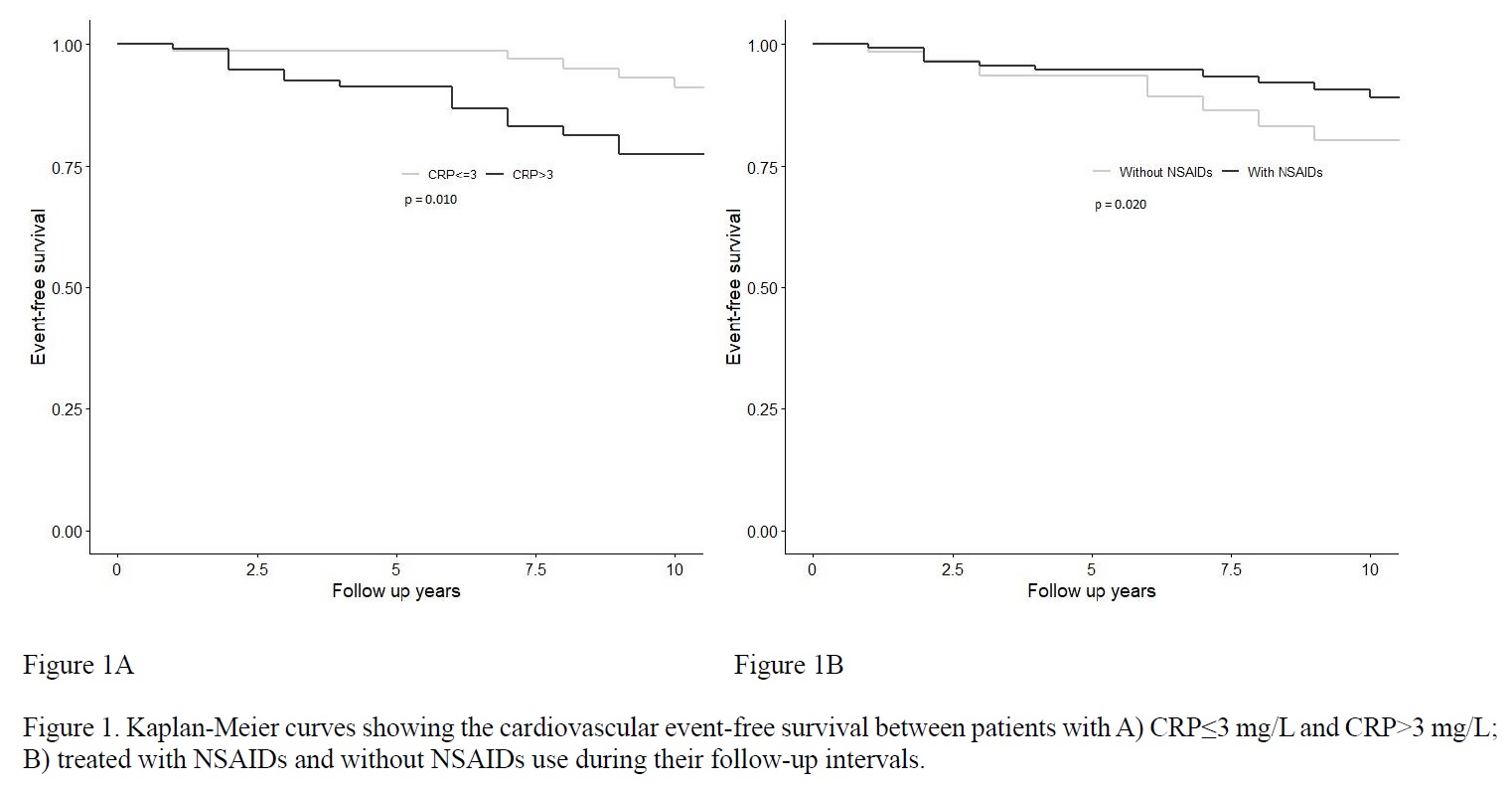
Results: 200 patients with PsA (median age: 47.5[40.0 – 56.0]; male: 119 [59.5%]) were recruited (Table 1). After a mean follow-up of 8.8±3.8 years, 30 (15%) patients developed a first CV event. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve and the log-rank test indicated a significant difference in the CV event-free survival between patients with and without CRP level >3 mg/L (Figure 1A) and an inverse relationship between time-varying NSAIDs exposure and CV event-free survival (Figure 1B). The multivariable Cox regression model showed that time-varying CRP level (HR 1.02, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.04) and NSAIDs exposure (HR 0.30, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.95) were significantly associated with CV events after adjusting for baseline FRS (HR 5.04, 95% CI 1.83 to 13.85).
Conclusion: Increased inflammatory burden as reflected by elevated CRP level was associated with increased risk of CV events, while the risk was significantly reduced with NSAIDs use in PsA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lam H, So H, Cheng I, Li E, Wong P, Li T, Lee A, Tam L. Association of C-reactive Protein and Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs with Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Time-dependent Cox Regression Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-c-reactive-protein-and-non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory-drugs-with-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-time-dependent-cox-regression-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-c-reactive-protein-and-non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory-drugs-with-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-time-dependent-cox-regression-analysis/