Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune rheumatic disease characterized by significant vascular abnormalities due to microvascular damage and intimal proliferation in the small arterioles. Additionally, SSc has been associated with macrovascular complications, including cardiovascular disease (CVDs) and peripheral vascular disease. Cerebrovascular accident, also known as stroke, is a macrovascular condition that can occur among patients with SSc. In this study, we conducted a meta-analysis to corroborate previous studies on the risk of ischemic stroke in SSc patients.
Methods: Two investigators searched published articles on Medline database using two subject heading (MeSH) terms. Term A was “SSc OR Systemic Sclerosis OR Scleroderma OR CREST syndrome”. Term B was “Stroke OR cerebrovascular accident OR cerebrovascular event”. Inclusion criteria were studies describing the association between SSc and ischemic and/or hemorrhagic stroke. Statistical calculation of pooled proportions was conducted in R language. The outcome of interest was the proportion of patients with SSc that developed stroke. The heterogeneity between studies was assessed by the I2 test.
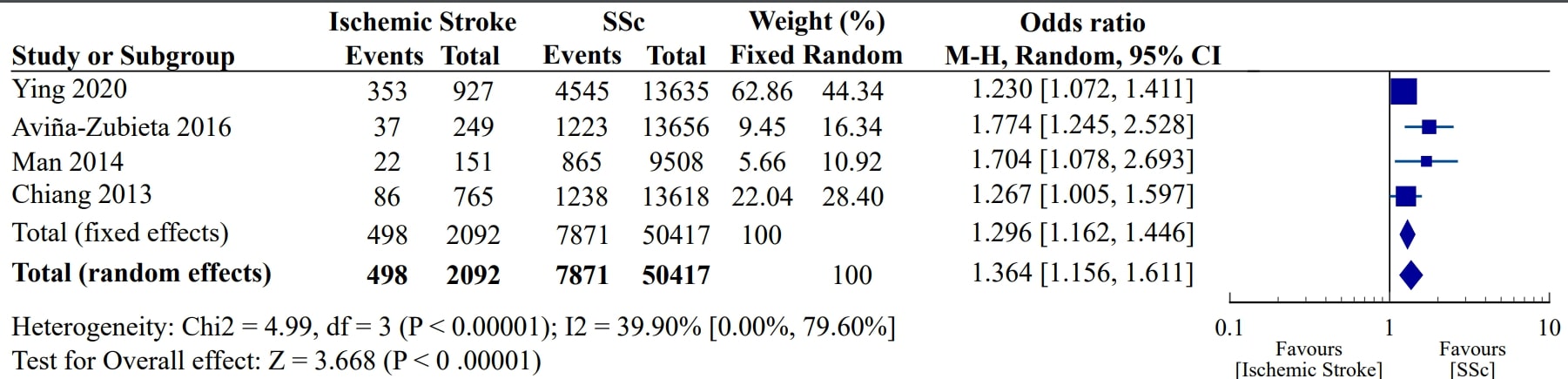
Results: Four studies (4 cohort studies) were met our criteria with 7871 patients with SSc. Our analysis demonstrated a statistically significant higher risk of ischemic stroke in patients with SSc compared with controls yielding a pooled risk estimate of 1.36 (95% CI, 1.16 to 1.61). The level of statistical heterogeneity was moderately low with an I2 of 39.9%. As shown in the respective forest plot, no significant asymmetry was observed between the included studies (Figure).
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this meta-analysis includes the largest number of SSc patients and provides robust evidence supporting an increased risk of ischemic stroke in SSc patients. These results underscore the importance of recognizing SSc as a potential risk factor for cerebrovascular complications and highlight the need for prevention and close monitoring in this patient population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Flourou C, Liampas A, Parperis K. Association Between Systemic Sclerosis and Increased Risk of Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-systemic-sclerosis-and-increased-risk-of-ischemic-stroke-a-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-systemic-sclerosis-and-increased-risk-of-ischemic-stroke-a-meta-analysis/