Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients have an increased risk of developing lymphoma compared to the general population. This increased risk is believed to be linked to higher disease activity. Methotrexate (MTX), a commonly used treatment for RA, has the potential to reduce the risk of lymphoma by lowering disease activity. However, existing research on the association between MTX use in RA and lymphoma development presents conflicting results. This study aimed to conduct a systematic literature review to evaluate this association.
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials on December 9, 2021. The search included observational studies and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in English, focusing on the relationship between MTX use in RA and lymphoma development. Case series and reports were excluded. Data were extracted from the selected articles by two independent authors using a predefined form, with conflicts resolved by a third reviewer. Quality assessments were conducted.
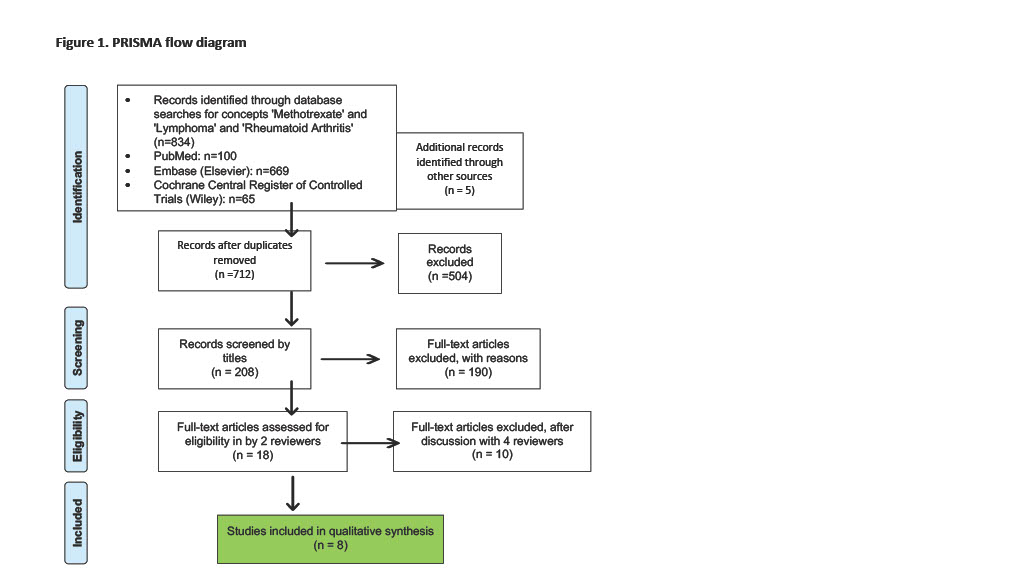
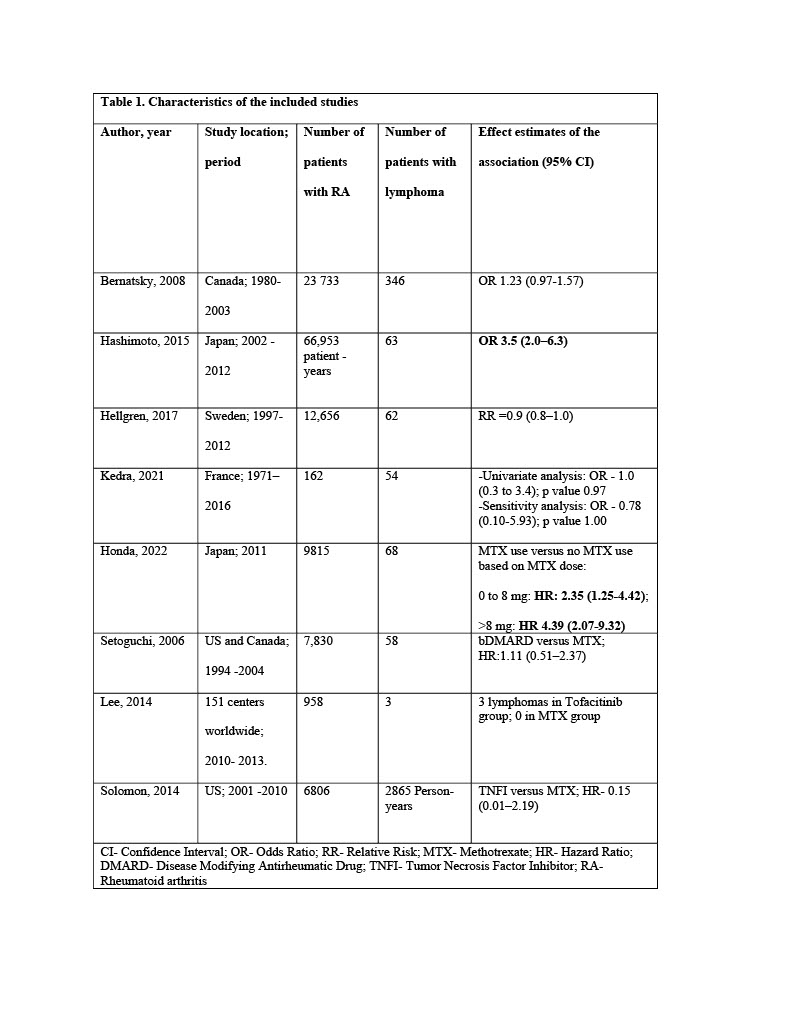
Results: The search process identified 839 articles, out of which only eight met the eligibility criteria (Figure 1). Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of these studies, which predominantly consisted of observational studies, with one RCT included. The sample sizes ranged from 160 to 20,000 RA patients. Five studies reported odds/hazard ratios for lymphoma occurrence in MTX-exposed versus non-exposed patients. Three studies (one of which was an RCT) compared the risk of lymphoma development in RA patients treated with MTX versus other biological DMARDs. Most studies adjusted for various factors, including age, sex, RA disease activity measures, inflammatory markers, concomitant RA medications, cancer risk factors, and RA-related variables. Six of the eight studies found no significant association between MTX use and lymphoma, while two studies from Japan reported a significant positive association. The included studies were of moderate to high quality, but heterogeneity prevented a meta-analysis.
Conclusion: While conflicting data exist regarding the role of MTX in lymphoma development in RA, the majority of high-quality epidemiological studies reviewed did not support an association between MTX use and lymphoma development. Only two studies, both from Japan, indicated a significant association between MTX use and lymphoma development.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alexander S, Starkebaum G, Louden D, Hughes G, Singh N. Association Between Methotrexate Use and Lymphoma in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Literature Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-methotrexate-use-and-lymphoma-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-literature-review/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-methotrexate-use-and-lymphoma-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-literature-review/