Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2177–2194) Sjögren’s Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sjӧgren’s syndrome (SS) may affect several aspects of patients’ daily lives, leading to impairment of quality of life and patient functioning. Aims of this study were: a) to investigate the relationship between disease activity, illness perception and psychopathological state in patients with SS; b) to specifically explore the impact of glucocorticoid (GC) therapy on patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs).
Methods: This is an observational cross-sectional study including consecutive SS patients (ACR/EULAR 2016) from November 2022 to May 2023. We collected demographic and clinical data including disease duration, ESSDAI, systemic manifestations and pharmacotherapy (GC therapy dose, antimalarial agents, psychotropic and DMARDs). We also assessed the following PROMs: ESSPRI, Visual analogue scale (VAS) for dry mouth, VAS for dry eyes, FACIT-Fatigue, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Patients were subdivided into two groups: no GC-treatment vs GC-treatment of ≥1 year. ANOVA, t-tests, Mann Whitney and χ2 tests were used to assess differences between the two groups. Spearman’s correlation was used to measure the correlations between continuous variables. Logistic regression analysis was used to assess independent variables associated with GC therapy.
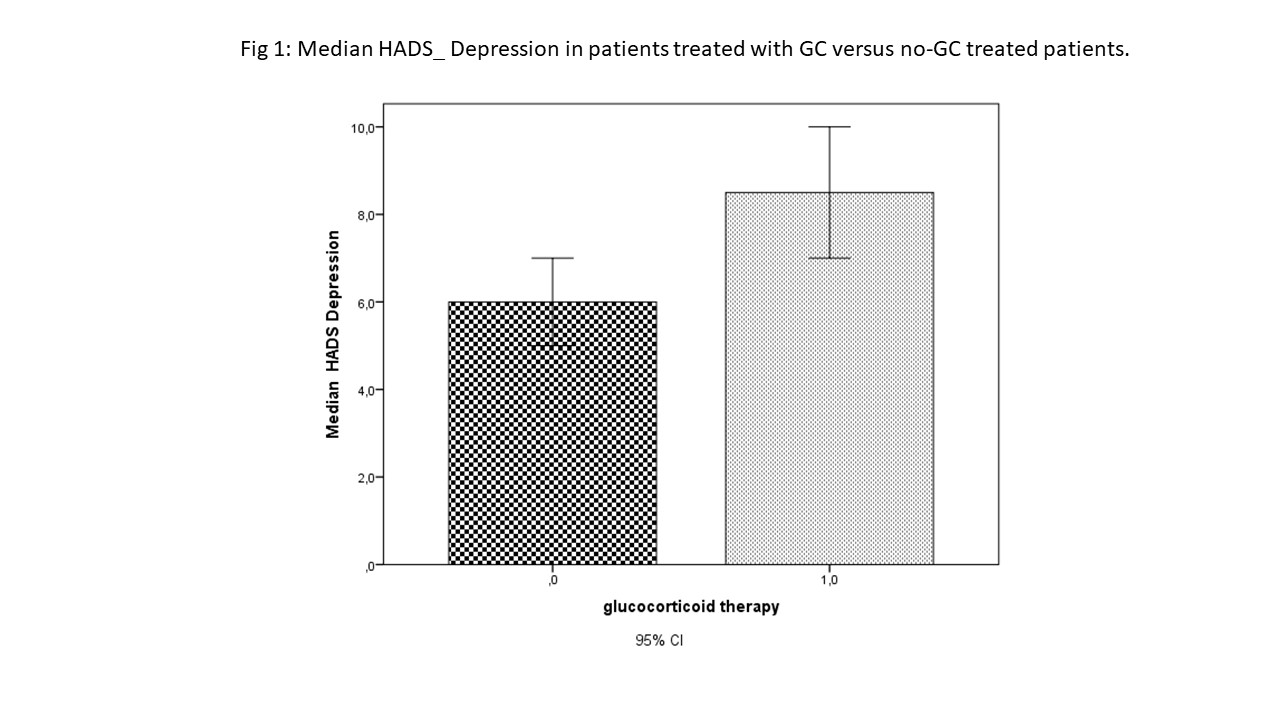
Results: We included 204 patients (197 F:7M), mean age (DS): 62.6(12.4) yrs; mean follow-up (DS): 9.9 (8-4) yrs. A fifth of the patients showed an ESSDAI≥5, 109/204 (53.4%) presented an ESSPRI≥5 and an ESSDAI< 5 and 55/204 (27%) had both an ESSPRI< 5 and an ESSDAI< 5. The ESSDAI did not correlate either with the ESSPRI nor with other PROMs. However, Cryo positive patients and subjects with moderate-to-high activity in the glandular domain of the ESSDAI presented significantly higher scores in the VAS questionnaire for dry mouth (8.7 (2.3) vs (6.2 (2.9), p=0.02 and 8.0 (2.1) vs 6.2 (2.9), p=0.02, respectively). By contrast, the ESSPRI scores were significantly lower in patients with low-to-moderate disease activity in the biological domain of the ESSDAI (5.2 (2.8) vs 6.3 (2.4), p =0.01). ESSPRI, HADS, VAS for dry mouth, VAS for dry eyes, and FACIT-Fatigue were statistically significantly correlated with each other (p< 0.001, Table 2). At the inclusion, 40/204 patients (19.6%) were assuming low-dose GC (i.e., ≤7.5 mg of prednisone or equivalent per day). Table 1 summarizes the demographic, disease characteristics and PROMs of the study population comparing patients treated with GC versus no-GC treated patients. The former had a longer disease duration, higher scores in ESSDAI, ESSPRI and HADS depression questionnaire and lower FACIT-Fatigue scores. GC therapy was independently associated with the ESSDAI (OR 1.073 (1.005-1.145), p=0.035) and with the HADS depression questionnaire (OR 1.134 (1.038-1.204), p=0.005)(Fig 1).
Conclusion: We confirmed a limited correlation between disease activity and PROMs in real life. GC therapy, even at the low dosage, contributes to patients’ perception of a poorer control of SS with a negative impact on self-reported depression scores.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baldini C, Elefante E, Navarro Garcia I, Ferro F, La Rocca G, Fulvio G, Fonzetti S, Moretti M, Mosca M. Association Between Illness Perception, Anxiety and Depression State, Disease Activity and Glucocorticoid Therapy in Patients with Sjӧgren’s Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-illness-perception-anxiety-and-depression-state-disease-activity-and-glucocorticoid-therapy-in-patients-with-sj%d3%a7grens-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-illness-perception-anxiety-and-depression-state-disease-activity-and-glucocorticoid-therapy-in-patients-with-sj%d3%a7grens-syndrome/