Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a widely used drug in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). It may cause cardiac alterations which includes short term arrhythmic events (via QT interval prolongation) and medium-late term dose dependent cardiomyopathy. The few research articles published on the medium-late term effects of HCQ in cardiac conduction disorder do not show relevant alterations. The purpose of the study was to assess the effect of HCQ in cardiac conduction in a consecutive SLE population.
Methods: Observational, single University hospital study of all consecutive SLE patients with an electrocardiogram (EKG) at HCQ onset and at least one EKG in follow-up, with a period of at least 3 months on HCQ treatment was performed. We assessed conduction alteration (CA) by EKG, defined as atrio-ventricular block, bundle branch block or QT interval prolongation. The EKGs were gathered from the clinical history and interpreted at the beginning of the treatment and during the 15.2 years (CI95% 13.24-17.16) follow-up period. We defined cumulated HCQ (cHCQ) as the multiple of the mean annual dose of the sample. A Multiple logistic regression model, adjusted by different variables according to statistical significance and clinical relevance, was performed.<
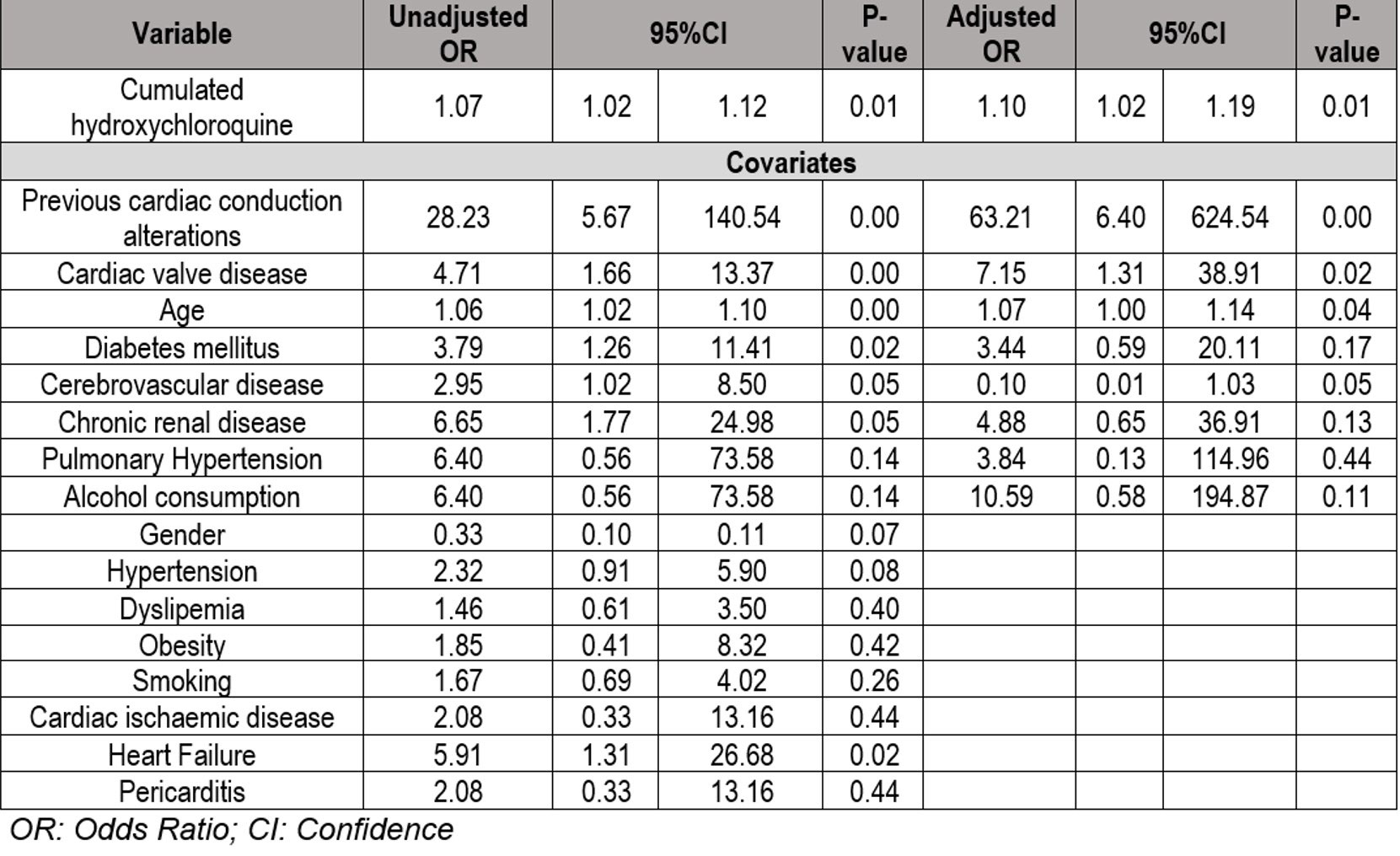
Results: We studied 109 (96 women/13 men) SLE patients with a mean (±SD) age of 61 ±. 2.78 years. A statistically significant association was observed between the cHCQ, and the development of CA [OR 1.1 CI95% 1.02-1.9; p = 0.011] (TABLE & FIGURE). A total of 8 covariates were included. Among them, those that had the greatest influence on the development of the primary event were previous CA [OR 4.15 CI95% 6.39-624.54; p < 0.01]; valvular heart disease [OR 7.15 CI95% 1.31-38.91; p = 0.023] and age [OR 1.07 95% CI 1.0-1.14; p = 0.04].
Conclusion: According to our study, it seems to be an association between the cHCQ and development of CA regardless of other variables evaluated. Wider longitudinal studies are required with a protocolized EKG performance in successive visits to further analyze this association.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Herrero-Morant A, Zubiaur-Zamacola J, Margarida-De Castro A, Pérez-Barquín R, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Association Between Cumulated Hydroxychloroquine in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Development of Cardiac Conduction Alterations: A Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-cumulated-hydroxychloroquine-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-development-of-cardiac-conduction-alterations-a-multiple-logistic-regression-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-cumulated-hydroxychloroquine-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-development-of-cardiac-conduction-alterations-a-multiple-logistic-regression-analysis/