Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Golimumab is a safe and effective treatment for RA. Biosimilars to the reference product (RP) may make treatment more accessible. We assessed comparable efficacy of AVT05 and RP in a confirmatory efficacy and safety study (NCT05842213) in patients with moderate to severe RA.
Methods: This was a randomized, double-blind, 2-arm, parallel group, active control study. We randomized 502 subjects at a 1:1 ratio to receive AVT05 (n = 251) or RP (n = 251), 50 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks to Week 12 inclusive. Randomization was stratified by baseline Disease Activity Score-28 for RA using C-reactive Protein (DAS28-CRP) score (≤5.1 and >5.1). The primary endpoint was change from baseline in DAS28-CRP at Week 16.
At Week 16, responder participants (DAS28-CRP decreased by >0.6 from baseline and disease activity DAS28-CRP ≤5.1) initially enrolled in the AVT05 arm, continued to receive AVT05 every 4 weeks. Participants initially randomized to RP were re-randomized 1:1 to either continue receiving RP or switch to AVT05. Non-responders were discontinued from study drug.
This abstract reports the primary endpoint, and safety and immunogenicity data up to Week 24. The study continues to Week 52.
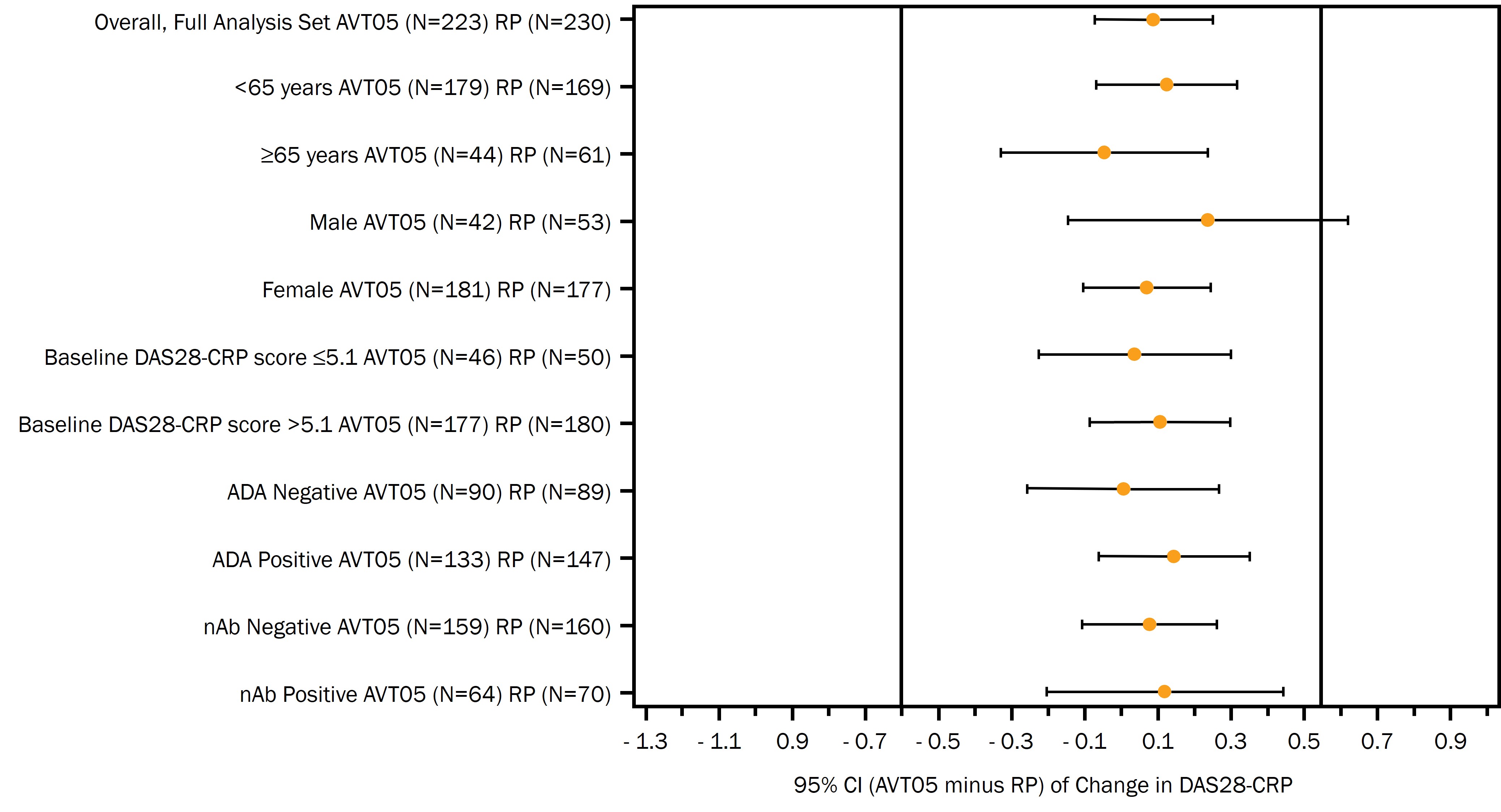
Results: At Week 16 the two-sided 90% confidence interval of the least squares mean difference between the two treatment groups was entirely contained within the prespecified equivalence margin of -0.6, 0.54 (-0.05, 0.22), supporting a demonstration of comparative efficacy. The primary endpoint was analyzed using Mixed Model for Repeated Measures excluding data of patients at and after Intercurrent Events. Two sensitivity analyses supported the robustness of the primary endpoint estimates. There were no notable differences in subgroup analysis (Figure 1).
Up to Week 16, the safety profile was similar across treatment arms, with 38.2% of participants reporting a TEAE in the AVT05 group, and 39.4% in the RP group. Most were mild in intensity. There were 4 serious TEAEs in the AVT05 group and 2 in the RP group, of which 1 in both groups was considered treatment-related. Both participants were discontinued from the study.
At Week 16, treatment-emergent ADAs had a similar incidence in AVT05 and RP treatment groups; 52.7% and 57.8% respectively. The incidence of nAb positive samples was also similar; 46.6% in AVT05 group and 47.6% in RP group.
At Week 24, no significant differences in the safety or immunogenicity profiles had emerged, including in participants who had switched from RP to AVT05.
Conclusion: Analysis of the change in DAS28-CRP from baseline to Week 16 supports the assessment of comparative efficacy between AVT05 and RP. AVT05 had a safety and immunogenicity profile similar to that observed for RP up to Week 16, persisting to Week 24.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Luque M, Zhelyazkova K, Vashishta L, Rai M, Sattar A, Bucknall R, Leutz S, BERTI F. Assessment of Comparative Efficacy Between Candidate Biosimilar AVT05 and Reference Golimumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-comparative-efficacy-between-candidate-biosimilar-avt05-and-reference-golimumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-comparative-efficacy-between-candidate-biosimilar-avt05-and-reference-golimumab/