Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Measurements (0739–0763)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Improvements in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were demonstrated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of baricitinib (BARI), an oral Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitor, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In these post-hoc analyses of BARI RCT data at baseline and 24 weeks, we examined the relative importance of PROs on the Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PtGA) and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and whether these differ in patients with good disease control compared with those not in low disease activity (LDA) or remission in different patient populations.
Methods: We analyzed data from three BARI phase 3 studies: 1) RA-BEGIN (NCT01711359) included 588 conventional synthetic DMARD-naive patients randomized 4:3:4 to receive methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy, BARI 4 mg, BARI + MTX; 2) RA-BEAM (NCT01710358) included 1307 MTX-inadequate response (IR) patients randomized 3:3:2 to placebo (PBO), BARI 4 mg, or adalimumab 40 mg; and 3) RA-BEACON (NCT01721044) included 527 biologic DMARD-IR patients randomized 1:1:1 PBO, BARI 2 mg, or BARI 4 mg. PtGA was measured by a visual analog scale (VAS, 0 to 100 mm) and HRQoL was measured by SF-36 physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS) scores. PROs included pain (VAS, 0 to 100 mm), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F), duration of morning joint stiffness (AMJtS), and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Good disease control was defined as either LDA or remission by Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI, ≤10 and ≤2.8, respectively). Within each RCT, treatment-agnostic correlation analyses at all time points from baseline to Week 24 were performed. Multiple regression analyses for the overall population and for patients in LDA, remission, or nonresponse were conducted; we present standardized parameter estimates from the regression analyses for each PRO to assess their relative importance on the PtGA, PCS score and MCS score.
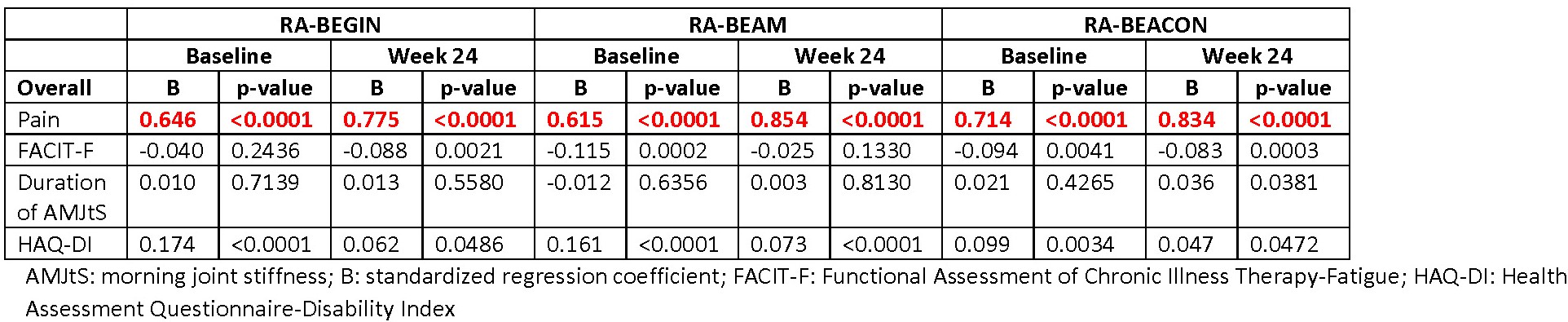
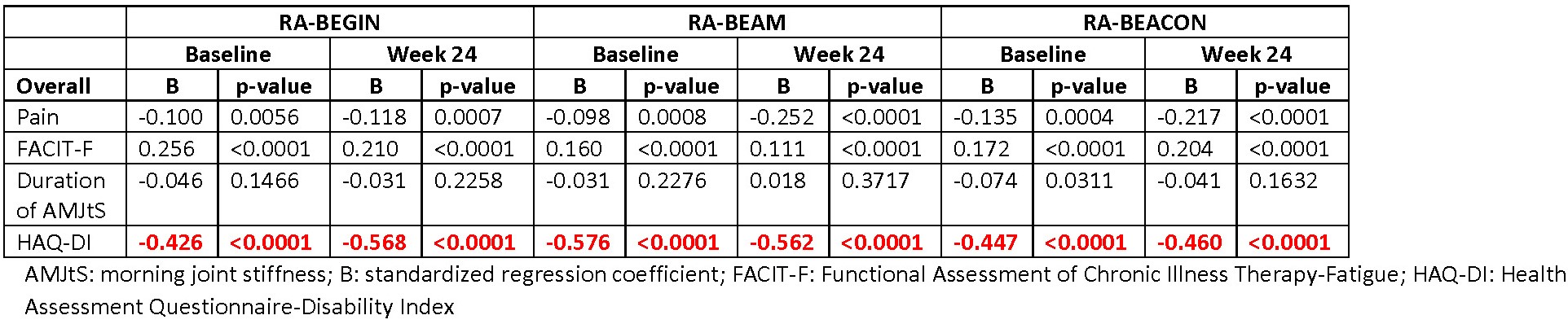
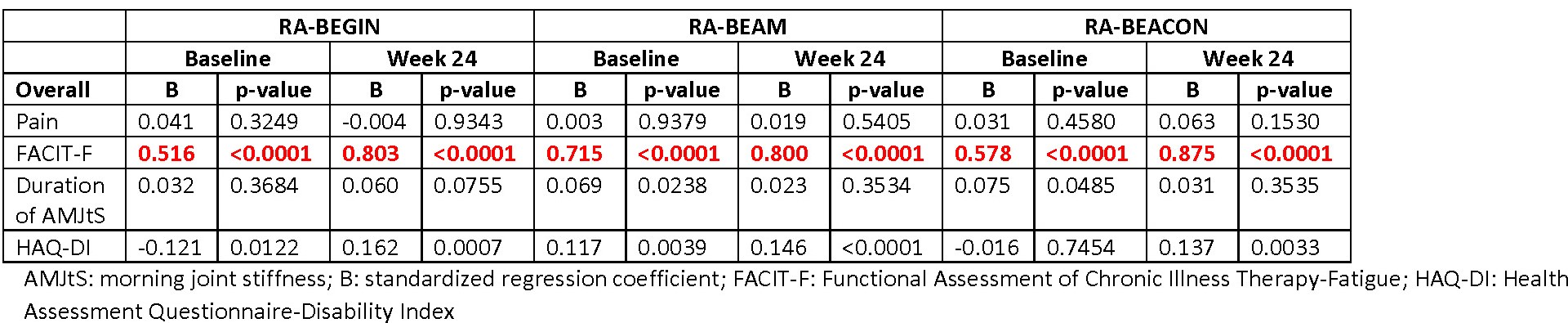
Results: Across RCTs, pain strongly correlated with PtGA (r: 0.9); FACIT-F moderately correlated with PtGA, PCS, and MCS scores (r: 0.6 to 0.7; FACIT-F and PtGA are negatively correlated); and HAQ-DI moderately-to-strongly correlated with PtGA and PCS score (r: 0.6 to 0.8; HAQ-DI and PCS are negatively correlated). Duration of AMJtS was weakly correlated with the other PROs (r: -0.2 to -0.3 for PCS and MCS and 0.3 to 0.4 for PtGA). In regression analyses across RCTs at baseline and Week 24 for the overall populations, the most significant factors were pain with PtGA (Table 1), HAQ-DI with SF-36 PCS score (Table 2]), and FACIT-F with SF-36 MCS score (Table 3). Similar results were observed in patients in LDA, remission, or nonresponse.
Conclusion: These results confirm prior findings, such as high correlations of pain with PtGA. We, however, observed that the relationships between other PROs with PtGA, PCS, or MCS scores were stable across time points over the first 6 months of treatment in differing patient populations, ranging from early to later disease. PtGA, PCS, and MCS scores were each associated with different PROs, indicating the importance of collecting multiple PROs in RCTs and real-world clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Sebba A, Scardo S, Quebe A, Zaremba-Pechmann L, Taylor P. Assessing the Relationship of Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity and Health Related Quality of Life by SF-36 with Other Patient-Reported Outcomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Post Hoc Analyses of Data from Phase 3 Trials of Baricitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-relationship-of-patient-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-and-health-related-quality-of-life-by-sf-36-with-other-patient-reported-outcomes-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-post-hoc-analyses/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-relationship-of-patient-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-and-health-related-quality-of-life-by-sf-36-with-other-patient-reported-outcomes-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-post-hoc-analyses/