Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0325–0344) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The IDEOM MSK-Q aims to assess MSK symptoms in individuals with psoriatic disease. It consists of 3 subscales: Intensity of MSK Symptom (3 items), Impact of MSK Symptoms (4 items), and Intensity of Fatigue (1 item). This study sought to evaluate the known-groups validity of the IDEOM MSK-Q.
Methods: Data from a cross-sectional survey of a random sample of individuals with psoriasis was used. To determine the known-groups validity of the IDEOM MSK-Q, we compared the IDEOM MSK-Q score among different groups based on: A). Disease status: patients with psoriasis-only vs psoriasis with PEST ≥ 3 vs PsA; B). PEST score: PEST < 3 vs PEST ≥ 3; and C.) Impact of PsA: Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID-9) < 4 vs PsAID ≥ 4. ANOVA and ANCOVA, adjusting for age and sex, were used.
Results: A total of 1,453 participants completed the survey. Equal proportions of participants reported a physician given diagnosis of psoriasis-only (47.9%) and psoriasis with concomitant PsA (47.7%), and 4.4% only having PsA. Participants were mostly female (58.4%) with mild psoriasis (52.3% – BSA 3%). Mean participant age was 54.8 (SD ± 15.73). Among all participants, 61% had a PEST score ≥ 3, indicating the potential presence of PsA. Among individuals with PsA and those with psoriasis-only with a PEST score ≥ 3, 65.5% had a PsAID score > 4 (i.e., unacceptable symptom state). For all participants, mean scores for the for the Intensity of MSK Symptom, Impact of MSK Symptoms, and Fatigue subscales were 18.4 (SD = ± 13.9), 5.0 (SD = ± 3.3), and 5.01 (SD = ± 3.28).
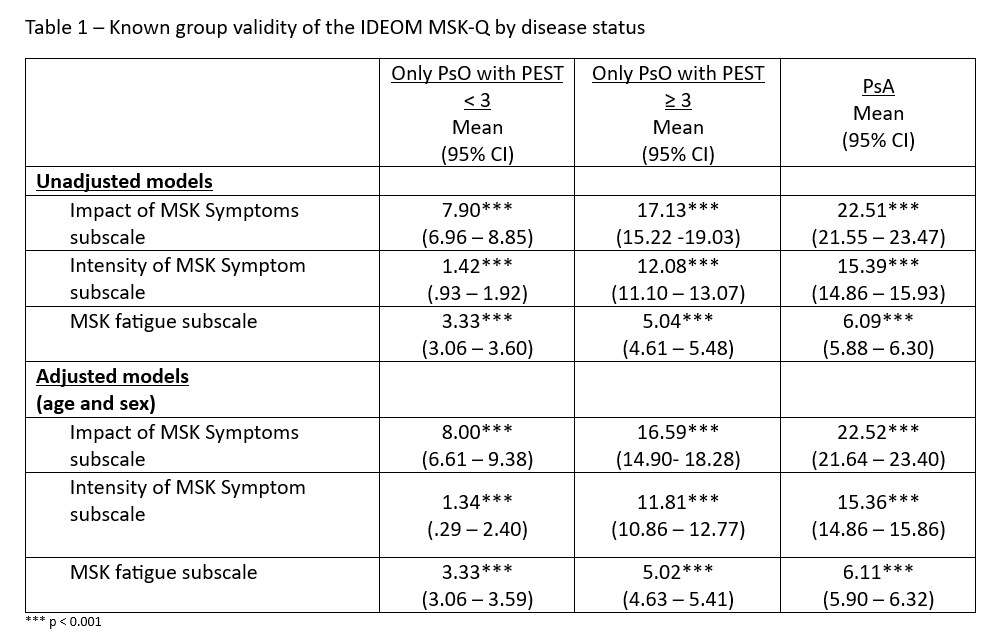
Results comparing the IDEOM MSK-Q subscales among different disease statues groups were statistically significant. Across all subscales, individuals with PsA scored higher than individuals with psoriasis with PEST score ≥ 3, and those with psoriasis-only (Table 1). These differences were maintained when adjusting for age and sex (see Table 1.)
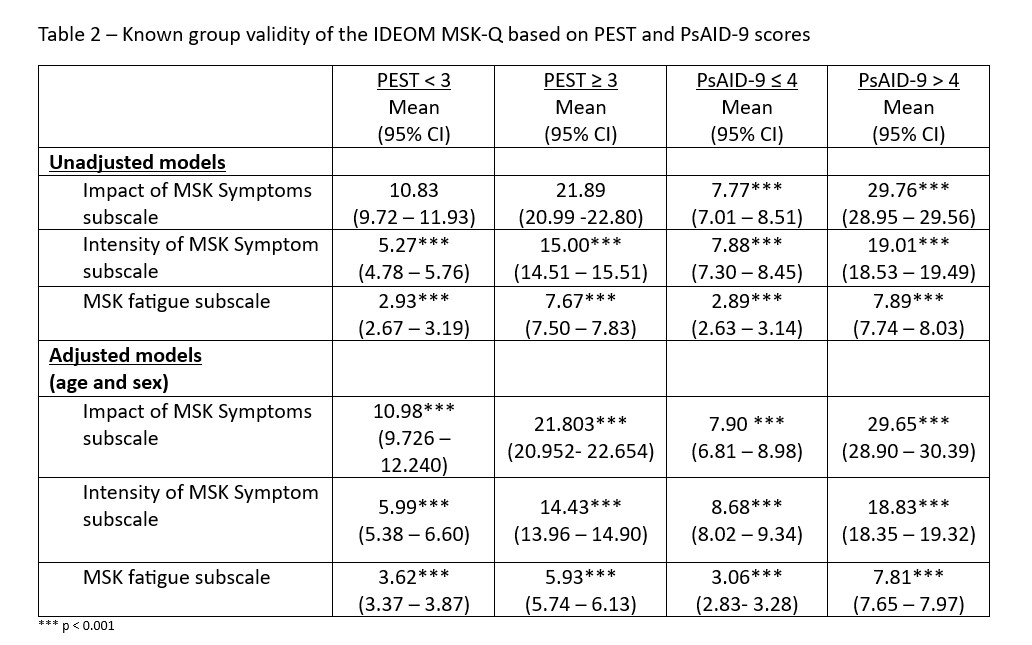
Unadjusted between group comparison based on PEST score (PEST < 3 vs PEST ≥ 3) were statistically significant for the Intensity of MSK Symptom and Impact of MSK Symptoms subscales. Participants who had a PEST > 3 scored higher across all components of the IDEOM MSK-Q (Table 2) compared to PEST < 3. Similarly, unadjusted group comparison based on PsAID score (PsAID ≤ 4 vs PsAID > 4) suggest that individuals at unacceptable symptom state (PSAID > 4) scored higher on all 3 subscales (Intensity of MSK Symptom, Impact of MSK Symptoms , and Fatigue) (Table2). After adjusting for age and sex, comparisons remained statistically significant (see Table 2).
Conclusion: Results from this study suggest that the IDEOM MSK-Q can discriminate between individuals based on disease status, PEST score, and impact of psoriatic arthritis reflecting it has good known group validity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Perez-Chada L, Gondo G, Merola J, Gottlieb A. Assessing the Known-group Validity of the IDEOM MSK-Q Using Data from the National Psoriasis Foundation Annual Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-known-group-validity-of-the-ideom-msk-q-using-data-from-the-national-psoriasis-foundation-annual-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-known-group-validity-of-the-ideom-msk-q-using-data-from-the-national-psoriasis-foundation-annual-survey/