Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Macrophages have been found to have a key role in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Depending on the microenvironment, macrophages exist in a dynamic functional state which could be mainly grouped in a pro-inflammatory state (M1 macrophages) and an anti-inflammatory state (M2 macrophages). In vitro, these conditions can approximately be reproduced by means of cytokines such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and IFNγ for M1 classically polarized macrophages or IL-4 and IL-13 for M2 alternatively polarized macrophages. Human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) are adult stem cells which have been found to exert immunomodulatory functions both by cell-to-cell contact and in a paracrine way. The aim of our study was to assess the ability of hDPSCs to modulate the phenotype of human macrophages.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from buffy coats by density-gradient centrifugation. PBMCs were differentiated to macrophages for 7 days in RPMI supplemented with M-CSF to obtain M0 macrophages. M0 macrophages were then polarized for 48 hours to M1 with LPS and IFNγ and to M2 macrophages with IL-4 and IL-13. hDPSCs were seeded at 1:1 ratio both directly on macrophages and into Transwell insert for indirect co-culture. Macrophages in direct co-culture with hDPSCs were separated with human anti CD14 micro beads. Protein expression was measured by Western Blot. Gene expression was assessed by RT-PCR.
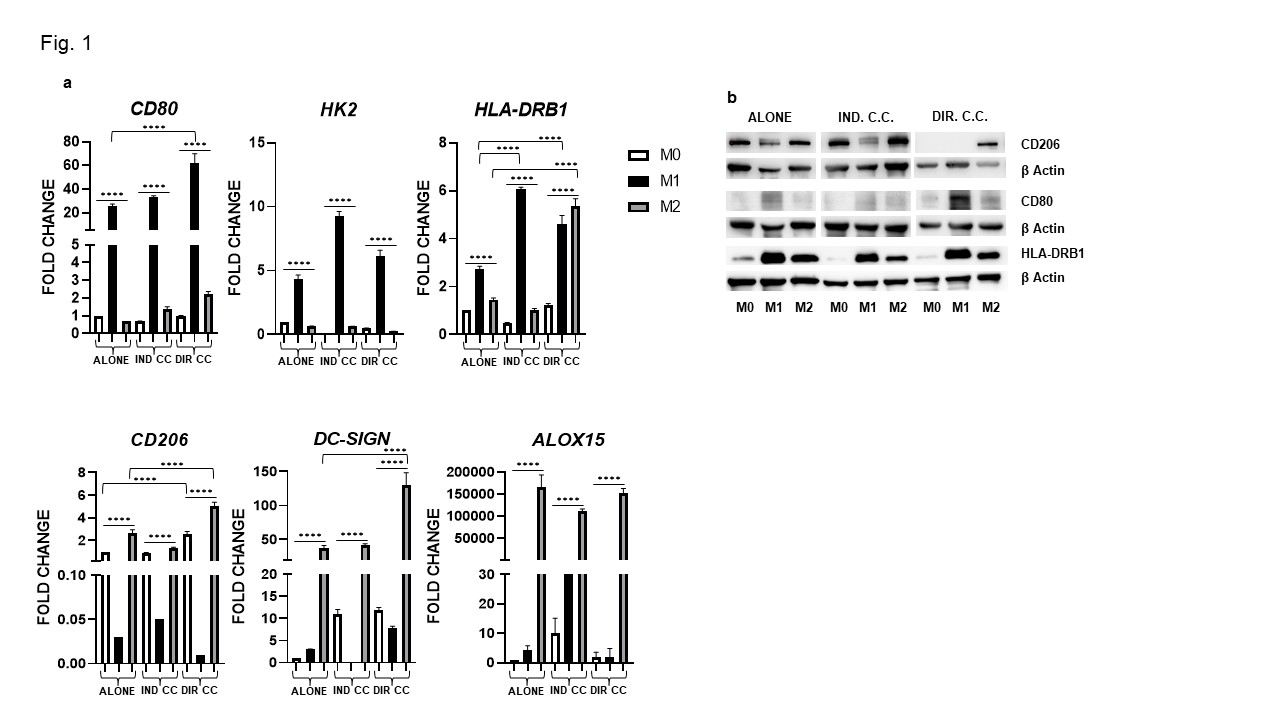
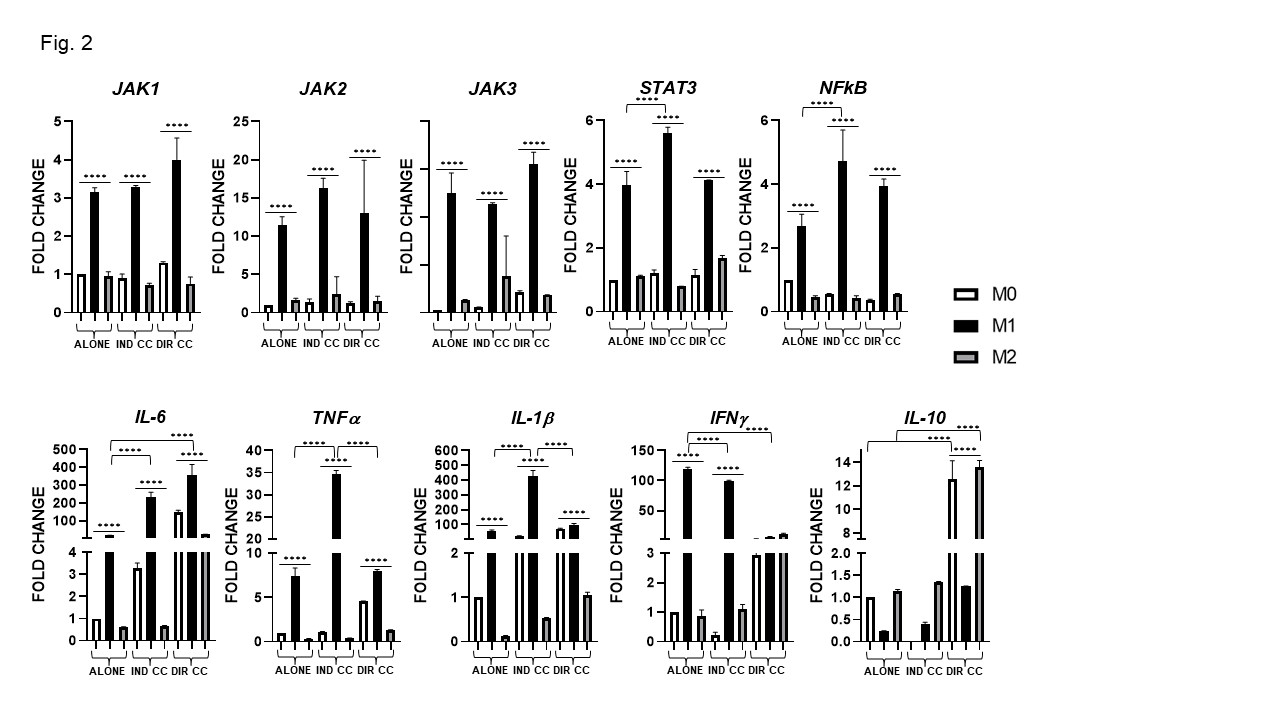
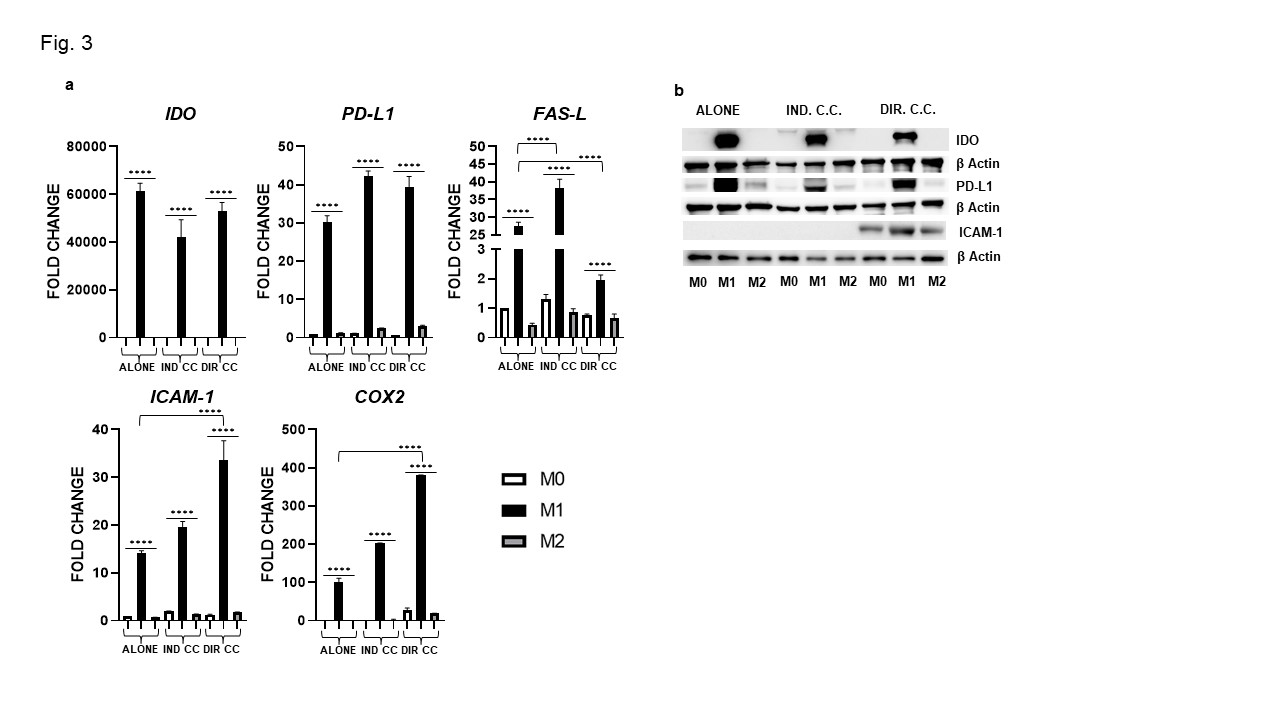
Results: Surface markers expression analysis showed that M1 macrophages were CD80+, HK2+, HLA-DRB1+(p < 0.0001). Following co-culture, CD80 and HLA-DRB1 gene expression was further increased (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 1a), data were also confirmed by protein expression (Fig. 1b). M1 macrophages showed elevated expression of the transcriptional regulators JAK-1, -2, -3,STAT3, NF-kB and of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNFα, IL-1β, IFNγ) levels (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 2). They also express elevated levels of the immune modulators IDO, PD-L1 and ICAM-1 confirmed by protein expression (Fig. 3a, -b) and, of Fas-L and COX2 (Fig. 3a). The indirect co-culture enhanced the expression of STAT3, NF-kB, IL-1β, IL-6, Fas-L and decreased IFNγ expression (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 2, 3). The direct co-culture increased IL-6,ICAM-1 and COX2 expression and diminished IFNγ and Fas-L expression (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 2, 3). M2 macrophages were CD206+, DC-SIGN+ and ALOX15+ and only the direct co-culture was able to enhance the HLA-DR, CD206, DC-SIGN and IL-10 expression (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 1, 2). The direct co-culture increased the expression of CD206 and IL-10 in M0 non-polarized macrophages too (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 1, 2).
Conclusion: The biological factors secreted by hDPSCs supported the macrophages response to inflammation activating the STAT3 and NF-kB pathways and, in contrast, enhancing the inhibitory membrane molecule FasL expression. The cell-to-cell contact was shown to be the best immunomodulatory way reducing the IFNγ expression in inflammatory condition. Further, in presence of anti-inflammatory cytokines, hDPSCs directly promoted the polarization of M0 macrophages towards M2 phenotype and enhanced IL-10 expression which is a key cytokine in limiting the host immune response.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maccaferri M, Pisciotta A, Carnevale G, Salvarani C, PIGNATTI E. Assessing the Ability of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells to Modulate the Macrophages Phenotype [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-ability-of-human-dental-pulp-stem-cells-to-modulate-the-macrophages-phenotype/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-ability-of-human-dental-pulp-stem-cells-to-modulate-the-macrophages-phenotype/