Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Plenary I
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 9:15AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: Synovial fibroblasts assume both inflammatory and tissue invasive roles in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Recent studies have shown that these inflammatory and invasive functions are enacted by transcriptionally distinct fibroblast subsets. Thus, a major question in the field is, what mechanism regulates these disparate pathologic states? Here, we show that the transcription factor Arid5b plays a dual role in inhibiting the inflammatory activation of fibroblasts while enhancing their invasiveness, providing a basis for the differential programming of these pathologic fibroblast phenotypes in RA.
Methods: We used single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data from our lab and published datasets to analyze ARID5B expression in synovial fibroblasts. We then stimulated human RA-derived synovial fibroblast lines with cytokines to assess regulation of ARID5B expression in vitro. Using CRISPR/Cas9, we deleted Arid5b in synovial fibroblasts and utilized RT-qPCR, RNA-seq, ELISA, Western blot, and transwell invasion assays to test the inflammatory and invasive functions of Arid5b. We identified target genomic regions bound by Arid5b with CUT&RUN sequencing and used co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) to determine the protein binding partners of Arid5b.
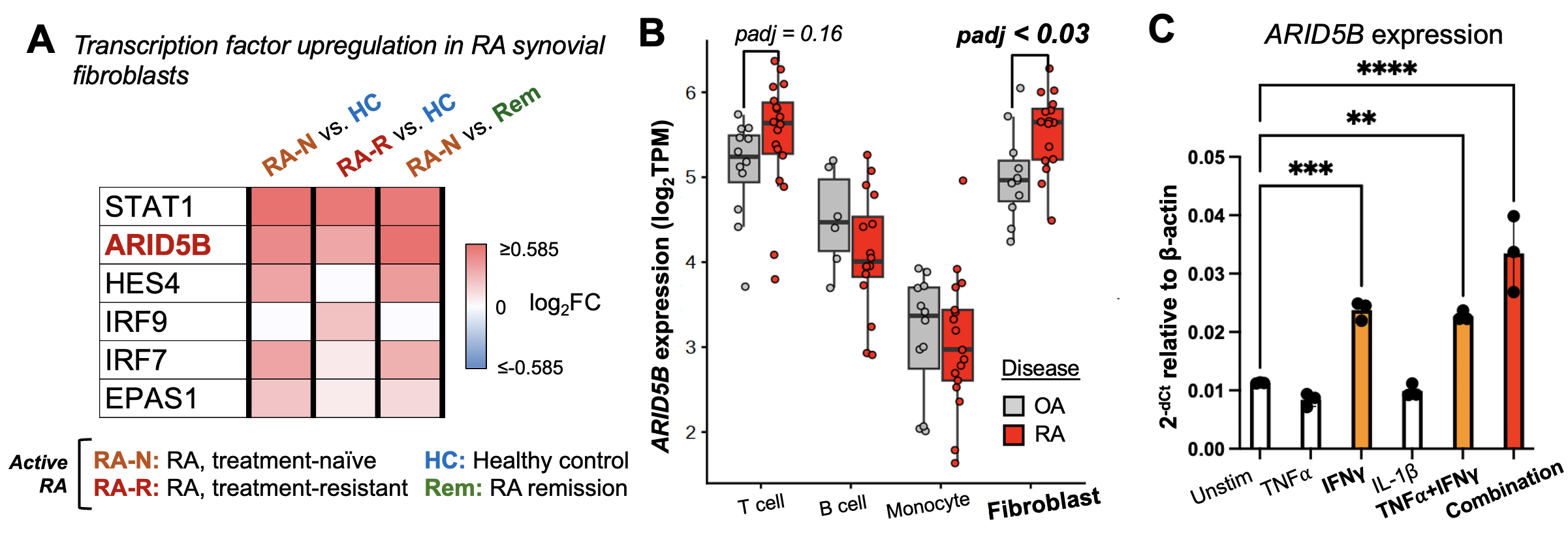
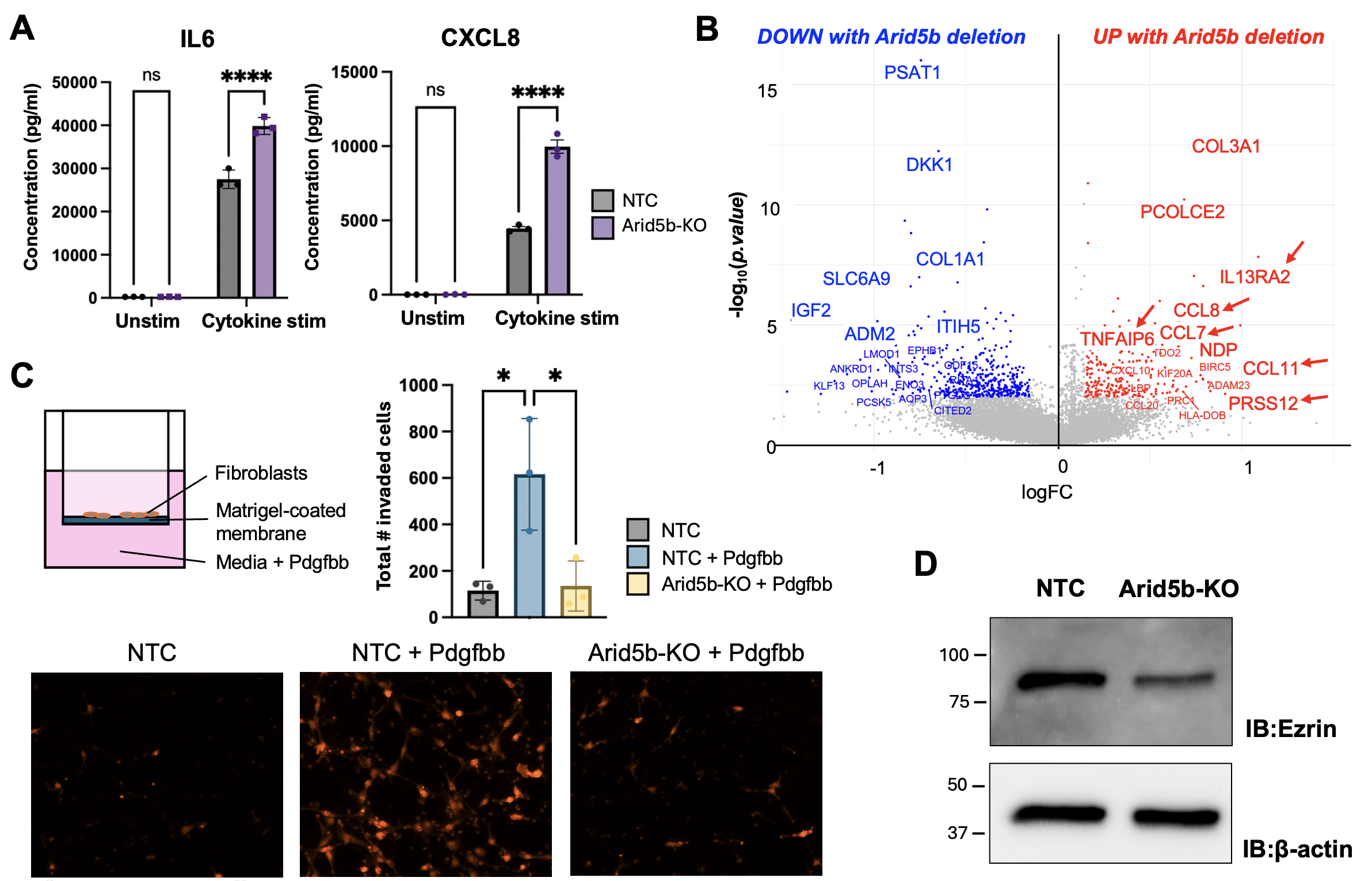
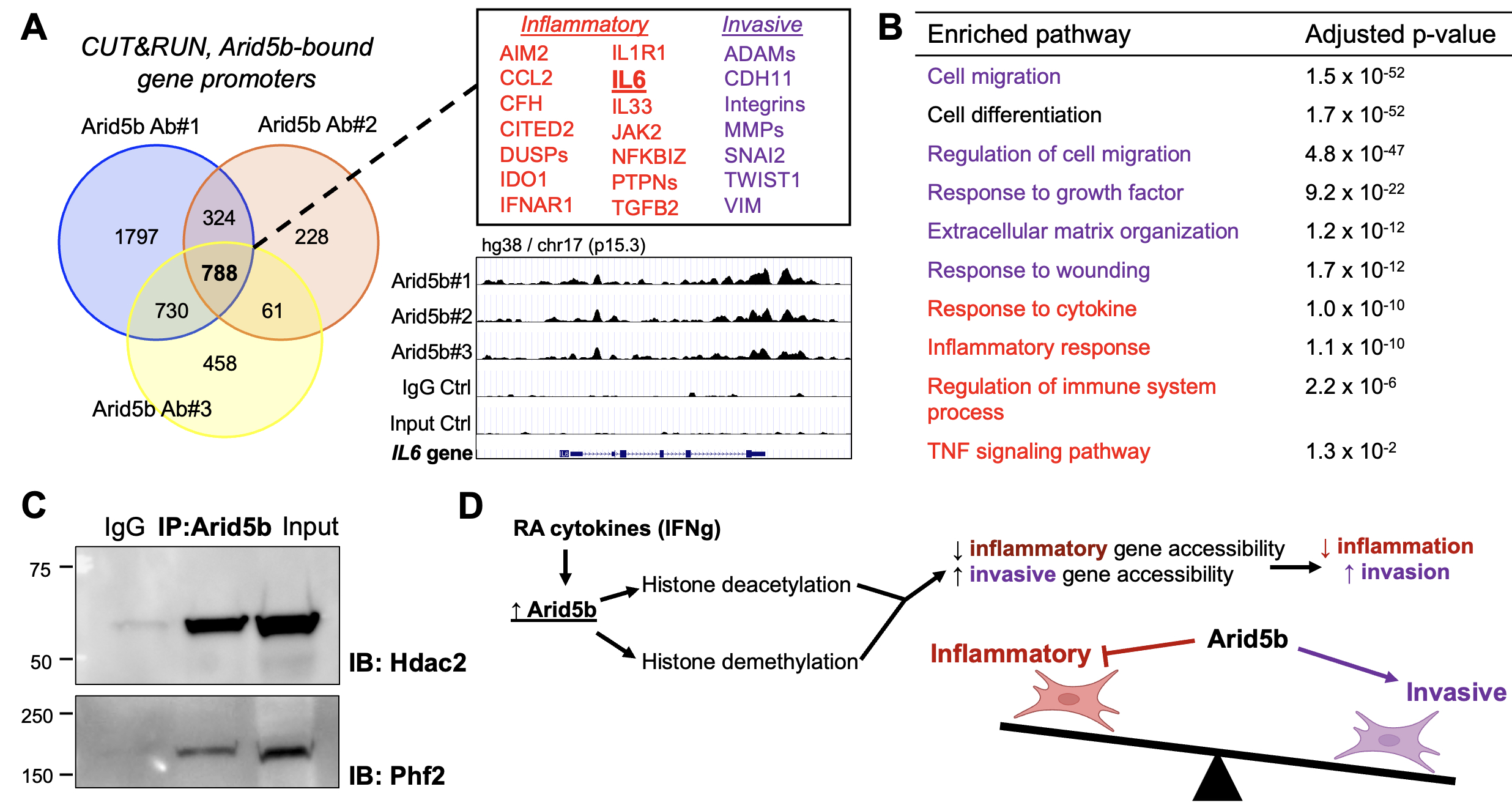
Results: Through single-cell RNA-seq analyses, we found several transcription factors (TFs) to be upregulated in synovial fibroblasts from active RA compared to healthy control or RA remission, including ARID5B (Fig 1A). While some TFs harbor known links to RA pathology via interferon (STAT1, IRFs), Notch (HES4), or hypoxia (EPAS1) pathways, ARID5B is poorly understood in fibroblasts. Moreover, through bulk RNA-seq analysis of synovial fibroblasts and leukocytes, we observed a fibroblast-specific upregulation of ARID5B in RA compared to osteoarthritis (Fig 1B). Among RA-associated cytokines, IFNγ in combination with TNFα, IL-17α, and IL-1β most bly induces ARID5B (Fig 1C). Upon Arid5b deletion, fibroblasts exhibit enhanced induction of IL6, CXCL8, and key inflammatory markers following cytokine stimulation (Fig 2A-B). Simultaneously, Arid5b deletion abrogates fibroblast invasiveness (Fig 2C) and reduces expression of Ezrin, a key actin cytoskeleton regulator and driver of cell invasion (Fig 2D). To ascertain how inflammation and invasion are reciprocally regulated by Arid5b, we identified direct target genes of Arid5b through CUT&RUN sequencing of Arid5b-bound DNA enriched via distinct antibodies. Peak enrichment analyses show that Arid5b binds both inflammatory and invasive gene loci in synovial fibroblasts (Fig 3A-B). By co-IP, Arid5b complexes with histone deacetylases (HDACs) and the Phf2 histone demethylase, suggesting that Arid5b modifies histones and chromatin accessibility at these target genes (Fig 3C-D).
Conclusion: Arid5b suppresses the fibroblast inflammatory program while activating the invasive program, thereby decoupling inflammatory and invasive fibroblast phenotypes. As Arid5b regulates histone editing, it may also serve as a mechanism for epigenetic control of fibroblast behavior. These advances may inform strategies to therapeutically reprogram pathologic fibroblast states in arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zou A, Kongthong S, Murphy C, Watts G, Mueller A, Brenner M. Arid5b Controls Pathologic Inflammatory versus Invasive Fibroblast Behavior [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/arid5b-controls-pathologic-inflammatory-versus-invasive-fibroblast-behavior/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/arid5b-controls-pathologic-inflammatory-versus-invasive-fibroblast-behavior/