Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite methotrexate (MTX) being the cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapy, uncertainty exists around who will respond to MTX. We aimed to determine the ability of clinical variables combined with serum protein biomarkers, assessed using an aptamer-based platform, to predict clinical remission and radiographic damage in treatment-naïve RA patients starting MTX.
Methods: DMARD-naïve patients with newly diagnosed RA who were starting MTX monotherapy were included. Patients were initially seen between 1998 and 2015 and followed per standard of care in two Canadian academic rheumatology clinics. Baseline demographics were recorded. Disease activity measures recorded at each visit were used to calculate Boolean response and Simple Disease Activity Index (SDAI). Annual radiographs were scored using the van der Heijde modification of Sharp Scores (vdHSS) method. Baseline sera was analyzed using the SOMAScan platform which allows assessment of 1307 proteins per sample. Outcomes assessed were clinical response defined by Boolean remission (0 active joints, normal ESR/CRP) at 12 months and clinically important progression of vdHSS (change of 4.6) at 2 years. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator classification were used to classify responders and non-responders based on clinical variables (age, sex, Rheumatoid Factor (RF)/cyclical citrullinated peptide antibody (CCP) positivity, baseline disease activity) and/or proteins. Model predictive ability was visualized by receiver operating curves and area under the curve (ROC-AUC) statistics reported. Differentially expressed proteins were analyzed using gene set enrichment analysis to identify pre-treatment biological pathway expression associated with MTX response.
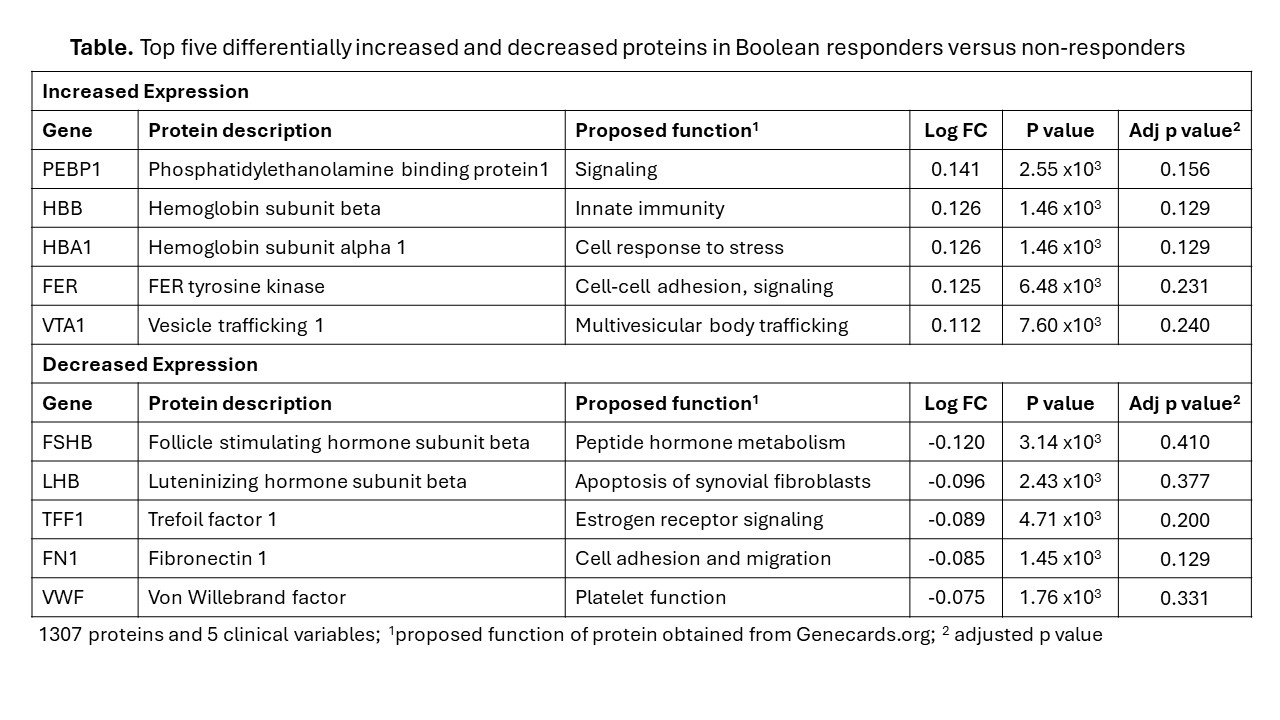
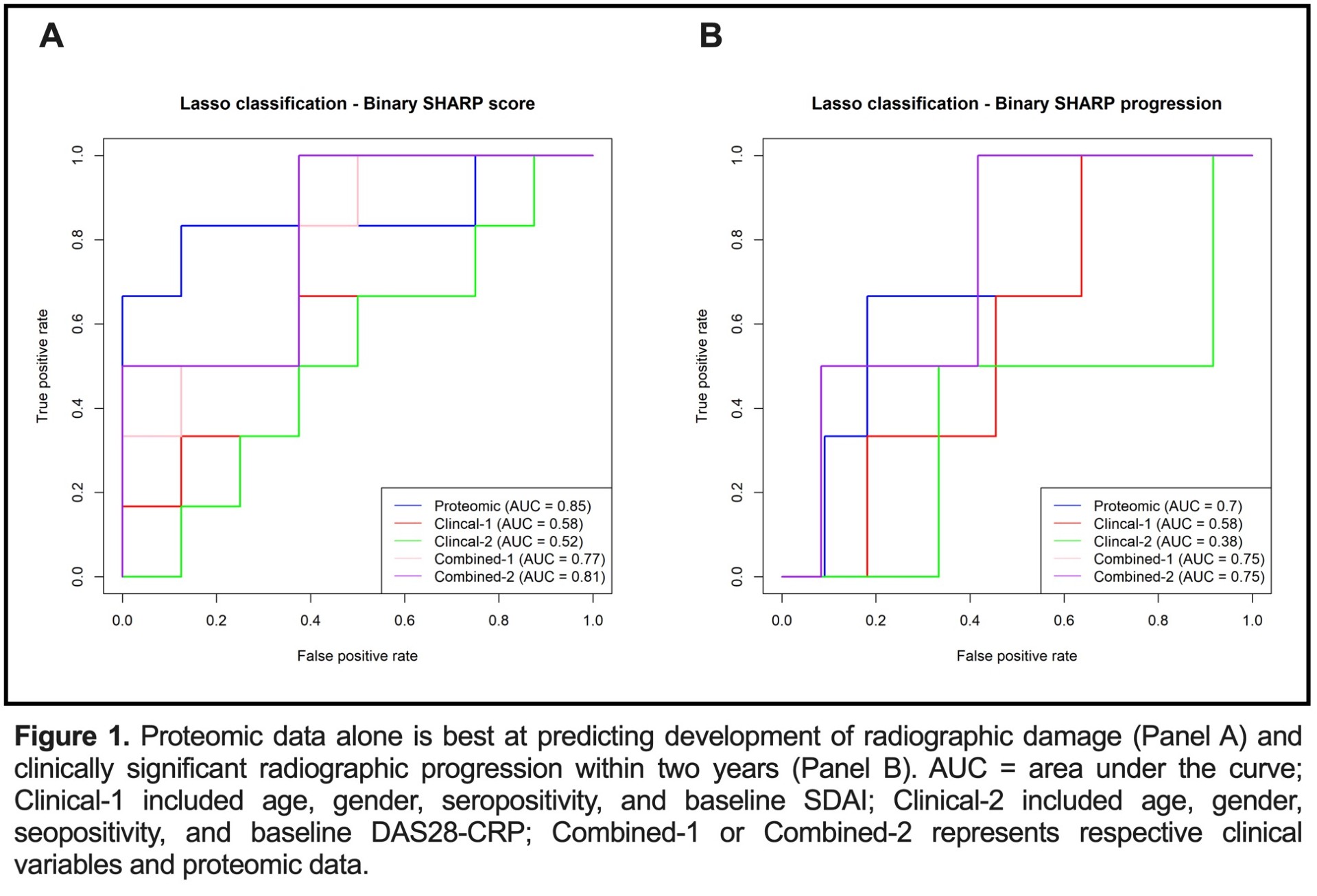
Results: We enrolled 73 patients (mean (standard deviation [sd])) baseline age 59.0 (14.7) years; 31.6% female; 53.4% seropositive for RF and/or CCP antibodies. All had high baseline disease activity [mean (sd) SDAI score 29.9 (13.5)]. Mean (sd) baseline vdHSS score was 5.7 (6.5). After two years, 46.1% of patients obtained Boolean remission and 15.1% had progressive vsHSS scores. We identified significant differences in protein profiles between Boolean responders versus non-responders (Table). Pre-treatment proteomic and clinical variables modestly predicted Boolean remission (proteomic alone AUC 0.7, clinical alone AUC 0.59, proteomic + clinical AUC 0.75). Proteomic data alone was best at predicting radiographic damage and progression (AUC 0.85; AUC 0.7) (Figure 1). Differences in protein profiles between clinical responders and non-responders corresponded with upregulation in pathways responsible for lymphocyte activation, platelet aggregation, and Fc receptor signaling in responders (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Serum protein biomarkers outperformed basic clinical measures in predicting clinical response to MTX monotherapy in newly diagnosed RA patients. Informative biomarkers contribute to upregulated biological pathways relevant to inflammation. Incorporation of protein profiles may aid prognostication and inform treatment approaches in patients with newly diagnosed RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gu K, Lac L, Carrier N, O'Neil L, Boire G, Hu P, Hitchon C. Aptamer Based Proteomic Profiling Demonstrates Significant Differences in Methotrexate Responders versus Non-responders in Newly Diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis and Adds Potential Value to Clinical Examination [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/aptamer-based-proteomic-profiling-demonstrates-significant-differences-in-methotrexate-responders-versus-non-responders-in-newly-diagnosed-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-adds-potential-value-to-clinical-exa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/aptamer-based-proteomic-profiling-demonstrates-significant-differences-in-methotrexate-responders-versus-non-responders-in-newly-diagnosed-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-adds-potential-value-to-clinical-exa/