Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Over the past years, novel biomarkers have been described in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, including autoantibodies to the protein-arginine deiminase (PAD) enzymes. Anti-PAD4 IgG are associated with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), worse baseline radiographic joint damage and a better response to treatment escalation. These data suggest that anti-PAD antibodies might play a role in RA pathogenesis. The objective of this study was to evaluate the presence of anti-PAD4 IgG and IgA in the sera of RA patients and to investigate their association with joint erosion and biological treatment use.
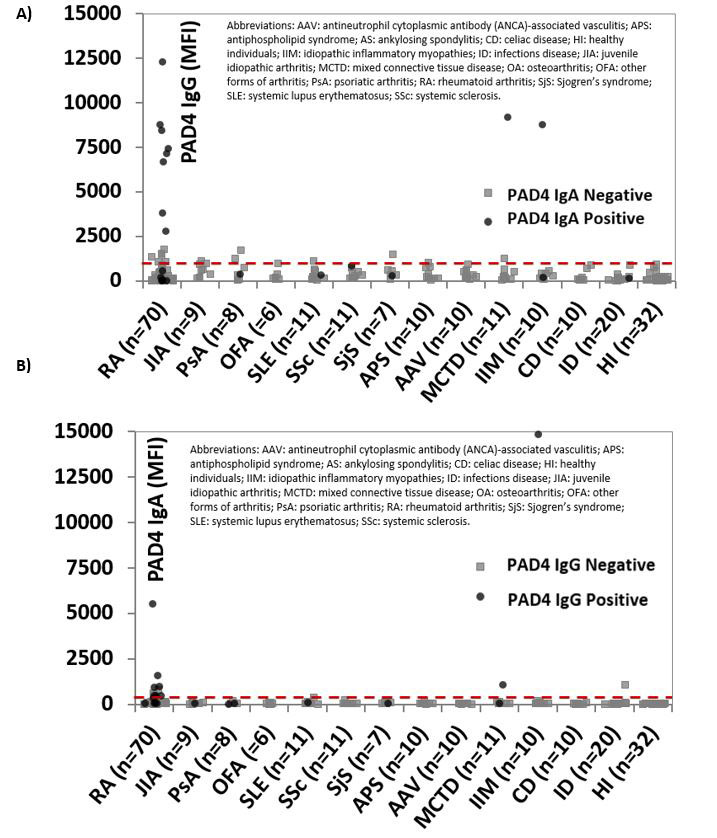
Methods: All the samples included in this study were tested for anti-PAD4 IgG and IgA using the novel particle-based multi-analyte technology (PMAT, research use only, research use only). In a first phase, sera from RA patients (n=70) and controls (n=155) were included (Figure 1). Next, anti-PAD4 IgG and IgA were measured in a second cohort of RA patients (n=40) for whom information on erosion status and biological treatment was available. ACPA IgG was also measured in these patients by QUANTA Flash CCP3 (Inova Diagnostics, CA, US).
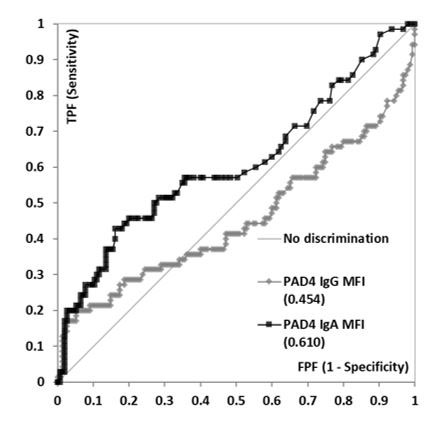
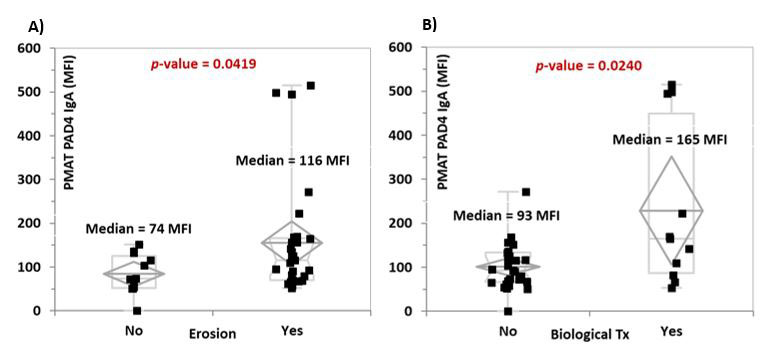
Results: Anti-PAD4 IgA but not IgG levels were significantly higher in RA patients vs. controls (p=0.0080 and p=0.2740, respectively) (Figure 1). Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis showed significant discrimination in the clinically relevant area (high specificity) for both IgG and IgA (Figure 2). Using the 95th percentile of the controls as cut-offs, anti-PAD4 IgG reported a sensitivity and specificity of 17.1%/94.8% for IgG and 20.0%/94.8% for IgA. Significantly higher levels of anti-PAD4 IgA but not anti-PAD4 IgG or ACPA were found in the RA patients with erosive disease vs. individuals without erosions (p=0.0419, p=0.2126, and p=0.7417, respectively) (Figure 3A), and in patients under biological treatment vs. those that were not on biologics (p=0.0240, p=0.1261, and p=0.8202, respectively) (Figure 3B).
Conclusion: Our study is the first to report anti-PAD4 IgA as a highly specific marker for RA showing strong association with erosive disease as well as biological treatment, suggesting a more severe phenotype. Anti-PAD4 antibodies of the IgA isotype represent a novel biomarker for RA patient stratification and prediction of prognosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martinez-Prat L, Martínez Taboada V, Lopez-Hoyos M, Mahler M. Anti-Protein-Arginine Deiminase (PAD) 4 IgA Are Present in the Sera of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Are Associated with Joint Erosion and Biological Treatment Use [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-protein-arginine-deiminase-pad-4-iga-are-present-in-the-sera-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-and-are-associated-with-joint-erosion-and-biological-treatment-use/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-protein-arginine-deiminase-pad-4-iga-are-present-in-the-sera-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-and-are-associated-with-joint-erosion-and-biological-treatment-use/