Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibody associated dermatomyositis (Anti-MDA5 DM) is known to be an aggressive disease. Earlier cohorts reported a 1-year mortality of 38%-57%, with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RPILD) as the leading cause of death within first 6 months of disease onset. While the optimal treatment strategy has not been well established, combination immunosuppressive treatment approach has been advocated. Use of Rituximab (RTX) and Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKi) have been reported to be useful. However, the strategy of initial treatment is much less well-defined. The use of initial combination of RTX, JAKi and glucocorticoids (GCS) in treatment of anti-MDA5 DM patients with ILD was assessed in this prospective cohort.
Methods: Since 1st Jan 2021, Anti-MDA5 DM patients with ILD presented to a regional hospital who were given initial combination of RTX, JAKi (tofacitinib or baricitinib) and GCS were recruited. Patient characteristics, treatments received and clinical course were prospectively collected, with follow up till 30th May 2024. Data from historical series were retrieved from database for survival comparison using log rank test and Kaplan-Meier technique. RPILD is defined as hospitalization or respiratory failure requiring oxygen supplement or ventilatory support within 3 months of respiratory symptoms onset.
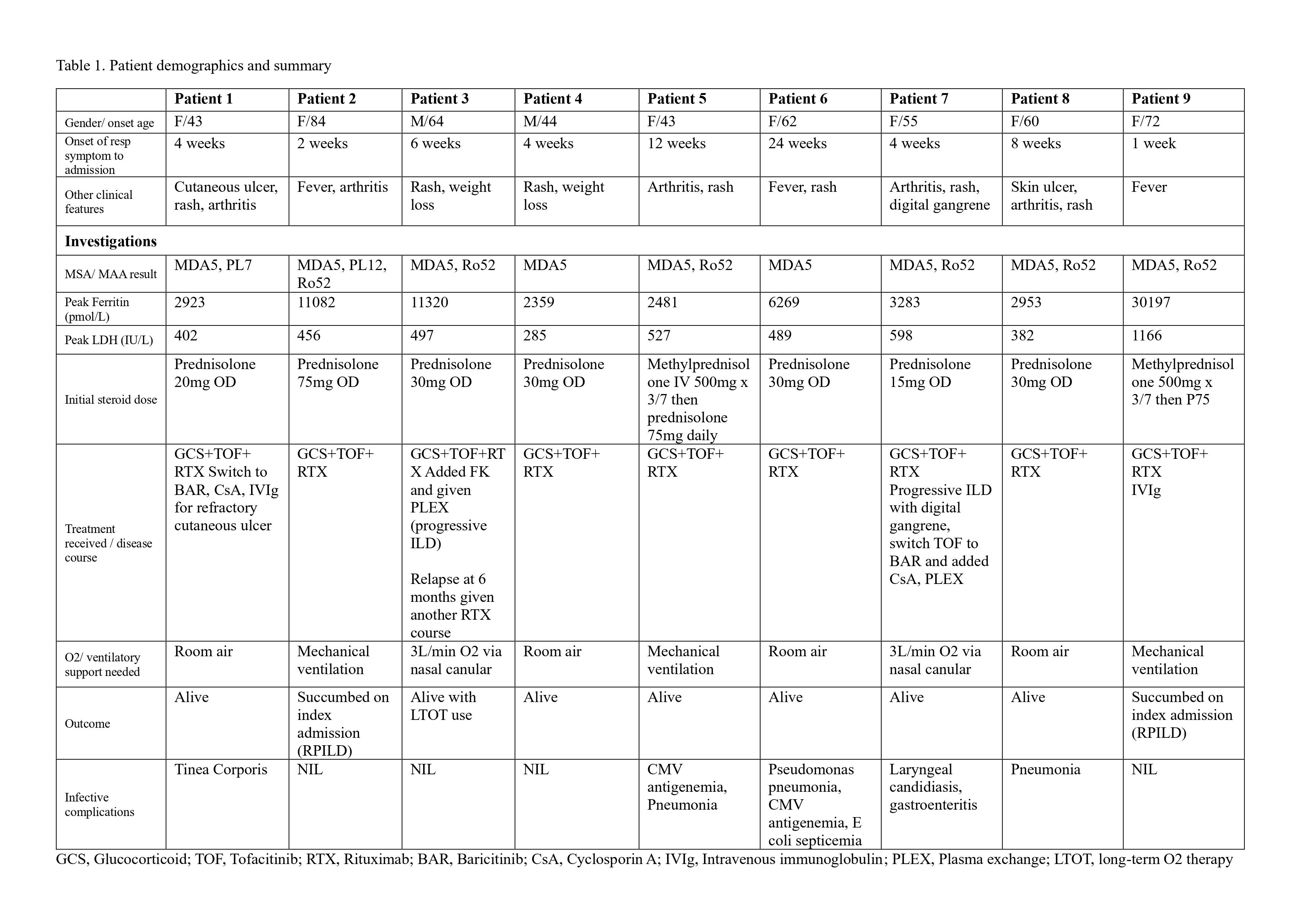
Results: Nine patients were treated with an initial combination of RTX, JAKi and GCS. Seven (78%) were female with mean age of disease onset 58.6±13.2 years, median time from onset of respiratory symptoms to hospitalization was 4 weeks (range 1-24). Eight (89%) presented with RPILD, among which 2 succumbed on index admission. The overall 1-year survival was 77.8% and duration of follow up was from 17 to 41 months for survivors. Four patients (44%) required additional therapy such as cyclosporin, intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapharesis for stabilization. Four had infective complications but none are fatal. [Table 1]
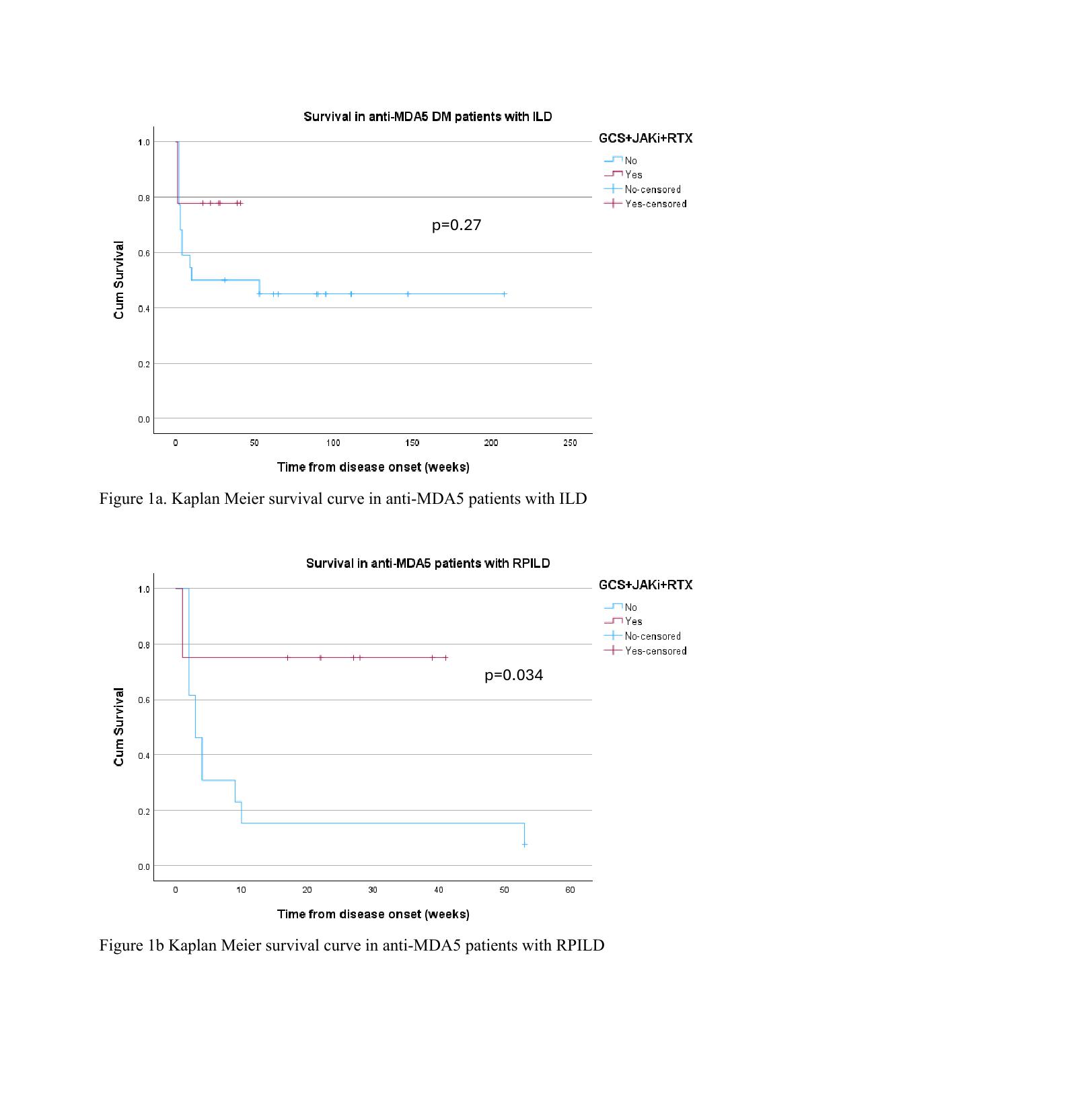
Historical series of 22 anti-MDA5 DM patients with ILD who were treated with other combination of immunosuppressants were identified (11 females; mean age 55.6±15.4years), 13 (59%) had RPILD. Overall 1-year survival was 45.5%. Comparing survival in the initial combination of RTX, JAKi and GCS with historical cohort, did not show statistical significance (log rank test p=0.270) [Figure 1a]. However, subgroup analysis of RPILD patients, demonstrated a statistical significant difference (log rank test p=0.034) with survival being 75% in combo versus 8% in historical series [Figure 1b].
Conclusion: This prospective cohort supported the use of RTX, JAKi and GCS as the initial combination therapy in anti-MDA5 DM patients with RPILD. Still, a significant portion of patients required additional treatments for disease stabilization. This reflects the complexity in managing this disease and a need for characterizing subgroups of patients that benefit from different treatment modalities. A larger size multi-centered randomized study is needed. To date, the key to patient survival remained an early diagnosis and prompt initiation of intensive therapy for disease control.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ng C, Kwok K, Ho C, Ho T, Ciang C, Leung M. Anti-MDA5 Antibody-positive Dermatomyositis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease – Survival Benefit of Treatment with Rituximab, Janus Kinase Inhibitor and Glucocorticoid Combination in a Prospective Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-mda5-antibody-positive-dermatomyositis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-survival-benefit-of-treatment-with-rituximab-janus-kinase-inhibitor-and-glucocorticoid-combination-in-a-prospective/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-mda5-antibody-positive-dermatomyositis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-survival-benefit-of-treatment-with-rituximab-janus-kinase-inhibitor-and-glucocorticoid-combination-in-a-prospective/