Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0280–0305) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a heterogeneous group of systemic autoinflammatory diseases that affect muscle tissue, often leading to muscle atrophy, weakness and myalgia. While IIM patients frequently present with myositis-specific or myositis-associated autoantibodies, less is known about the presence and function of natural anti-cytokine autoantibodies (ACAAs). Some studies report their presence in healthy individuals, suggesting a role in tissue homeostasis and regeneration, while others have found elevated levels in autoimmune diseases. The aim of this study was to measure serum levels of ACAAs directed against interleukin-6 (anti-IL-6) in IIM patients and assess their potential impact on IL-6 signalling, a pathway associated with inflammation-induced muscle wasting.
Methods: Serum samples were collected from 44 consecutive IIM patients treated at the Department of Rheumatology, University Medical Centre Ljubljana, and from 36 healthy controls (HC, Fig. 1). Patients were stratified into treatment-naive (n=13) and previously treated groups (n=31). ELISA was used to quantify serum IL-6 (BioLegend), soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R, Proteintech), and anti-IL-6 levels (in-house ELISA). To assess the functional effects of anti-IL-6 antibodies, sera were mixed with recombinant human IL-6 (rhIL-6) and applied to a reporter gene assay (RGA, SVAR Life Science) that detects IL-6 signalling pathway activity. In treatment-naive patients, the relationship between RGA activity and markers of muscle damage was evaluated.
Results: Serum IL-6 levels were significantly higher in IIM patients than in HC, while sIL-6R levels showed no significant difference. Anti-IL-6 levels tended to be lower in IIM patients, but this difference did not reach statistical significance (p=0.08). RGA activity, indicating IL-6 signalling pathway activation, was markedly higher in IIM patients (p < 0.0001) and tended to be higher in individuals with low anti-IL-6 levels (Fig. 2). To rule out interference from endogenous IL-6 present in serum samples, control experiments were performed without the addition of recombinant human IL-6 (rhIL-6), confirming that the observed increase in RGA activity was not due to endogenous IL-6. Treatment status had no significant effect on the measured parameters, although treatment-naive patients exhibited higher IL-6 and lower anti-IL-6 levels. Among these patients, those with higher RGA activity tended to have lower manual muscle test scores and higher serum creatine kinase (CK) levels (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: Sera from IIM patients showed enhanced IL-6 signalling activity, independent of the treatment status and serum IL-6, or sIL-6R levels. Based on the inverse relationship between anti-IL-6 levels and RGA activity, we hypothesise that these autoantibodies may neutralise IL-6 signalling. In treatment-naive patients, elevated RGA activity was associated with markers of muscle damage, indicating a pathological role of IL-6 signalling activity in muscle function in these patients.
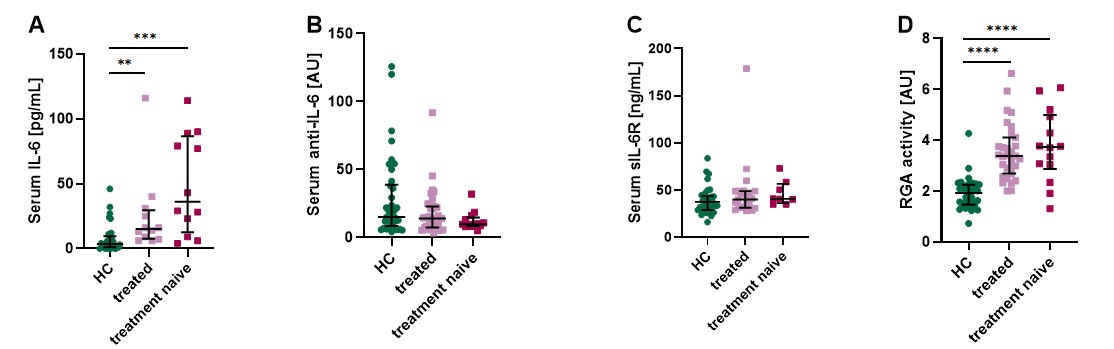 Figure 1: Number of IIM patients included in the study.
Figure 1: Number of IIM patients included in the study.
.jpg) Figure 2: Serum levels of IL-6 (Fig. 2A), anti-IL-6 autoantibodies (Fig. 2B), soluble IL-6 receptor (Fig. 2C) and serum RGA activity (Fig. 2D) in treatment-naive or treated IIM patients and healthy controls. Kruskal-Wallis test: ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
Figure 2: Serum levels of IL-6 (Fig. 2A), anti-IL-6 autoantibodies (Fig. 2B), soluble IL-6 receptor (Fig. 2C) and serum RGA activity (Fig. 2D) in treatment-naive or treated IIM patients and healthy controls. Kruskal-Wallis test: ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
.jpg) Figure 3: Correlation of RGA activity with anti-IL-6 autoantibodies in serum of treatment-naive or treated patients and healthy controls (Fig. 3A). Correlation of serum creatine kinase levels (Fig. 3B) and manual muscle testing score (Fig. 3c) with RGA activity in treatment-naive patients.
Figure 3: Correlation of RGA activity with anti-IL-6 autoantibodies in serum of treatment-naive or treated patients and healthy controls (Fig. 3A). Correlation of serum creatine kinase levels (Fig. 3B) and manual muscle testing score (Fig. 3c) with RGA activity in treatment-naive patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Srpcic A, Ogric M, Cucnik S, Pirkmajer S, Lakota K, Perdan Pirkmajer K. Anti-IL-6 Autoantibodies and IL-6 Signalling in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-il-6-autoantibodies-and-il-6-signalling-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-il-6-autoantibodies-and-il-6-signalling-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/
