Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The production of antibodies to modified self-antigens is a hallmark in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Antibodies to citrullinated (ACPAs) and carbamylated proteins (CarP) are of special interest due to their high prevalence and emergence during preclinical RA. While citrullination and carbamylation generate nearly identical amino acid residues (citrulline and homocitrulline, respectively), these modifications differ significantly in biology. Arginine citrullination is a physiological process toward which immune tolerance is developed, while lysine carbamylation is environmentally driven (e.g., tobacco smoking) and thus immunogenic. How ACPAs and anti-CarP antibodies are related is unclear, but recognizing the inciting event in the production of these antibodies may shed light on the origins of RA.
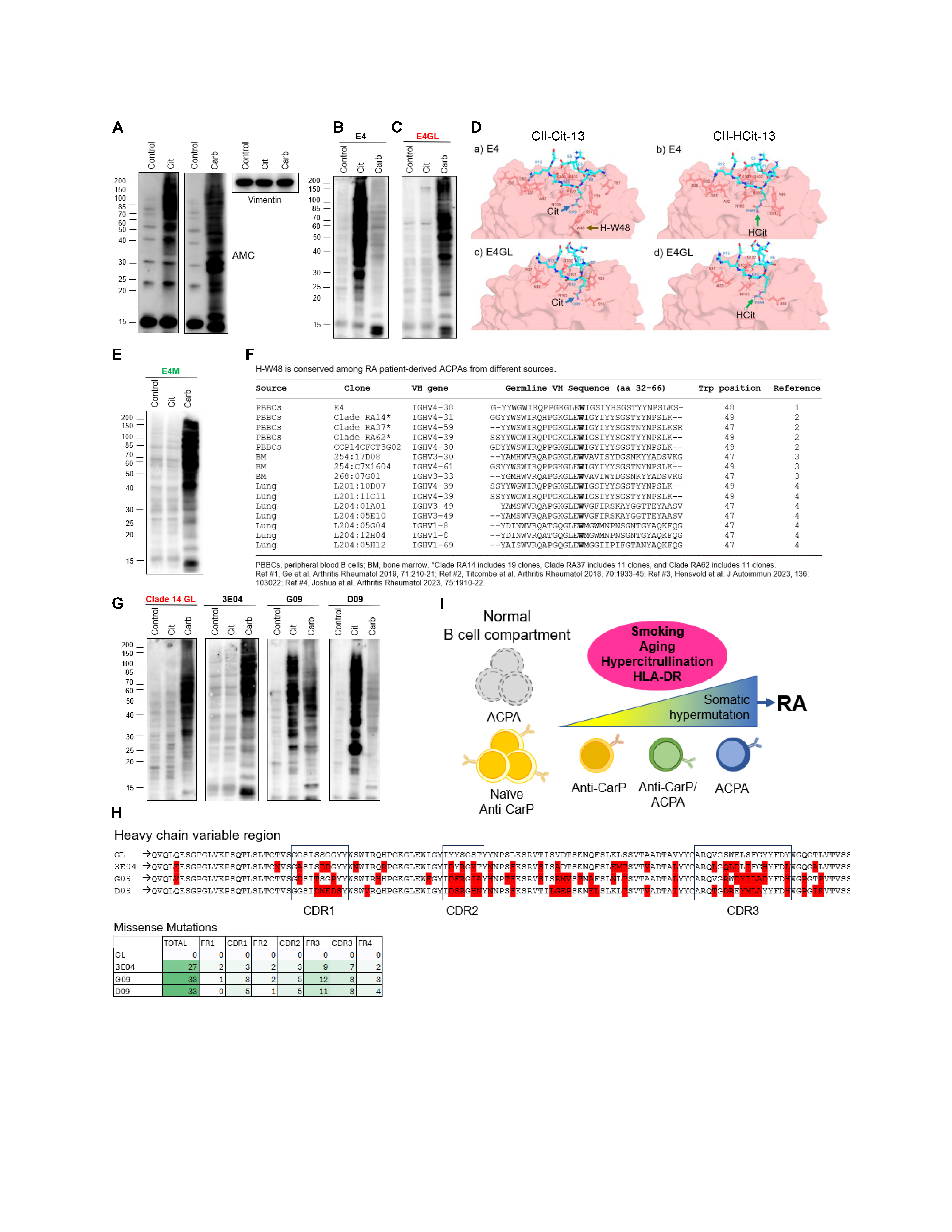
Methods: RA patient-derived monoclonal ACPAs were cloned from published sequences1,2, reverted to their germline (GL) form, or mutated to change the heavy chain tryptophan residue 48 (H-W48) to methionine, and expressed in ExpiCHO cells. Control, citrullinated or carbamylated 293T cells (Fig. A) were used to test antibody reactivity to modified cellular substrates by immunoblotting. The structure of one ACPA (both original and GL sequences) bound to a citrullinated or carbamylated peptide was determined using a starting structure (crystal1 or AlphaFold2-predicted), and the Rosetta MutateResidue and FlexPepDock Protocols.
Results: E4 is an RA-derived ACPA that has been extensively studied1. Compared to control and carbamylated cells, E4 showed prominent binding to hypercitrullinated cells (Fig. B), demonstrating that citrullinated proteins are the major target of E4. When E4 was reverted to its germline form (E4GL), citrullination was no longer detected (Fig. C), indicating that reactivity to citrullinated proteins by E4 is acquired via affinity maturation. Unexpectedly, while E4 had poor recognition for CarP (Fig. B), E4GL showed prominent binding to CarP (Fig. C), implying that CarP is a primary target of E4GL. Structural analysis of E4 vs. E4GL pointed to H-W48 as a critical residue in the differential recognition of citrulline vs. homocitrulline (Fig. D). Indeed, a single change of H-W48 to methionine in E4 (E4M) shifted the antibody specificity from ACPA to anti-CarP (Fig. E). Notably, H-W48 in E4 is GL-encoded and highly conserved (either as W47 or W49) among different published ACPAs (Fig. F). Further analysis of a set of ACPAs derived from a common precursor confirmed that the GL form is specific for CarP and that the antibody transitions from anti-CarP to double positive (CarP/ACPA) to ACPA according to the pattern and number of somatic hypermutations (Fig. G, H), explaining their coexistence and diverse specificity in RA.
Conclusion: The presence of GL-encoded antibodies to CarP is explained because CarP is environmentally driven and thereby absent during B cell development. The data indicate that GL anti-CarP antibodies are the first step in the production of autoantibodies (both anti-CarP and ACPAs, via antigen-driven affinity maturation) during the development of RA (Fig. I).
References
1. Ge et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019, 71:210-21
2. Titcombe et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018, 70:1933-45
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Escarra-Senmarti M, Chungyoun M, Ferris D, Gray J, Andrade F. Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies Arise During Affinity Maturation of Germline-Encoded Antibodies to Carbamylated Proteins in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-citrullinated-protein-antibodies-arise-during-affinity-maturation-of-germline-encoded-antibodies-to-carbamylated-proteins-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-citrullinated-protein-antibodies-arise-during-affinity-maturation-of-germline-encoded-antibodies-to-carbamylated-proteins-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/