Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Cardiovascular Pulmonary Disease (0268–0295)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with an increase in cardiovascular (CV) risk, attributed, among other factors, to the existence of an abnormal lipid profile. The axis made up of angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4), apolipoprotein C3 (ApoC3) and lipoprotein lipase (LPL) has been associated with cardiovascular mortality in healthy population. However, this axis has not been yet characterized in patients with RA. The objective of this study was to evaluate whether there are differences between RA patients and controls in the serum levels of the molecules of this axis, and to analyze their relationship with the activity of the disease or the markers of systemic inflammation as well as with the subclinical atheromatosis that is present in the disease.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional study that encompassed 569 individuals; 323 patients with RA and 246 controls. Full lipid profile was assessed including serum levels of ANGPTL4, apoC3 and LPL. Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) and carotid plaques were assessed in patients. A multivariable analysis, adjusted for standard CV risk factors, was performed to evaluate if there were differences in this axis between patients and controls, and to study the relationship of this axis with data associated with the disease and the presence of subclinical atheromatosis.
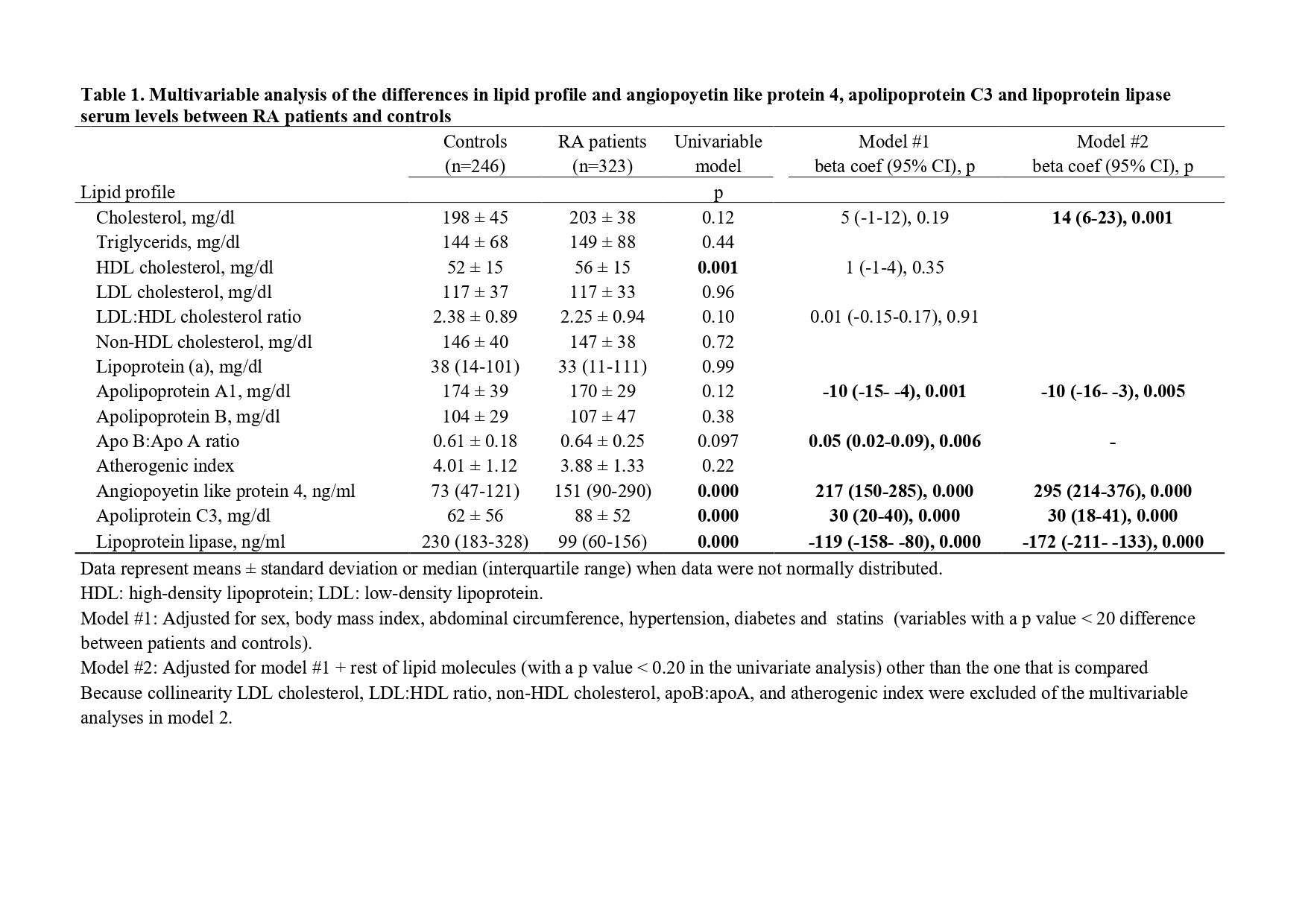
Results: After multivariable analysis, adjusted for CV risk factors and for the changes that the disease produces itself over other lipid profile molecules, patients with RA showed higher levels of ANGPTL4 (beta coef. 295 [95% CI 214-376] ng/ml, p=0.000) and ApoC3 (beta coef. 30 [CI95% 18-41] mg / dl, p=0.000), but lower circulating LPL (beta coef. -172 [CI95% -211-133] ng/ml, p=0.000).
Regarding the data related to the disease, an association was found between ESR and ANGPTL4 (beta coef. -3 [CI95% -6–1] ng/ml, p = 0.02), and C-reactive protein and apoC3 (beta coeff. 0.53 [IC95% 0.12-0.95] mg/dl, p=0.01). Likewise, ESR was positively associated with LPL levels (beta coef. 1 [95% CI 0-3] ng/ml, p=0.03). An association was also found between the use of certain treatments and higher serum levels of LPL (hydroxychloroquine, beta coef. 116 [95% CI 30-202] ng/ml, p=0.008; salazopyrin, beta coef. 143 [95% CI 41 -245] ng/ml, p=0.006 and anti-TNF therapy, beta coefficient 101 [95% CI 33-169] ng / ml, p=0.004).
The ANGPTL4-Apoc3-LPL axis did not show a relationship with the presence of carotid plaque in patients with RA. However, while ApoC3 and LPL levels were not associated with cIMT, ANGPTL4 serum levels showed a positive association with it after multivariate analysis (beta coef. 0.06 [95% CI 0.02-0.09] microns, p=0.000).
Conclusion: RA patients have an abnormal ANGPTL4-Apoc3-LPL axis compared to controls. Certain characteristics of the disease related to inflammation justify this alteration. ANGPTL4 serum levels show an independent and significant positive relationship with IMT in patients with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Quevedo j, de Armás-Rillo L, de Vera-González A, Cáceres L, Almeida C, González-Delgado A, Ferraz-Amaro I. Angiopoietin-Like Protein 4, Apolipoprotein C3 and Lipoprotein Lipase Axis in the Abnormal Lipid Profile of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Relation to Subclinical Atheromatosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/angiopoietin-like-protein-4-apolipoprotein-c3-and-lipoprotein-lipase-axis-in-the-abnormal-lipid-profile-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-relation-to-subclinical-atheromatosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/angiopoietin-like-protein-4-apolipoprotein-c3-and-lipoprotein-lipase-axis-in-the-abnormal-lipid-profile-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-relation-to-subclinical-atheromatosis/