Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RORγt+Foxp3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells, designated as Tr17 is one of the new subset of Treg cells, having the potential to regulate the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) thorough a specific repression of Th17 mediated inflammation. The function of Tr17 remain unclear in the development of other autoimmune diseases such as collagen induced arthritis (CIA)./To clarify the role of RORγt+Foxp3+ Tr17 in the development CIA.
Methods: 1) Lymphocytes in draining lymph node were harvested from C57BL/6 mice on 10 days after immunization of type II collagen (CII) emulsified with complete Freund’s adjuvant. The expression of RORγt in Foxp3+Treg cells was analyzed by flow cytometry and compared them with lymphocytes of non-immunized mice. 2) At 10 days after CII immunization, C-C chemokine receptor type 6 (CCR6), CD25, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4), and Glucocorticoid-induced TNF-receptor (GITR) expression on Tr17, RORγt–Treg cells, and RORγt+ T cells (Th17) in lymph node were analyzed by flow cytometry. 3) Lymphocytes in draining lymph node were harvested from Foxp3IRES-gfp reporter mice on 10 days after first CII immunization. CD4+GFP+ Treg and CD4+GFP– T cells were isolated and stimulated with PMA and Ionomycin in vitro. The expression of IL-10 and IL-17 in RORγt+GFP+ Tr17 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry and compared with that in RORγt–GFP+ cells or RORγt+GFP– cells. 4) After the induction of CIA, lymphocytes in inflamed ankle joints and draining lymph node were harvested from Foxp3IRES-gfp reporter mice. The expression of CCR6, CD25, and CTLA-4 were analyzed in RORγt+GFP+ cells, RORγt–GFP+ cells or RORγt+GFP– cells by flow cytometry.
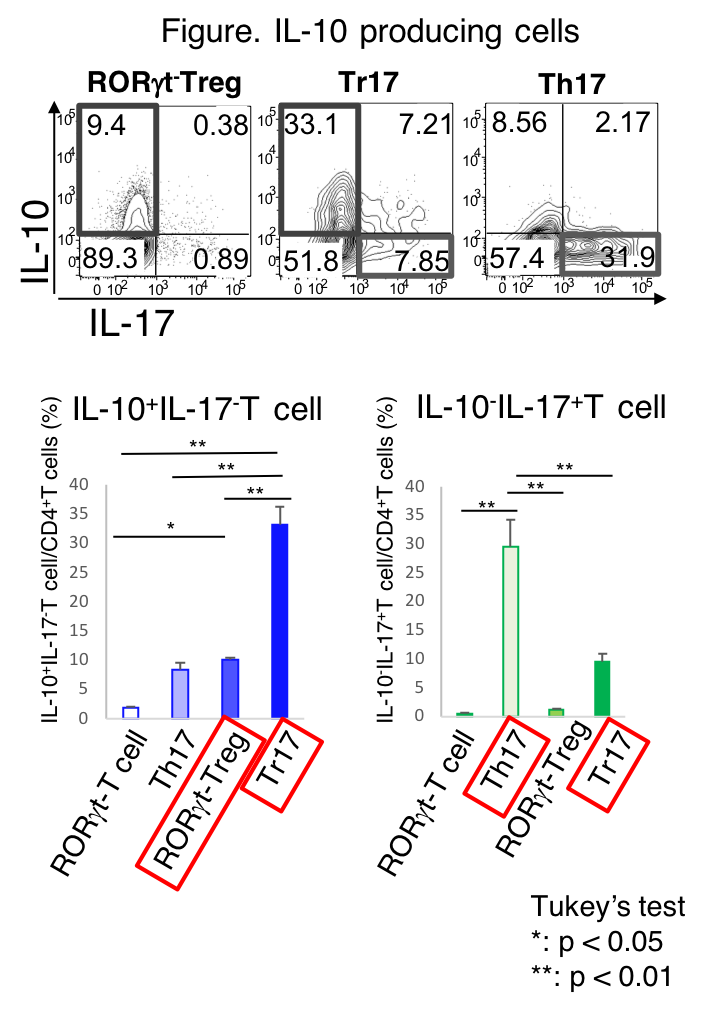
Results: 1) RORγt+Foxp3+ Tr17 cells in draining lymph nodes were significantly increased in CII-immunized mice compared with non-immunized mice. 2) CCR6 and CD25 expression was elevated on Tr17 cells compared with RORγt–Treg cells and Th17 cells and CTLA-4 and GITR expression was also up-regulated on Tr17 cells compared with RORγt–Treg cells. 3) IL-10 producing cells were increased in Tr17 cells compared with RORγt–Treg cells (33.2 +/- 2.95, p < 0.001). On the other hand, IL-17 producing cells were decreased in Tr17 cells in spite of the high expression of RORγt compared with RORγt+Th17 cells (9.57 +/- 1.25, p = 0.002) (Figure). 4) CCR6+Treg cells were increased in inflamed ankle joints compared with draining lymph node after the induction of CIA. CD25 expression was elevated on joint infiltrating CCR6+Treg cells compare with CCR6–Treg cells. There was no difference of CTLA-4 expression between CCR6+ and CCR6–Treg cells in inflamed joints.
Conclusion: Tr17 cells were increased in the course of CIA and might preferentially infiltrated into inflamed joints. Moreover, Tr17 cells had the potential to regulate the development of CIA thorough the high expression of suppressive molecules such as IL-10 and CTLA-4 in inflamed joints.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furuyama K, Kondo Y, Shimizu M, Akira I, Yokosawa M, Segawa S, Tsuboi H, Matsumoto I, Sumida T. Analysis of the Role of RORγt+Foxp3+ T Regulatory 17 (Tr17) Cells in Murine Autoimmune Arthritis Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-the-role-of-ror%ce%b3tfoxp3-t-regulatory-17-tr17-cells-in-murine-autoimmune-arthritis-model/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-the-role-of-ror%ce%b3tfoxp3-t-regulatory-17-tr17-cells-in-murine-autoimmune-arthritis-model/