Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Conventional radiography of the sacroiliac joints is the first imaging method if axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is suspected. The presence of definite radiographic sacroiliitis is needed to classify as radiographic (r-axSpA) based on the modified New York Criteria (mNYc). However, the reliability of radiographic sacroiliitis assessment is low, especially if performed locally. Expert central reading for classification purposes in clinical trials is time-consuming and still has high inter-reader variability.
A possible solution to detect radiographic sacroiliitis with consistent reproducibility, could be the use of an artificial intelligence analysis of radiographs. Recently an artificial neural network showed an expert-level performance for classification and diagnostic settings1,2.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of this previously trained artificial network in a completely new cohort of patients previously evaluated as r-axSpA or nr-axSpA by central readers.
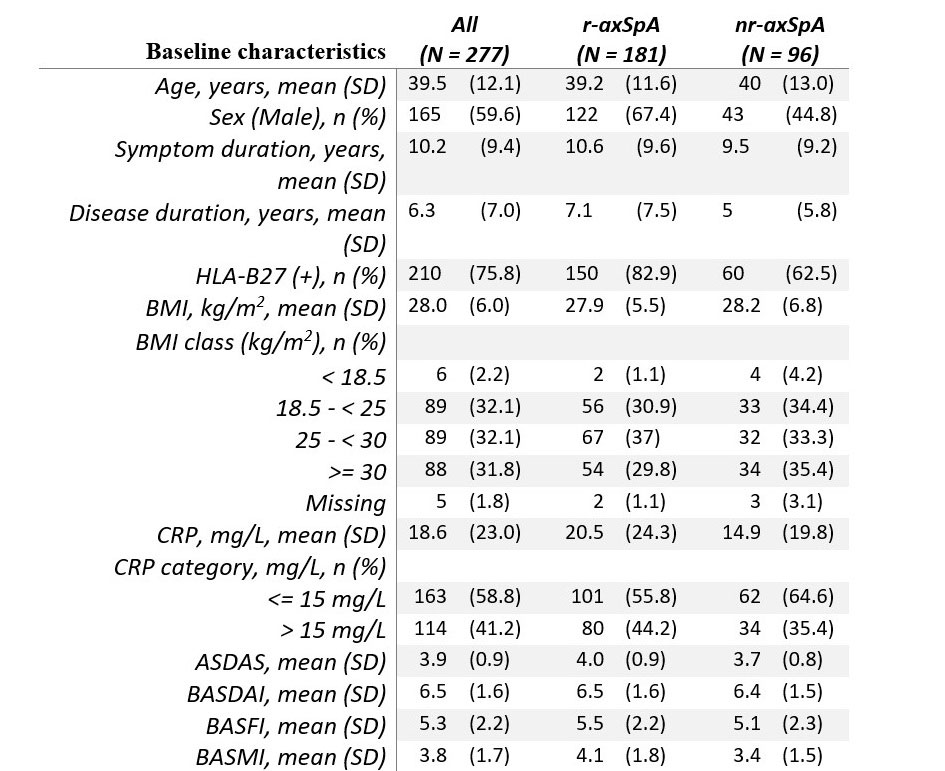
Methods: Baseline radiographs of sacroiliac joints from RAPID-axSpA (NCT01087762, N=277) were evaluated by 3 central reader experts and the majority decision of fulfillment the mNYc was used as a reference. None of the patients nor any of the central readers participated in the studies used to pre-train the artificial network.
For performance evaluation of the neural network, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was calculated. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) for the prediction cut-offs were calculated along with their 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) using accelerated bootstrapping. Cohen’s Kappa and the absolute agreement were used to assess the agreement between the neural network and the human readers.
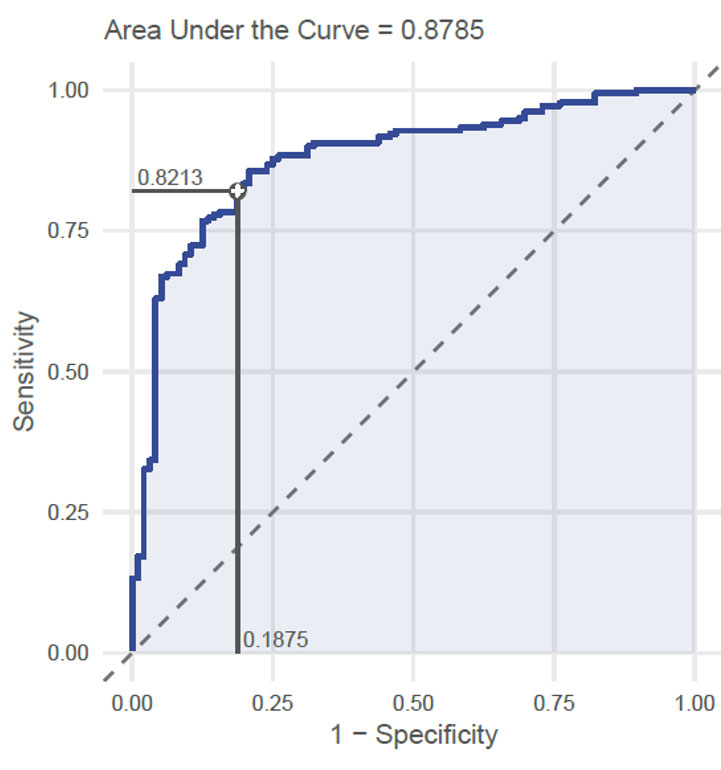
Results: Baseline characteristics are presented in table 1. Sensitivity and specificity for the cut-off weighting both measurements were 0.82 (95% CI: 0.78, 0.86) and 0.81 (95% CI: 0.75, 0.87). The Cohen’s kappa between the neural network and the reference judgements was 0.61 (95% CI: 0.51, 0.70), and the absolute agreement on the classification yielded 82% (95% CI: 0.78, 0.85). The neural network achieved an 0.89 (95% CI: 0.86, 0.93) PPV and a 0.70 (95% CI: 0.64, 0.77) NPV in recognition of definite radiographic sacroiliitis with AUROC of 0.88 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: A pre-trained artificial neural network can enable the accurate detection of definite radiographic sacroiliitis relevant for the diagnosis and classification of axSpA close to expert performance. In the present study, the previously trained network showed an excellent ability to generalize data that was completely new to the network. Our results show the potential for classification purposes in multi-center axSpA trials in the future, providing a reproducible and cost-effective tool without unnecessary time delays.
Evaluating Performance of the Neural Network to Detect Radiographic Sacroiliitis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Proft F, Vahldiek J, Nicolaes J, Tham R, Hoepken B, Ufuktepe B, Poddubnyy D, Bressem K. Analysis of the Performance of an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for the Detection of Radiographic Sacroiliitis in an Independent Cohort of axSpA Patients Including Both Nr-axSpA and r-axSpA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-the-performance-of-an-artificial-intelligence-algorithm-for-the-detection-of-radiographic-sacroiliitis-in-an-independent-cohort-of-axspa-patients-including-both-nr-axspa-and-r-axspa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-the-performance-of-an-artificial-intelligence-algorithm-for-the-detection-of-radiographic-sacroiliitis-in-an-independent-cohort-of-axspa-patients-including-both-nr-axspa-and-r-axspa/