Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Despite several effective targeted therapies, biomarkers that predict whether a patient with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) will respond to a particular treatment are currently lacking.
Methods: We analysed proteomics data from serum samples of nearly two thousand PsA patients in placebo-controlled phase-III clinical trials of the IL-17A blocking mAb secukinumab, using the SomaScan platform. To discover predictive biomarkers of clinical response, we used statistical learning with controlled feature selection. The top candidate was validated using an ELISA and was separately assessed in a trial of almost eight hundred PsA patients treated with the anti-IL-17A mAb secukinumab or a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi).
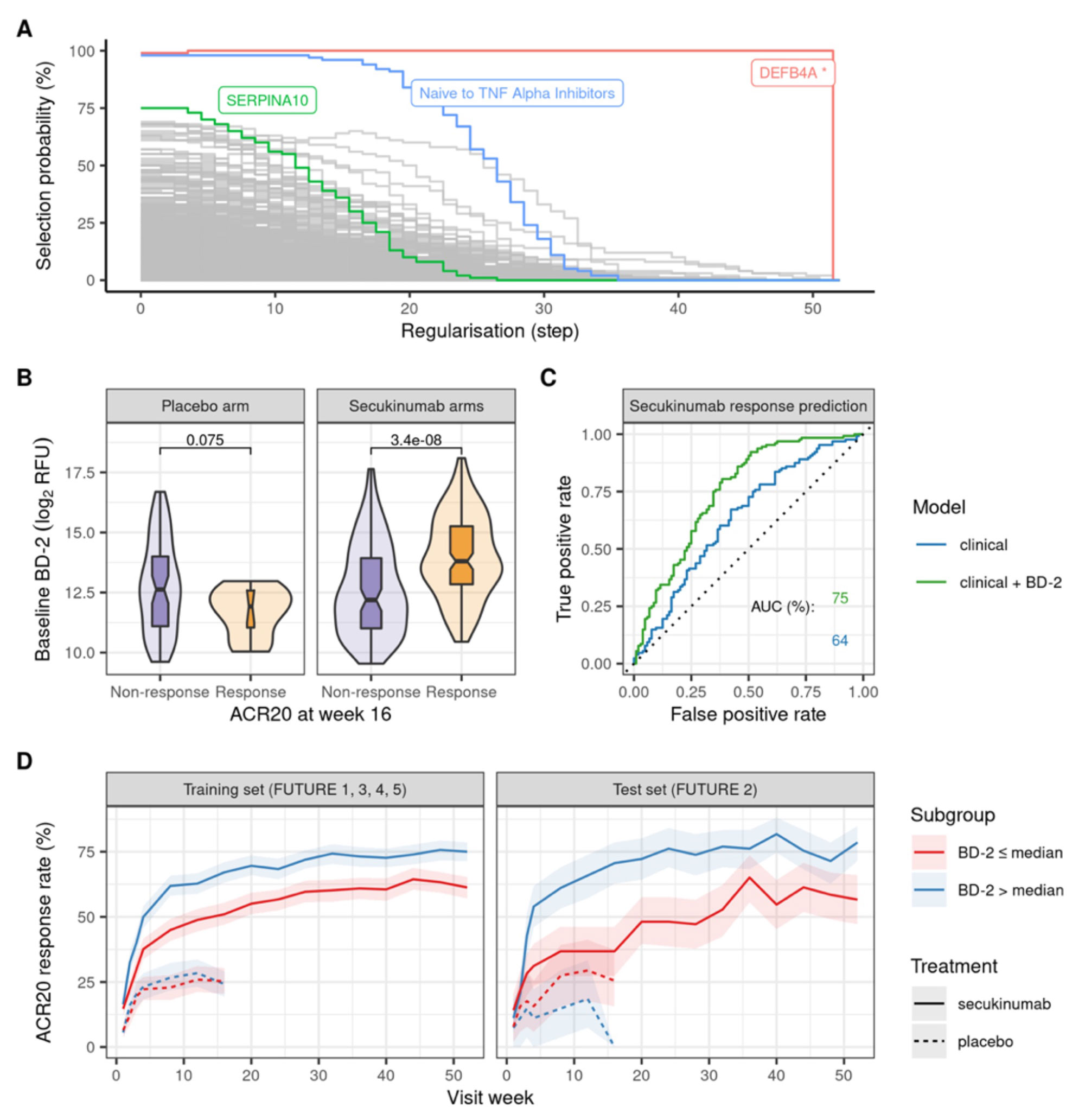
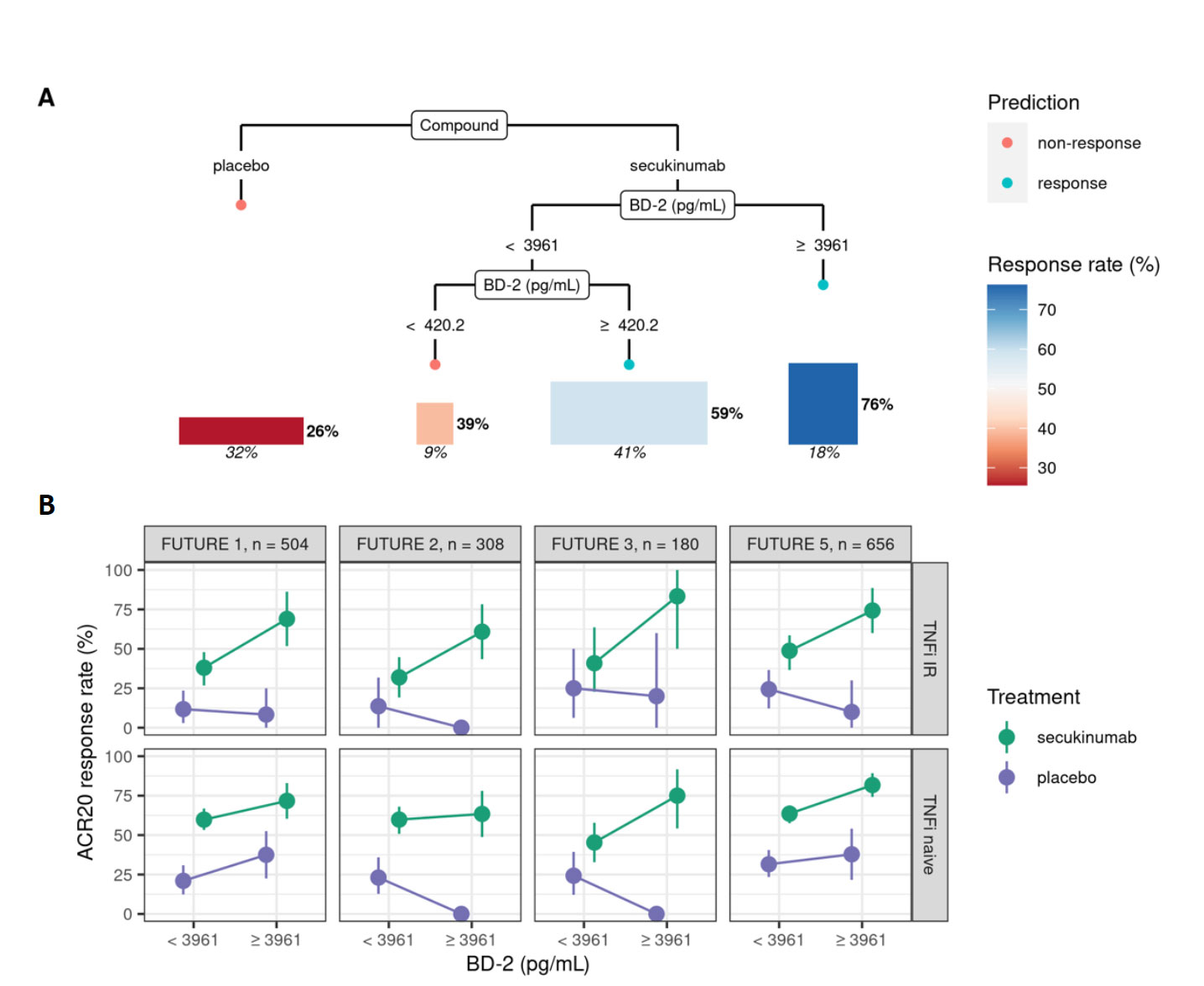
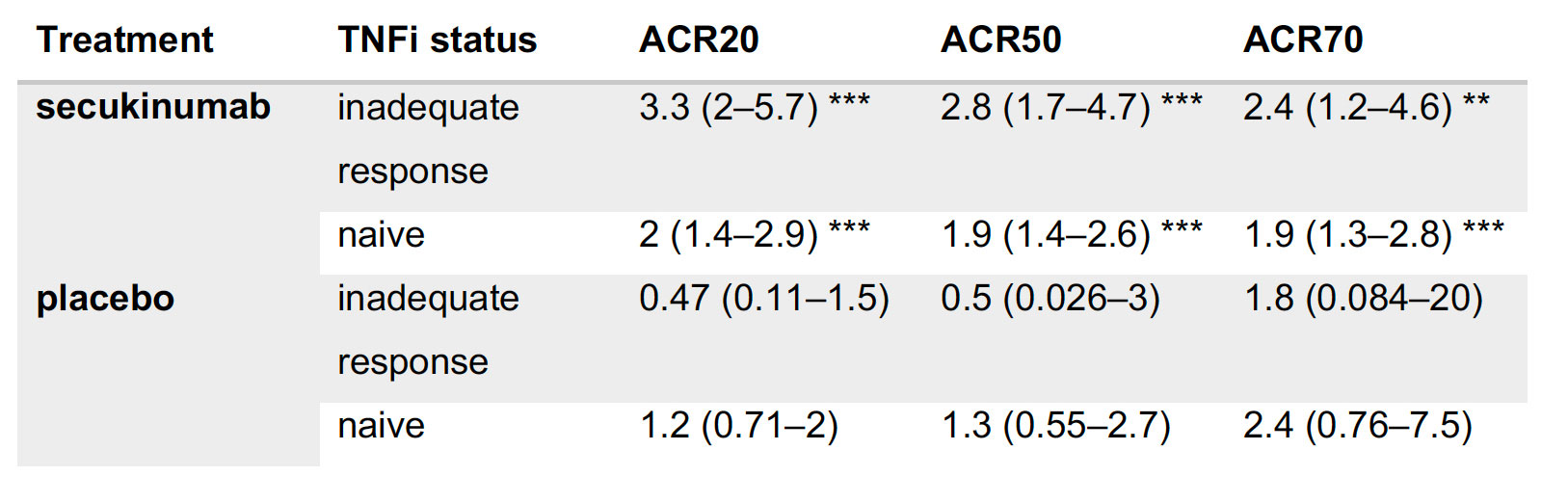
Results: A statistical learning model trained on the FUTURE 1, 3, 4, and 5 studies of secukinumab in PsA (n=1626) identified serum levels of the anti-microbial peptide beta-defensin 2 (BD-2) at baseline as the only serum protein predictive of ACR20 response to secukinumab but not placebo. SERPINA10 was prognostic of ACR20 but not predictive of response to sekukinumab. Baseline BD-2, but not SERPINA10, was validated in an independent test data set from the FUTURE 2 trial (Figure 1B) adding 11 percentage points to the predictive performance (ROC AUC) of a logistic regression model based on clinical predictors (Fig 1C). Although BD-2 is known to be associated with psoriasis severity, the predictivity of BD-2 was independent of baseline PASI. The association between BD-2 and ACR20 response to secukinumab was observed as early as 4 weeks and maintained up to 52 weeks (Fig 1D). Validation and quantification of BD-2 by ELISA allowed modelling a classification tree showing that baseline BD-2 is the most important factor in predicting response, and that the subset of patients with higher levels of BD-2 at baseline are highly enriched for responders to secukinumab (76%, Fig 2A). BD-2 prediction of response was enhanced in TNF-IR patients (Fig 2B), and also significantly predictive of ACR50 and 70 responses (Table 1). Analysis of samples from the EXCEED trial which compared adalimumab to sekukinumab treatment in PsA showed that BD-2 was also predictive of response to treatment with a TNFi, though this was not sustained longitudinally as it was for secukinumab. Analysis across three treatment trials showed that BD-2 levels were not significantly predictive of response to secukinumab in RA.
Conclusion: BD-2 is a novel, PsA-specific predictive biomarker of clinical arthritis response to secukinumab. Patients with high levels of BD-2 at baseline reach and sustain higher rates of clinical response after treatment with secukinumab.
Abbreviations: relative fluorescence unit (RFU), receiver operating characteristic (ROC), area under the curve (AUC).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cardner M, Tuckwell D, Kostikova A, Forrer P, Siegel R, Marti A, Vandemeulebroecke M, Ferrero E. Analysis of Serum Proteomics Data Identifies Beta-Defensin 2 as a Predictive Biomarker of Clinical Response to IL-17 Blockade in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-serum-proteomics-data-identifies-beta-defensin-2-as-a-predictive-biomarker-of-clinical-response-to-il-17-blockade-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-serum-proteomics-data-identifies-beta-defensin-2-as-a-predictive-biomarker-of-clinical-response-to-il-17-blockade-in-psoriatic-arthritis/