Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder related to disability and premature mortality. Nowadays, the burden of RA is needed for healthcare planning, resource allocation, and prevention. Considering the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2019, we analyze updated estimates of the prevalence of RA and its associated disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) and mortality by age, sex, year, and location, with forecasted prevalence to 2040.
Methods: We analyzed the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and burden of suffering of RA based on epidemiological data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) current dataset from the Institute of Health Metrics, Seattle. National trends from 1990 to 2019 of RA for all ages were compiled. Forecast estimates were obtained using the SPSS Time Series Modeler.
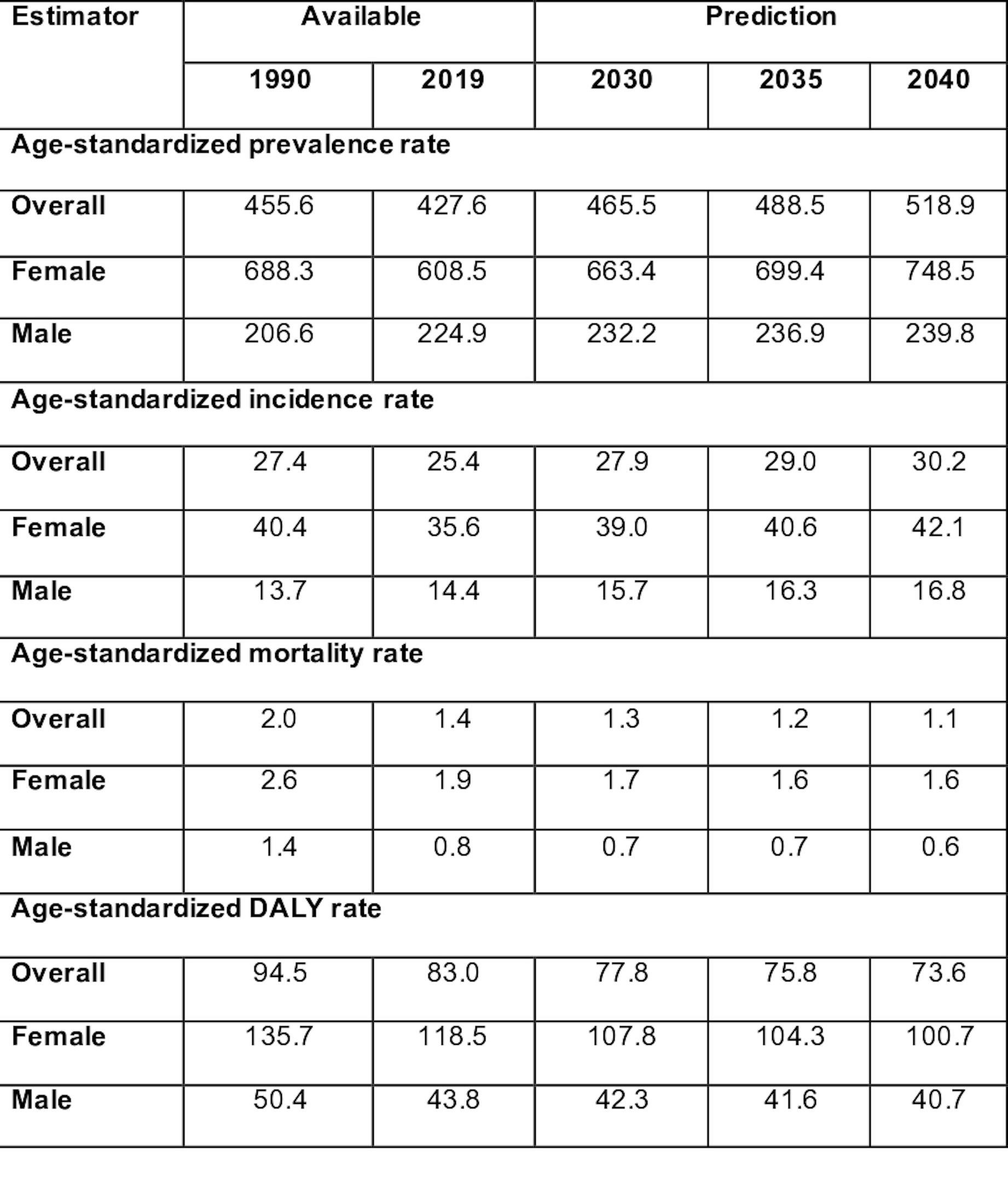
Results: In 2019, approximately 530,000 individuals were affected by RA, corresponding to 0.5% of the Mexican population (64.0% were females, and 35.9% were aged 15–49 years). The age-standardized prevalence and incidence rates were 427.6 cases and 25.4 per 100,000 inhabitants, respectively. In 2019, the Mexican states with the highest age-standardized prevalence, DALY, and YLD rates were Oaxaca, Tlaxcala, and Zacatecas. The national prevalence and incidence rates of RA are projected to increase to 465.5 and 27.9 by 2030 and 518.9 and 30.2 per 100,000 inhabitants, higher in females than males. In contrast, the overall age-standardized mortality and DALY rates are projected to decrease to 1.2 and 77.8 by 2030 and 1.1 and 73.6 by 2040 per 100,000 inhabitants.
Conclusion: RA continues to increase in burden, particularly in disability burden. Despite significant investments in clinical care, research, and public health interventions, there appears to be no sign of a reduction in the rate of increase. Certain regions of Mexico, such as Mexico City, Oaxaca, and Zacatecas, are experiencing a disproportionately high burden.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MENDOZA-PINTO C, ETCHEGARAY MORALES I, MUNGUIA-REALPOZO P, Méndez-Martínez S, Montiel-Jarquín Á, Berra-Romani R, Solis-Mendoza F, García-Carrasco M. Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Epidemiology in Mexico Using the GBD 2019 Study and Forecasting Future Trends for 2030 and 2040 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-epidemiology-in-mexico-using-the-gbd-2019-study-and-forecasting-future-trends-for-2030-and-2040/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-epidemiology-in-mexico-using-the-gbd-2019-study-and-forecasting-future-trends-for-2030-and-2040/