Session Information
Date: Thursday, March 30, 2023
Title: Plenary Abstracts Session I
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a rare and serious systemic autoimmune condition, and much remains unknown about the pathogenesis, the immune cell types and cell-specific disease associated pathways. Increasing knowledge of immune dysregulation in JDM with detailed immunophenotyping at the cellular level could lead to insight into disease mechanisms.
Methods: Multiplexed single cell RNA and protein sequencing was applied to 27 peripheral blood samples to simultaneously profile the gene expression and cell surface antibody (ADT) signatures associated with JDM (n=15, samples=22) compared to healthy pediatric controls (HC)(n=5). Data processing was performed using Demuxlet, SoupX, Harmony, DSB, and Seurat and included doublet removal, quality control, dimensionality reduction, clustering, and cell type annotation using canonical ADT and gene markers. To determine changes associated with JDM, we performed: 1) cell type proportion analysis between individual groups (treatment naïve (TN), inactive, flare, HC) and for different distributions of abundances pr. cell type, 2) correlation analysis between cell type proportion and disease activity measures for all JDM samples, 3) differential expression (DE) between TN JDM and HC pr. cell type using DESeq2 for genes and likelihood-ratios for ADTs (FDR < 0.05), and 4) gene overrepresentation analysis (GOA) with clusterProfiler.
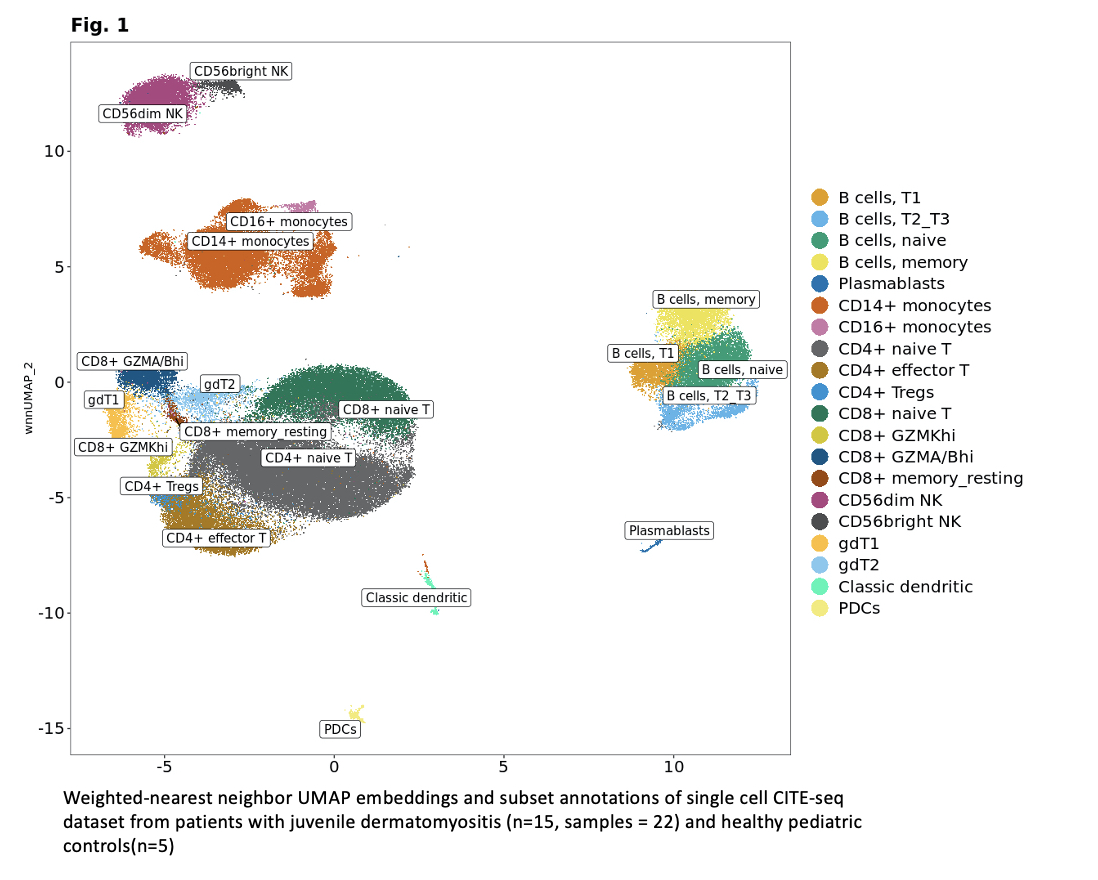
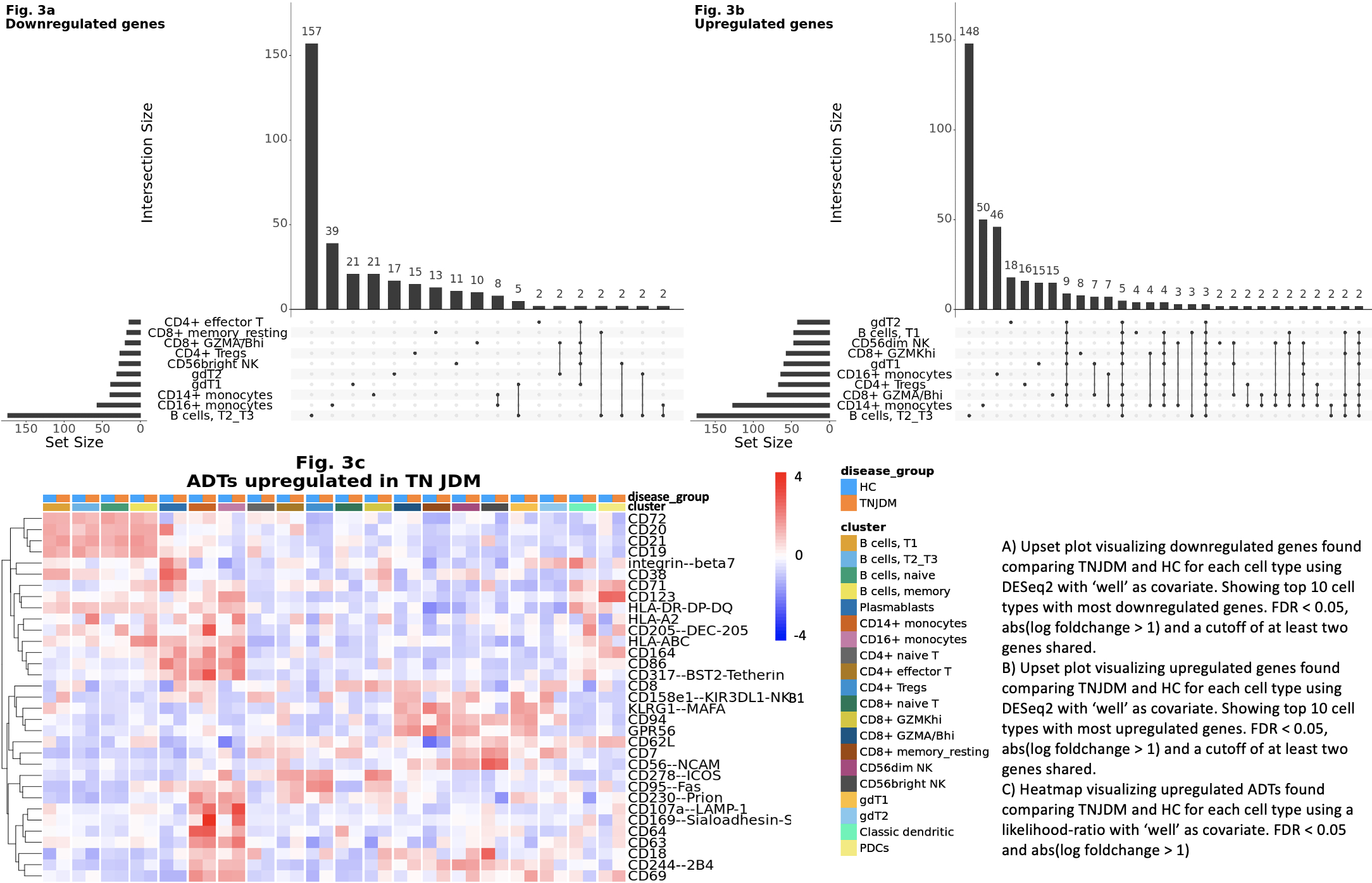
Results: ~110,000 immune cells were analyzed across 26,057 genes and 268 ADTs. Using unsupervised clustering, we identified 29 clusters, which compromised 20 unique immune cell populations (Fig 1). TN patients had statistically significantly higher levels of transitional and naïve B cells compared to inactive JDM and HC, and cell type proportion was significantly positively correlated with measures of disease activity (Fig 2, pval < 0.05). Patients with inactive disease had significantly higher proportions of memory B cells compared to TN patients, and the proportion of memory B cells was significantly negatively correlated with disease activity measures (Fig 2, pval < 0.05). TN patients had significantly fewer NK and gd T cells than both healthy controls and other JDM disease states, and cell type proportion was significantly negatively correlated with disease activity measures (Fig 2, pval < 0.05). Tregs were elevated in JDM irrespective of disease state compared to HC (Fig 2, pval < 0.05). Most DE genes were found within transitional B cells, monocytes, and Tregs (Fig 3). However, many DE genes were shared among cell types, and GOA revealed overrepresentation in genes involved in type 1 interferon and interferon gamma pathways for most cell types. Differential protein analysis revealed upregulation of SIGLEC-1 and LAMP-1 on the surface of both CD14+ and CD16+ monocytes (Fig 3).
Conclusion: Alterations in immune cell composition within the B, CD4+ T, gd T, and NK cell compartments are associated with disease activity in JDM. Monocytes and transitional B cells show major gene expression changes during disease, but all cell types are heavily influenced by interferon signaling. Future directions include characterization of JDM-associated immunophenotypes at the transcriptomic and proteomic levels as well as network analysis.
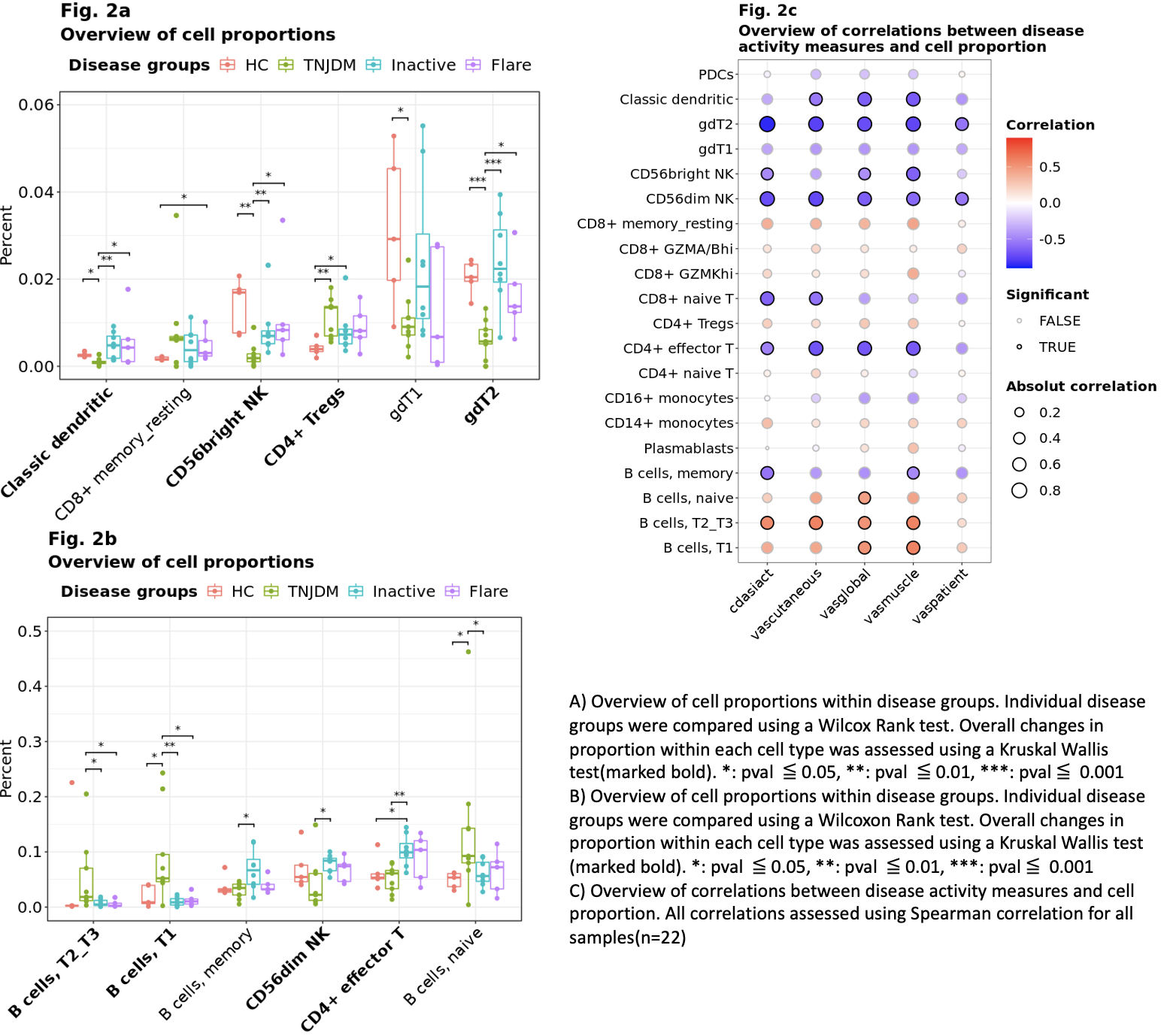 Cell proportion and correlation
Cell proportion and correlation
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wibrand C, Flynn E, Rabadam G, Hartoularos G, Sun Y, Ye C, Kim S, Sirota M, Neely J. Analysis of Patients with Juvenile Dermatomyositis Compared to Healthy Controls Using CITE-seq Identifies Differences in Cell Composition and Gene and Epitope Expression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-patients-with-juvenile-dermatomyositis-compared-to-healthy-controls-using-cite-seq-identifies-differences-in-cell-composition-and-gene-and-epitope-expression/. Accessed .« Back to 2023 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-patients-with-juvenile-dermatomyositis-compared-to-healthy-controls-using-cite-seq-identifies-differences-in-cell-composition-and-gene-and-epitope-expression/