Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Synovial inflammation is common in knee osteoarthritis (OA) and is associated with pain and disease severity. Previous studies have suggested short-term (approximately 2 weeks) effects on synovial tissue from intra-articular (IA) steroid injection. This open-label Phase 3b study evaluated a single 32 mg intra-articular (IA) injection of triamcinolone acetonide extended release (TA-ER) on synovial tissue volume (STV), pain, stiffness, function, and quality of life (QOL) (NCT03529942).
Methods: Patients with KL grade 2-3 painful (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC)-A total sum score ≥ 6) knee OA received TA-ER at baseline (BL). Assessments occurred at BL, Weeks 6, 12, 18, and 24, and included gadolinium MRI at BL, Weeks 6 and 24 using automated segmentation. MRIs were used to determine STV, with synovitis at BL defined as STV ≥3000 mm3. Patients who had quality MRI data available at BL and at least one post-baseline timepoint were included in the Imaging Population. The primary study endpoint was mean standardized change in STV from BL to Week 6. Additionally, WOMAC-A (pain), WOMAC-B (stiffness), and WOMAC-C (function) were assessed at BL and Weeks 6, 12, 18, and 24; the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score – QOL (KOOS-QOL) was assessed at BL, Weeks 6 and 24. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were recorded.
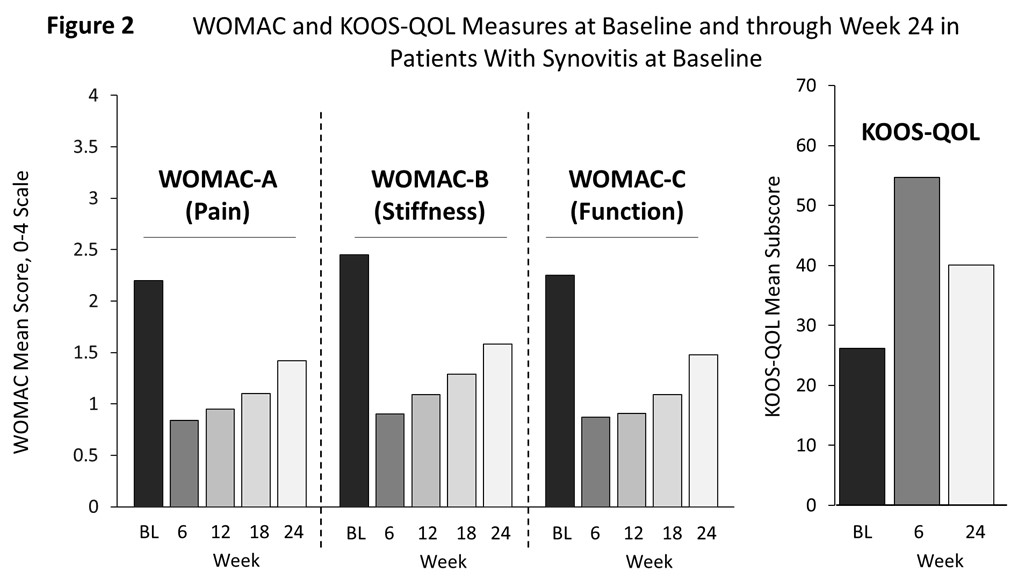
Results: We enrolled 129 patients with typical knee OA characteristics (Table); 102 (79%) demonstrated BL synovitis (STV ≥3000 mm3; range 3,005-45,113 mm3). In patients with BL synovitis who were part of the Imaging Population (n=85), STV was significantly reduced at Week 6 (P< 0.0001; (Figure 1). The primary endpoint was met: standardized least squares mean (LSM) STV change at Week 6 was −0.90 (95% CI, −1.06 to −0.73; P< 0.001); at Week 24, STV change was 0.20 (95% CI, 0.04 to 0.36). In patients with BL synovitis following TA-ER, WOMAC-A, B, and C improved from BL at Weeks 6, 12, 18, and 24; also, KOOS-QOL improved from BL at Weeks 6 and 24 (Figure 2). Although STV returned to BL by Week 24, the clinical improvements observed in WOMAC and KOOS measures persisted through Week 24. Thirty-one patients (24%) experienced TEAEs; 9 (7.0%) patients had ≥1 index-knee TEAE. Most TEAEs were considered mild or moderately severe, however, one severe adverse event of nephrolithiasis occurred. None of the TEAEs were considered related to the study drug.
Conclusion: In patients with knee OA and BL synovitis, a single IA injection of TA-ER improved six-week synovitis, measured as reduced STV. TA-ER reduced OA symptoms of pain and stiffness and improved function and OA-related quality of life through Week 24. Overall, a single IA injection of TA-ER was well tolerated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huffman K, Kivitz A, Conaghan P, Bowes M, Brett A, Kraus V, Maloney W, Parvizi J, Cinar A, Bodick N, Kelley S. An Open-Label Study to Evaluate the Effect of Intra-articular Triamcinolone Acetonide Extended Release on Patients with Baseline Synovitis and Osteoarthritis of the Knee [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-open-label-study-to-evaluate-the-effect-of-intra-articular-triamcinolone-acetonide-extended-release-on-patients-with-baseline-synovitis-and-osteoarthritis-of-the-knee/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-open-label-study-to-evaluate-the-effect-of-intra-articular-triamcinolone-acetonide-extended-release-on-patients-with-baseline-synovitis-and-osteoarthritis-of-the-knee/