Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) spectrum diseases, myositis-specific and myositis-associated autoantibodies (MSAs/MAAs) are key markers of disease subtype and prognosis and are considered routine clinical tests. At present, no MSA/MAA testing guidance exists, and detection and reporting protocols vary between laboratories. Concerns have been raised regarding the sensitivity, specificity and interlaboratory variability of some commonly used MSA assays, particularly line immunoassay (LIA).
By dispatching multiple aliquots of individual patient sera to serology labs around the world, this study aimed to compare the usage and effectiveness of available myositis autoantibody (AAb) detection methods and identify best practice for patient benefit.
Methods: Fourteen diagnostic labs were recruited, 7 of which were actively involved in IIM research, together with one research-only centre. Sera from 20 patients with MSAs, and 4 with systemic sclerosis AAbs, were provided by the University of Bath Serology Service, where AAbs had been identified using immunofluorescence (IFA), 35S-labelled-protein immunoprecipitation (IP) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Each group typically received 18 X 100 µl of sera containing MSAs/MAAs, ostensibly from patients with a preliminary diagnosis of IIM, and were asked to carry out their standard “myositis panel” as a minimum. Protein-IP was the assumed reference standard for comparison of results.
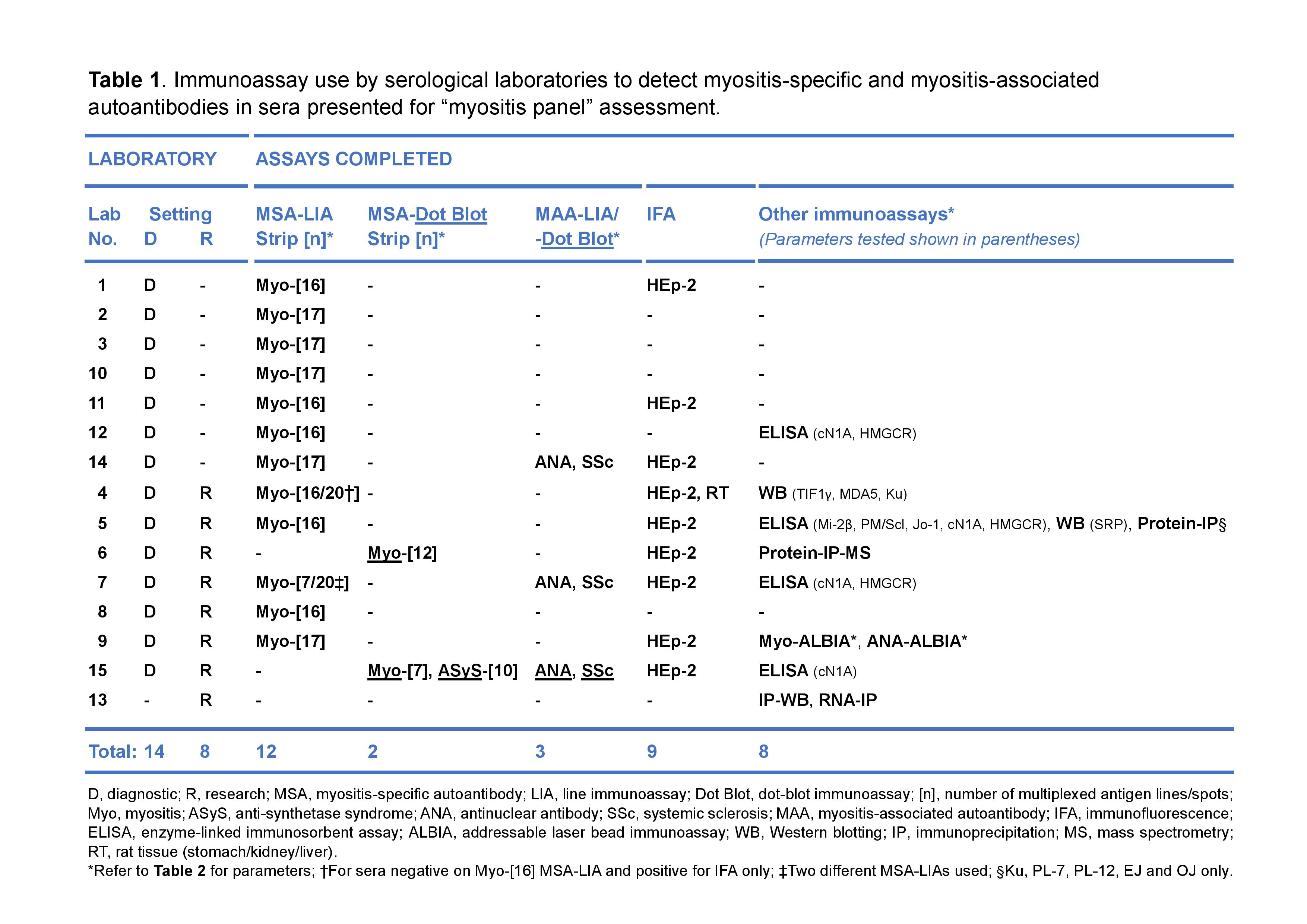
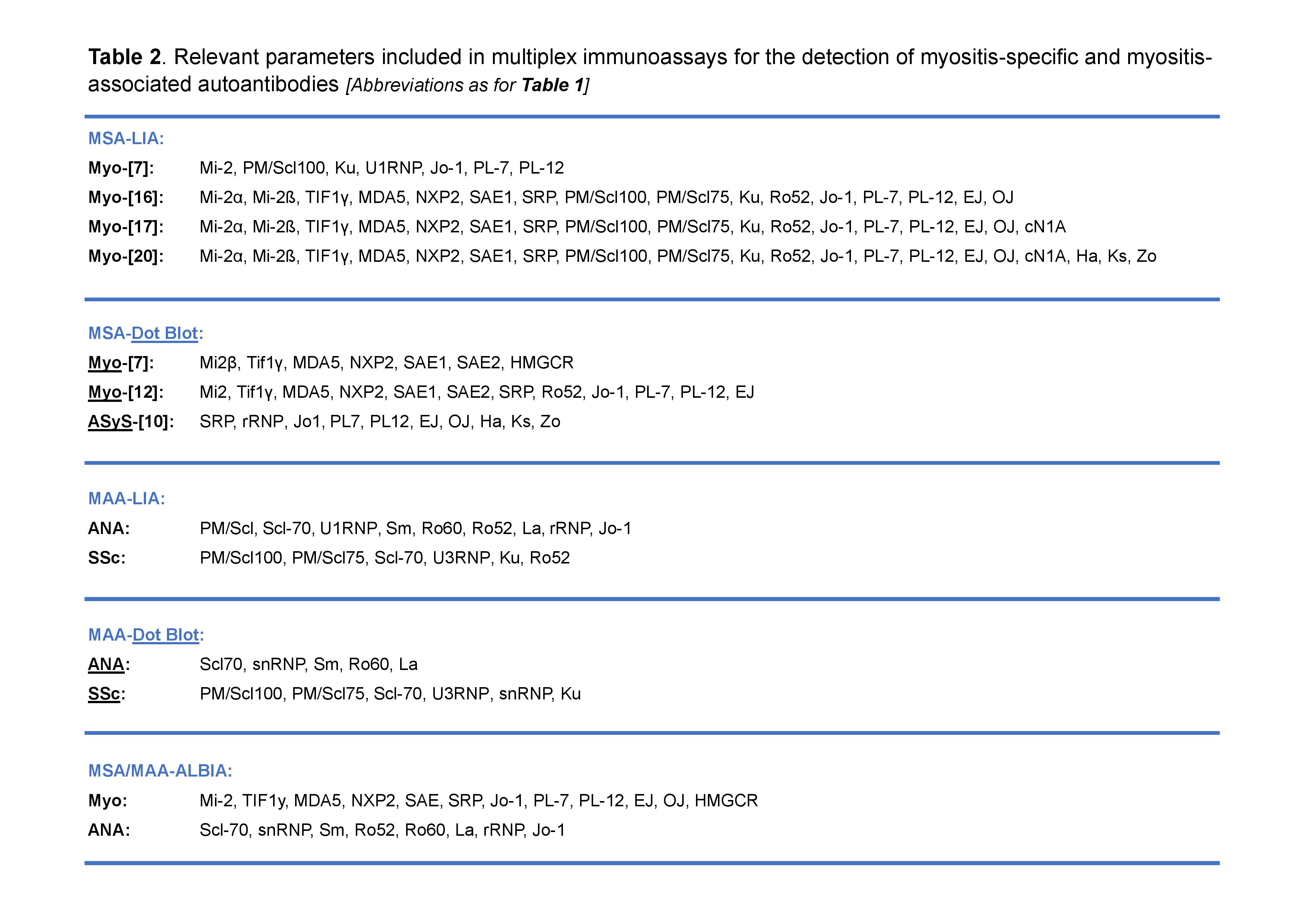
Results: All 14 diagnostic labs used a commercially available MSA-LIA or -Dot Blot (-DB), with most (11; 79%) selecting versions omitting certain MSAs, and only 3 (21%) adding in an MAA-LIA/-DB (Table 1). Frequently, HMGCR, cN1A, Zo and MAA specificities were not included and therefore not detected (Table 2). While IFA was used to complement LIA testing in most (9; 64%) labs, 4 (29%) used an MSA-LIA as their sole assay. The use of ELISAs, Western Blotting (WB), IP and/or addressable laser bead assay (ALBIA) was restricted to 7 (50%) labs, of which 6 (86%) were research active (Table 1).
Although MSA-LIAs worked well for a majority of MSAs, with sensitivities of 90-100%, for TIF-1γ, EJ and OJ, sensitivities ranged between 0-67%. More AAbs were initially detected by LIAs than by IP, but many results showed low band intensities, and were not reported by most. The MSA-ALBIA detected all IP-positive MSAs evaluated, including TIF-1γ, EJ and OJ.
All labs detected Jo-1 AAbs by LIA/ALBIA in one sample originally deemed negative by protein-IP: however, DB, RNA-IP, IP-WB and IP-Mass Spectrometry all found this sample to be negative. This was an unexpected outcome that may be due to an internal, linear epitope of Jo-1.
Conclusion: Participating laboratories utilised several different AAb panels for their MSA/MAA screen. Key MSAs/MAAs, such as HMGCR, were often not included or followed up using other assays. Line IAs had poor sensitivity to detect TIF-1γ, OJ and EJ, with variability in results between centres using the same product. Until these issues are addressed, the use of LIA alone to detect TIF-1γ, EJ and OJ AAbs is questionable.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harvey G, Ashur I, Bossuyt X, Bluethner M, Brusch A, Bundell C, Chinoy h, Coeshott C, Donald C, Dunphy J, Fritzler M, Heaps A, Hudson m, Kuwana M, Landon-Cardinal O, Lu H, MCMORROW F, Mayrhofer M, Meyer A, Michiels B, Nespola B, O'Loughlin S, Putova I, Rönnelid J, Sadler R, Sanz-Martinez M, Sciore P, Selva-O’Callaghan A, Storfors H, Trallero-Araguás E, Troyanov Y, Tyson J, Vencovský J, Yoshida A, Tansley S. An Interlaboratory Variability Study of Detection Methods for Myositis-Specific and Myositis-Associated Autoantibodies in Sera from Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-interlaboratory-variability-study-of-detection-methods-for-myositis-specific-and-myositis-associated-autoantibodies-in-sera-from-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-interlaboratory-variability-study-of-detection-methods-for-myositis-specific-and-myositis-associated-autoantibodies-in-sera-from-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/