Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: 5T117: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease (2816–2821)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
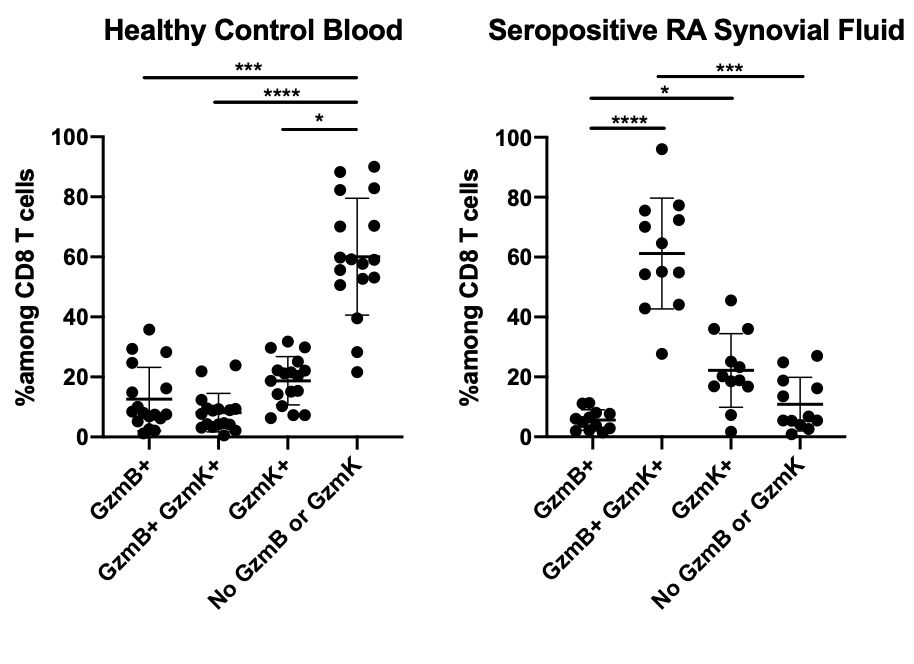
Background/Purpose: CD8 T cells represent nearly half of T cells in inflamed synovium from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Research to date has focused on CD4 T cells, yet we have found that synovial CD8 T cells express IFNgat a higher frequency and TNF at a similar frequency compared to CD4 T cells. Recent single-cell transcriptomic analysis of RA synovial tissue has suggested that CD8 T cells form sub-populations characterized by expression of secreted proteases granzyme K (GzmK) and granzyme B (GzmB).
Methods: We have assembled a single-cell RNA-seq data set of approximately 20,000 CD8 T cells by integrating new and publicly available data from synovial tissue (N=22) and fluid (N=1) from patients with RA and from blood (N=3) from healthy controls. RA patients met the 2010 ACR criteria for RA. Additional data were collected by flow cytometry or low-input RNA-seq from synovial tissue, synovial fluid, and blood from patients with clinical diagnoses of rheumatoid arthritis or healthy controls. In in vitro cultures, human synovial fibroblast cells were treated with recombinant granzyme K. Cytokine production was measured by ELISA, and reactive oxygen species were measured by a H2DCFDA fluorescence assay.
Results: At both the mRNA and protein levels, the vast majority of CD8 T cells in synovial tissue and fluid from patients with seropositive RA express GzmK, either alone or together with GzmB, a marked enrichment compared to blood (Figure 1). Very few synovial CD8 T cells express GzmB alone, which is the pattern seen in late differentiated cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Unlike GzmB, GzmK does not activate apoptotic caspases. Instead, we find that GzmK has pro-inflammatory effects on synovial fibroblasts, inducing them to produce IL-6, CCL2, and reactive oxygen species (ROS), all of which are upregulated in inflamed synovium. GzmK+ CD8 T cells in blood express high frequencies of chemokine receptors CCR2, CCR5, and CXCR3, while CD8 T cells expressing GzmB alone express CX3CR1, suggesting that GzmK+ CD8 T cells and CTLs are recruited to sites of inflammation through different pathways. Interestingly, preliminary analysis of a large,integrated single-cell RNA-seq dataset of CD8 T cells from synovial tissue, synovial fluid, and blood shows selective expression of genes encoding Nur77, Ki67, and activation markers in distinct CD8 subsets, suggesting that some CD8 T cell subsets receive T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated signals whereas others are activated through TCR-independent mechanisms.
Conclusion: The vast majority of CD8 T cells in RA synovial tissue and fluid express GzmK and express a phenotype and transcriptome distinct from typical GzmB+ CTLs. GzmK+ CD8 T cells appear to traffic to sites of inflammation using different chemokine receptors than CTLs. GzmK induces synovial fibroblasts to produce pro-inflammatory effector molecules including IL-6, CCL2, and ROS. Preliminary analysis of a large single-cell RNA-seq data set suggests differential TCR-mediated and cytokine-mediate activation of CD8 T cell subsets in inflamed joints. Together, these findings form the basis of a new model of CD8 T cell migration and function in RA and potentially other rheumatologic diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jonsson A, Zhang F, Watts G, Wei K, Rao D, Raychaudhuri S, Brenner M. An Expanded Granzyme K+ CD8 T Cell Population Induces Inflammatory Responses in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovium [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-expanded-granzyme-k-cd8-t-cell-population-induces-inflammatory-responses-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-synovium/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-expanded-granzyme-k-cd8-t-cell-population-induces-inflammatory-responses-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-synovium/