Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) is a significant extra-articular manifestation of RA with high morbidity/mortality, but the underlying pathogenesis remains poorly understood. There is a relative paucity of mouse models to study RA-ILD. The K/BxAg7 mouse is a well-established animal model for arthritis and cardiovascular disease (Rose S, et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013). This study aimed to evaluate the development of ILD in an aged K/BxA mouse model, to evaluate the association of arthritis and ILD, and the relationship of ILD with immune activation measured by lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP), and a panel of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Methods: Analysis included 13 aged K/BxA mice (44 weeks +4, 8 (62%) female), and 13 age and sex matched C57BL/6 wild type (WT) controls. Masson’s trichrome staining was performed on the lung tissue and pulmonary fibrosis was calculated via the Ashcroft scoring system by an experienced assessor. CD3 staining of lung tissue was used to assess for bronchus-associated T-cell (BATc) aggregates; this analysis was done by two blinded assessors and the mean score was used. Arthritis was assessed by a blinded assessor using calipers to measure the ankle width of the hindlimbs to calculate a mean hindlimb (mHL) score. Luminex multiplex immunoassays were done for 32 mouse cytokines/chemokines/growth factors, and LBP was measured by ELISA.
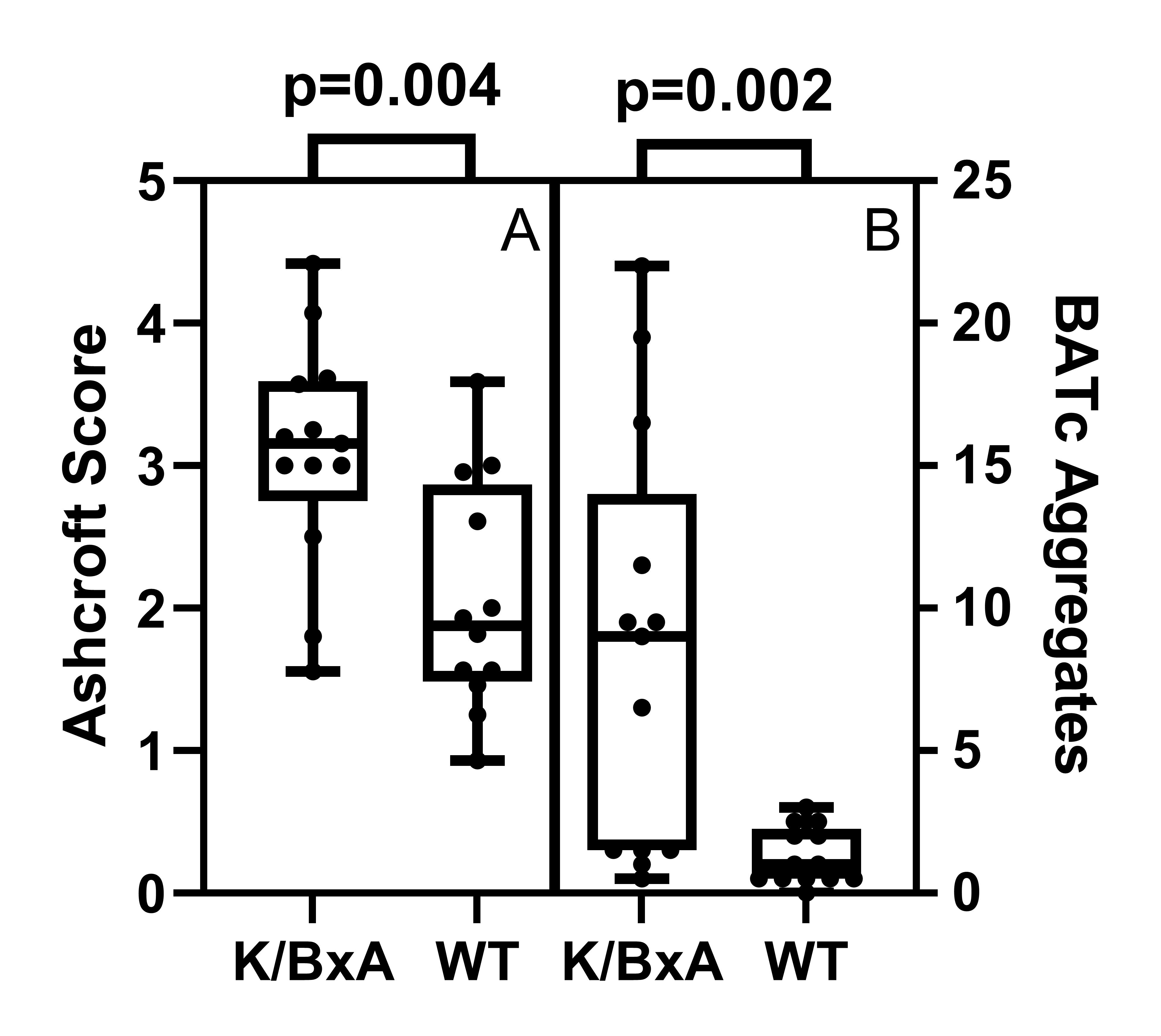
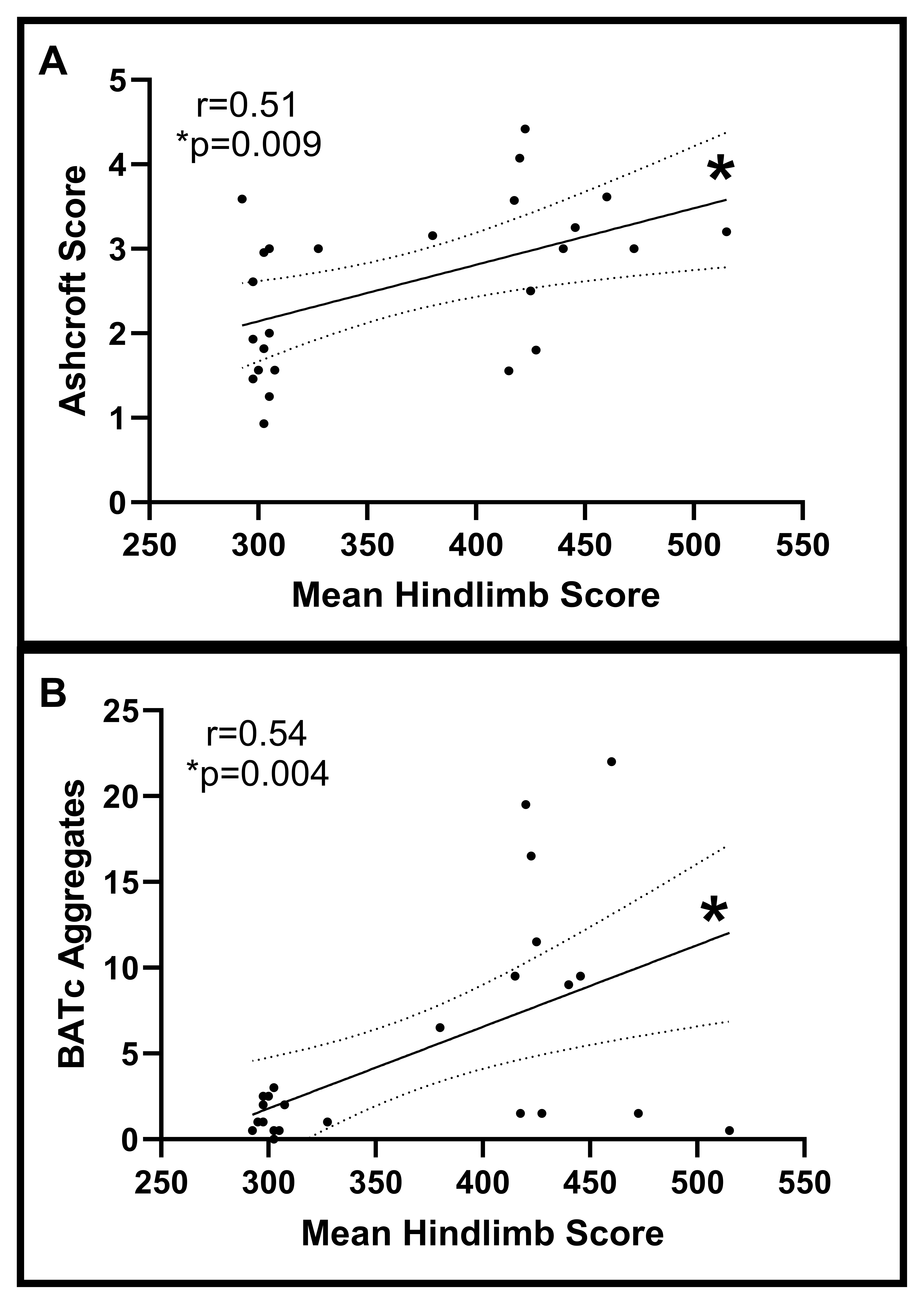
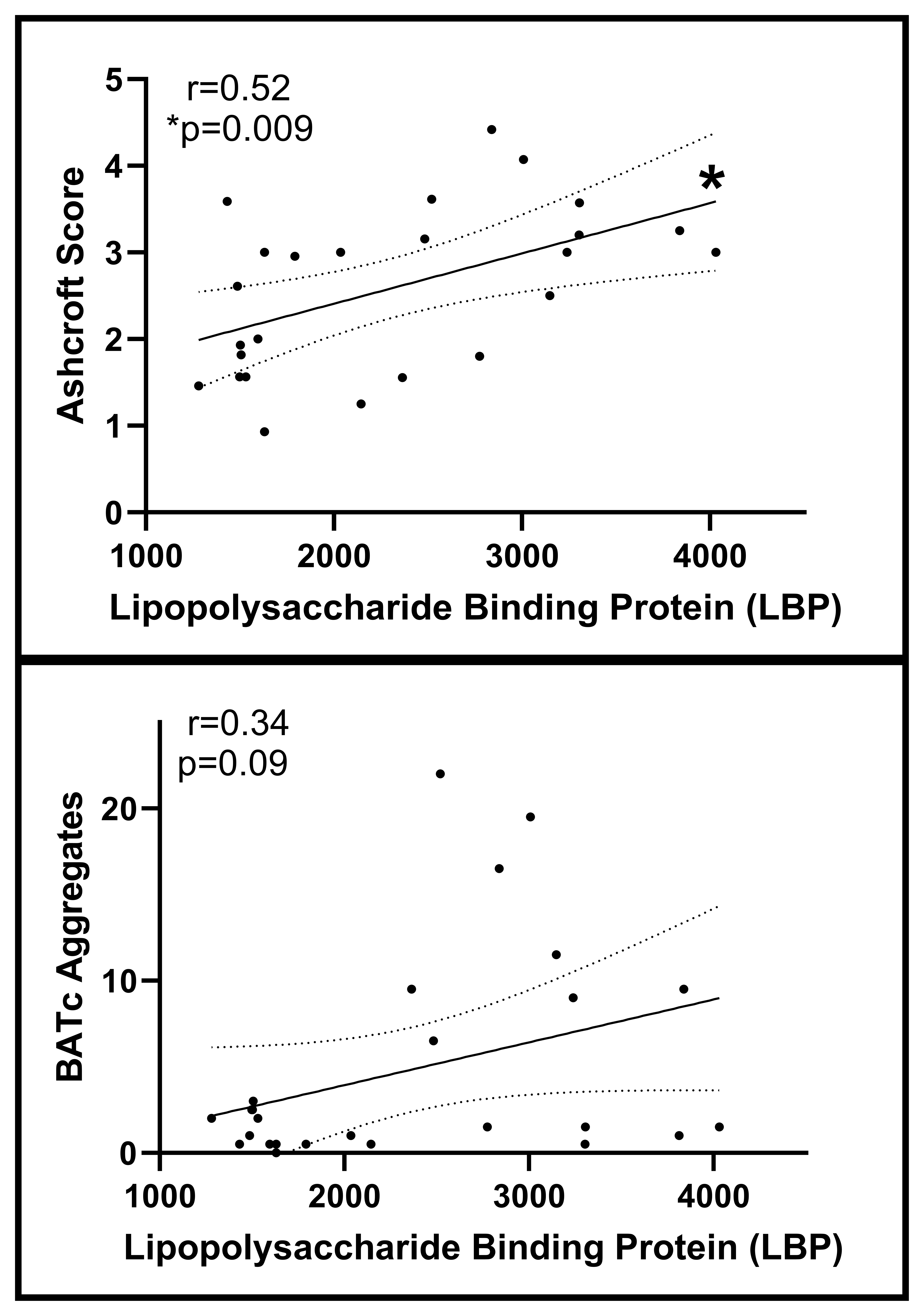
Results: Aged K/BxA mice demonstrated significantly higher amounts of pulmonary fibrosis by Ashcroft scoring than did WT mice (mean +SD of 3.1 +0.8, 2.1 +0.8, p=0.004), significantly higher BATc aggregates (8.5 +7.4, 1.3 +1.0, p=0.002), as well as significantly higher mHL scores (428 +45, 301 +4.5, p< 0.0001)(Figure 1). There was significant positive correlations between increasing mHL scores and increased Ashcroft scores (r=0.51, p=0.009), as well as with increased BATc aggregates (r=0.54, p=0.004)(Figure 2). Higher LBP levels correlated significantly with increased mHL scores and Ashcroft scores (r=0.77, p< 0.0001, and r=0.52, p=0.009, respectively), but fell short of significance with BATc aggregates (r=0.34, p=0.09)(Figure 3). Ashcroft scores correlated significantly with increasing TNF-alpha, IL-2, and CCL-3, and correlated negatively with Eotaxin, while BATc aggregates correlated significantly and positively with increasing IL-1(alpha), IL-1(beta), and CXCL-1. There were significantly higher levels of LBP, IL-6, and CXCL-1 in K/BxA mice versus WT.
Conclusion: Without pulmonary insult, aged K/BxA mice developed ILD at higher degrees than matched WT mice, and the ILD mirrored several features of RA-ILD in humans with increased pulmonary fibrosis, bronchus-associated T-cell aggregates. Additionally, as occurs in RA patients with ILD, K/BxA mice demonstrated significant associations between increasing arthritis scores and worsening ILD. Additionally, measures of immune activation, most significant being LBP demonstrated positive associations with ILD. The aged K/BxA mouse model for arthritis may represent a promising model for the study of RA-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Razmjou A, Watson R, Shahbazian A, Wang J, Charles-Schoeman c. An Aged K/BxA Arthritis Mouse Model Develops Features of Interstitial Lung Disease with Pulmonary Fibrosis and Bronchus-Associated T-Cell Aggregates Without a Pulmonary Insult, and Correlates with Worsening Arthritis Scores [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-aged-k-bxa-arthritis-mouse-model-develops-features-of-interstitial-lung-disease-with-pulmonary-fibrosis-and-bronchus-associated-t-cell-aggregates-without-a-pulmonary-insult-and-correlates-with-wor/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-aged-k-bxa-arthritis-mouse-model-develops-features-of-interstitial-lung-disease-with-pulmonary-fibrosis-and-bronchus-associated-t-cell-aggregates-without-a-pulmonary-insult-and-correlates-with-wor/